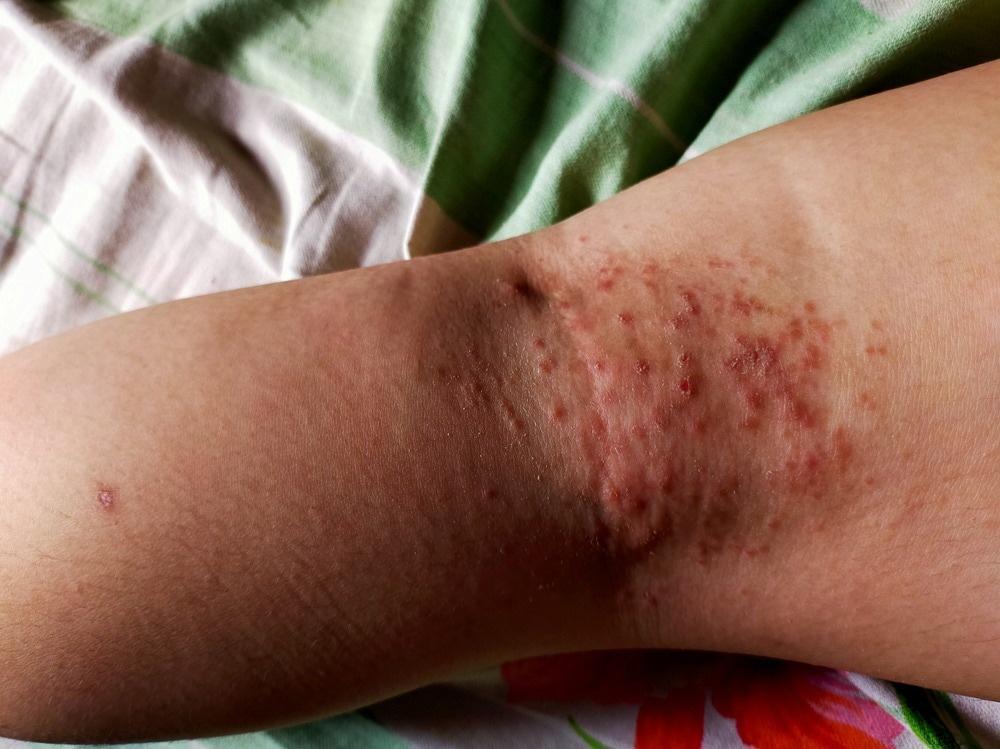
Title: Understanding Skin Infections: A Deep Dive into the Unseen Battle
In the intricate landscape of human health, our skin serves as the first line of defense, a resilient barrier protecting us from countless external threats. Yet, beneath its surface lies a complex world where microbes—both friendly and harmful—coexist and, at times, clash. Skin infections, often underestimated, reveal the delicate balance of our body’s ecosystem and the vulnerabilities that can arise when this balance is disrupted. From the commonplace itch of a minor rash to the alarming signs of a more serious condition, these infections can affect anyone, regardless of age or background. This article explores the nature of skin infections, shedding light on their causes, symptoms, and treatments, while empowering readers with the knowledge to navigate this often-misunderstood aspect of health. Join us as we delve into the nuances of skin infections, uncovering the stories they tell about our bodies and the vital care they demand.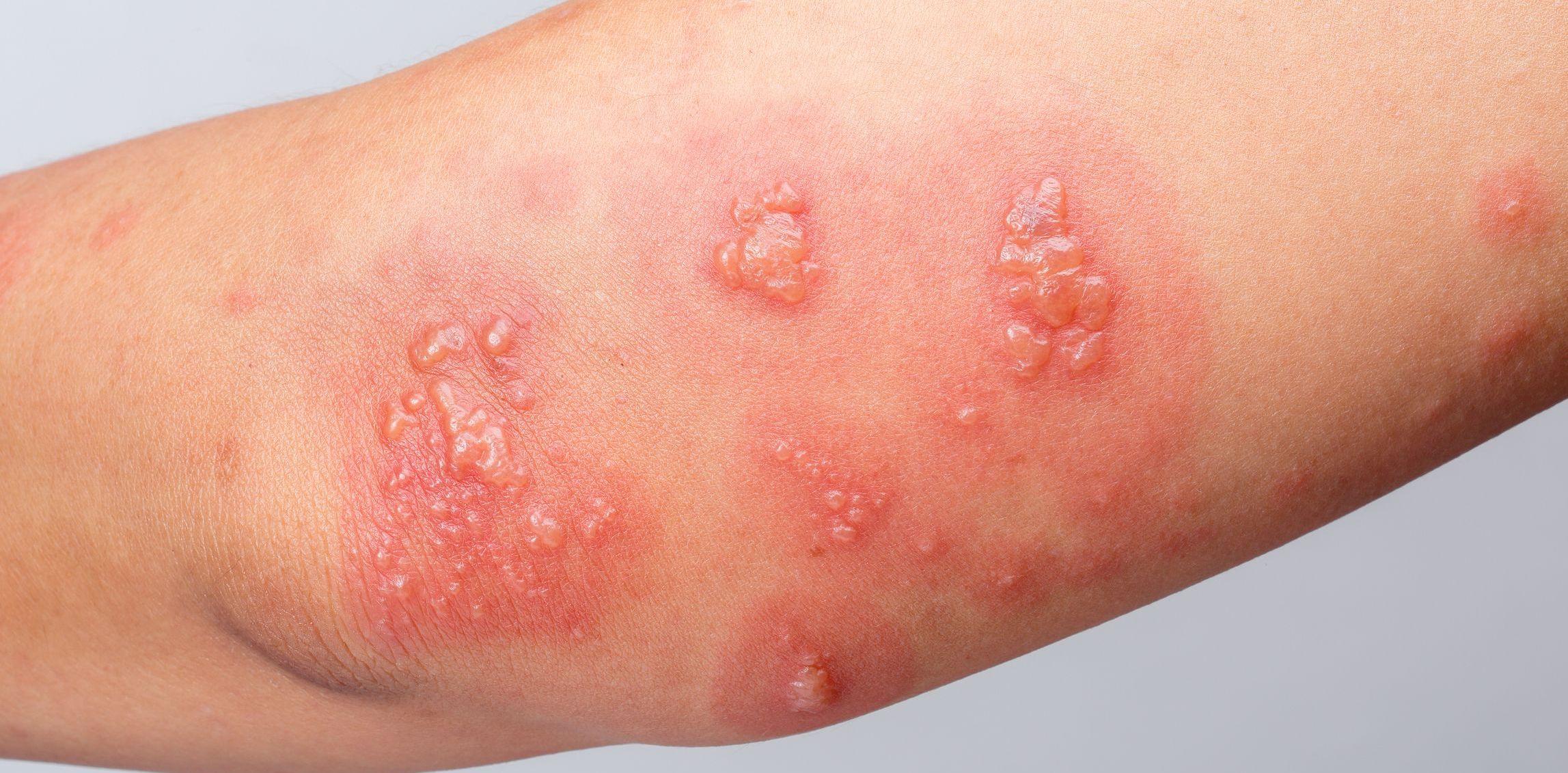
Understanding Skin Infections: Causes and Types
Skin infections can arise from a variety of sources, often caused by bacteria, fungi, viruses, or parasites. These microorganisms can invade the skin through cuts, abrasions, or even healthy skin under certain conditions. Common causes include:
- Bacterial infections – Often caused by Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus species, leading to conditions like cellulitis or impetigo.
- Fungal infections – Such as athlete’s foot or ringworm, typically resulting from an overgrowth of fungi.
- Viral infections – Including herpes simplex and warts, which are caused by viruses that thrive in specific environments.
- Parasitic infections – Such as scabies, where parasites infest the skin.
Understanding the types of skin infections can aid in prompt and effective treatment. Some of the most prevalent types include:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Cellulitis | Infection of the deeper layers of the skin, often resulting in swelling and redness. |
| Impetigo | A highly contagious bacterial infection, often seen in children, characterized by blisters and honey-colored crusts. |
| Fungal Nail Infection | Involves fungal growth under the nails, causing discoloration and thickening. |
| Scabies | Caused by tiny mites burrowing into the skin, resulting in intense itching. |
Recognizing Symptoms: Early Signs of Skin Infections
Identifying the early signs of skin infections is crucial for prompt treatment and minimizing complications. Common initial symptoms often include:
- Redness: Affected areas may appear inflamed or unusually red, signaling irritation or infection.
- Swelling: The skin may become puffy and swollen, indicating fluid buildup.
- Pain or Tenderness: You might experience discomfort or heightened sensitivity in the infected region.
- Warmth: The skin may feel warmer than surrounding areas, a telltale sign of infection.
- Itching: Persistent itching can be a precursor to more severe symptoms, prompting the need for examination.
If you observe any combination of these symptoms, it’s essential to monitor them closely. In some cases, the infection can progress, leading to more severe signs, which include:
| Advanced Symptoms | Indications |
|---|---|
| Fever | Rising body temperature may indicate systemic involvement. |
| Pus or Discharge | Presence of yellow or green fluid suggests bacterial infection. |
| Blisters | Fluid-filled sacs can signify more severe skin conditions. |
| Worsening Symptoms | Deteriorating condition despite home care may require medical attention. |
Preventive Measures: Keeping Your Skin Healthy
Maintaining healthy skin is essential to prevent infections that can arise from various sources. Daily hygiene practices are the first line of defense. Ensure you wash your skin regularly with mild soap and water, removing dirt and bacteria that can lead to skin issues. Additionally, consider the following key practices:
- Moisturize
- Sun Protection: Use sunscreen with at least SPF 30 to protect against harmful UV rays that can damage skin cells.
- Wear Protective Clothing: In environments with high risk for cuts or abrasions, protective garments can significantly reduce injury risk.
- Hydration: Drinking adequate water supports overall skin health, keeping it supple and resilient.
Another critical aspect is being mindful of your environment. Avoid contact with irritants such as harsh chemicals, and opt for natural products whenever possible. Regularly inspect your skin for any unusual changes, as early detection of potential issues can make a significant difference. Consider implementing these essential habits to maintain your skin’s integrity:
| Practice | Description |
|---|---|
| Regular Check-ups | Schedule dermatological check-ups to monitor skin health. |
| Healthy Diet | Incorporate antioxidants and vitamins A, C, and E to enhance skin repair. |
| Stress Management | Engage in relaxation techniques to minimize stress, which can trigger skin problems. |
Treatment Options: From Home Remedies to Medical Interventions
When it comes to combating skin infections, a variety of treatment options are available, ranging from simple home remedies to more complex medical interventions. Home remedies can be an effective first line of defense for minor infections and may include:
- Warm compresses - Applying a warm compress can help reduce inflammation and promote healing.
- Tea tree oil - Known for its antimicrobial properties, tea tree oil can be diluted with a carrier oil and applied to the affected area.
- Honey - With natural antibacterial properties, honey can be used as a topical treatment to soothe and heal the skin.
- Aloe vera – This soothing gel is beneficial for its anti-inflammatory and hydrating effects.
For more severe infections or when home remedies do not provide relief, professional medical interventions may be necessary. Healthcare providers often recommend treatments such as:
| Medical Intervention | Description |
|---|---|
| Antibiotics | Prescribed to target bacterial infections effectively. |
| Antifungal creams | Used for fungal infections; helps to eliminate the infection. |
| Corticosteroids | Reduces inflammation and itching associated with skin infections. |
| Drainage procedures | Performed for abscesses to remove pus and promote healing. |
Complications and Risks: When to Seek Professional Help
While many skin infections can be managed at home with proper care, certain signs and symptoms indicate that professional medical help is necessary. If you experience increased redness, swelling, or warmth around the infected area, this may signify the infection is worsening. Additionally, watch for persistent pain, fever, or the development of pus or drainage. These symptoms can indicate a more serious condition that requires medical intervention. Ignoring these signs may lead to complications, such as cellulitis or an abscess, which could necessitate surgical treatment.
Understanding when to seek help can be crucial in effectively managing a skin infection. Consider consulting a healthcare professional if you notice any of the following:
- Symptoms that do not improve within a few days
- Infection spreading beyond the initial site
- Severe pain that does not subside with over-the-counter medications
- Underlying health conditions, such as diabetes or a weakened immune system
Being proactive in seeking treatment can prevent complications and ensure a smoother recovery process.
Caring for Your Skin Post-Infection: Recovery and Aftercare Tips
After experiencing a skin infection, your skin is in a vulnerable state, requiring gentle care and attention. Begin by keeping the affected area clean and dry to prevent any further irritation or the risk of re-infection. Use mild, fragrance-free cleansers, and avoid scrubbing the area harshly. It’s also crucial to monitor for any signs of recurrence or worsening symptoms, such as increased redness, swelling, or pain. In such cases, consult a healthcare provider promptly. To facilitate healing, consider the following tips:
- Moisturize Regularly: Apply a hypoallergenic moisturizer to keep the skin hydrated and support the recovery process.
- Sun Protection: Use broad-spectrum sunscreen to protect the healing skin from UV damage, as it can become more sensitive post-infection.
- Wear Loose Clothing: Opt for breathable fabrics that allow your skin to recover without added friction or irritation.
Incorporating a balanced diet rich in vitamins and antioxidants can also promote faster healing. Foods high in Vitamin C, like citrus fruits and leafy greens, help repair skin, while zinc-rich options such as nuts and seeds support immune function. Staying hydrated is equally important, so aim to drink ample water throughout the day. Consider the following foods that can aid in your recovery:
| Food | Nutritional Benefit |
|---|---|
| Citrus Fruits | Rich in Vitamin C |
| Nuts | High in zinc |
| Leafy Greens | Aids skin repair |
| Fish | Anti-inflammatory properties |
Q&A
Q&A: Understanding Skin Infections
Q1: What exactly is a skin infection?
A1: A skin infection occurs when harmful microorganisms, such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites, invade the skin or its underlying tissues. These invaders can disrupt the skin’s natural barrier, leading to various symptoms such as redness, swelling, pain, and sometimes pus formation.
Q2: What are the common types of skin infections?
A2: Skin infections can be broadly categorized into three main types: bacterial, viral, and fungal. Common bacterial infections include impetigo and cellulitis. Viral infections often manifest as warts or cold sores, while fungal infections include athlete’s foot and ringworm. Each type requires specific treatments, so proper identification is crucial.
Q3: What are the symptoms of a skin infection?
A3: Symptoms can vary based on the type and severity of the infection. However, common signs include redness, swelling, warmth, pain, and the formation of blisters or pustules. In more severe cases, fever and chills might accompany these local symptoms, signaling a more systemic infection.
Q4: How are skin infections diagnosed?
A4: Diagnosis typically starts with a physical examination by a healthcare provider, who will assess the appearance and symptoms of the affected area. Sometimes, further testing, like a culture or biopsy, may be necessary to identify the specific pathogen responsible for the infection.
Q5: What causes skin infections, and how can they be prevented?
A5: Skin infections can arise from a variety of factors, including cuts, abrasions, insect bites, or even underlying medical conditions like diabetes. To prevent infections, maintain good hygiene, keep wounds clean and covered, avoid sharing personal items, and be cautious in communal environments like gyms and pools.
Q6: How are skin infections treated?
A6: Treatment depends on the type of infection. Bacterial infections are often treated with antibiotics, while antiviral medications may be prescribed for viral infections. Fungal infections typically require antifungal creams or oral medications. In some cases, drainage of abscesses or blisters may be necessary.
Q7: When should someone see a doctor for a skin infection?
A7: It’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional if you notice any persistent or worsening symptoms, have a fever, or if the infection spreads rapidly. Early intervention can prevent complications and ensure effective treatment.
Q8: Can skin infections be serious?
A8: While many skin infections are mild and easily treatable, some can lead to serious complications if left untreated, such as sepsis or the spread of infection to deeper tissues. It’s essential to stay vigilant and seek medical attention when needed to avoid potential risks.
Q9: Are there any home remedies for skin infections?
A9: While professional medical treatment is often necessary for skin infections, some home remedies may help alleviate mild symptoms. Keeping the area clean and dry, applying aloe vera or honey, and using over-the-counter anti-itch creams can provide relief. However, these should not replace proper medical care for significant infections.
Q10: Can skin infections be recurring?
A10: Yes, some individuals may experience recurring skin infections due to factors like a weakened immune system, chronic skin conditions, or lifestyle choices. Identifying and addressing underlying causes can help reduce the frequency of these infections.
—
This Q&A aims to provide a clear understanding of skin infections, equipping readers with the knowledge they need to recognize, prevent, and seek appropriate treatment for these common health issues.
Wrapping Up
understanding skin infections is essential for safeguarding our skin’s health and overall well-being. These conditions can range from mild irritations to more serious complications, emphasizing the importance of early detection and appropriate treatment. By staying informed about the causes, symptoms, and preventive measures, we empower ourselves to take proactive steps in maintaining not just the health of our skin, but also our confidence and comfort. As we navigate this intricate landscape of dermatological health, let us remember that our skin, often referred to as our body’s first line of defense, deserves our attention and care. With the right knowledge and practices, we can protect this vital organ and foster a healthier future, one layer at a time.