How is an overactive thyroid diagnosed?
Understanding Overactive Thyroid: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatments
Overactive thyroid, medically known as hyperthyroidism, is a condition where the thyroid gland produces excess amounts of thyroid hormones. This hormonal imbalance can lead to a variety of health issues and significantly impact daily life. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the symptoms, causes, treatment options, and practical tips for managing an overactive thyroid.
What is Hyperthyroidism?
Hyperthyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland, located at the base of your neck, produces too much thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). These hormones play a crucial role in regulating metabolism, energy levels, and overall body functions.
Common Symptoms of Overactive Thyroid
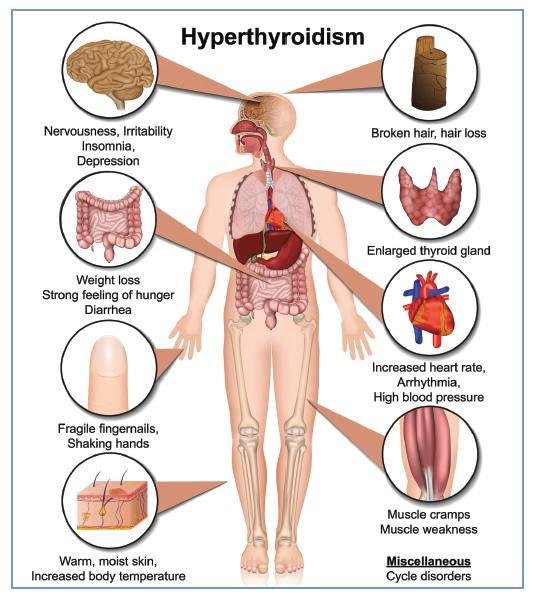
The symptoms of hyperthyroidism can vary from person to person, but common signs include:
- Increased heart rate or palpitations
- Weight loss despite increased appetite
- Excessive sweating and heat intolerance
- Nervousness, anxiety, and irritability
- Sleep disturbances
- Tremors in hands or fingers
- Fatigue and muscle weakness
- Menstrual changes in women
- Goiter (enlargement of the thyroid gland)
Causes of Overactive Thyroid
Several factors can contribute to the development of hyperthyroidism, including:
- Graves’ disease: An autoimmune disorder that causes the thyroid to become overactive.
- Thyroid nodules: Overproduction of hormones from nodules in the thyroid gland.
- Thyroiditis: Inflammation of the thyroid can lead to excess hormone release.
- Excessive iodine intake: Consuming too much iodine can trigger hyperthyroidism.
Diagnosis of Overactive Thyroid
Diagnosing an overactive thyroid typically involves a combination of physical examinations, medical history evaluations, and specific tests such as:
- Blood tests: Measuring levels of T4, T3, and Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH).
- Radioactive iodine uptake test: Evaluates how much iodine the thyroid absorbs.
- Thyroid scan: Images the thyroid gland to identify functioning nodules.
Treatment Options for Overactive Thyroid
Treatment for hyperthyroidism focuses on reducing the production of thyroid hormones and managing symptoms. Common treatment options include:
- Medications: Antithyroid medications, such as methimazole and propylthiouracil, can help lower hormone levels.
- Radioactive iodine therapy: This treatment destroys overactive thyroid cells, reducing hormone production.
- Beta-blockers: These medications help manage symptoms like rapid heartbeat and anxiety.
- Surgery: In severe cases, partial or total thyroidectomy may be recommended.
Benefits of Treatment
Effective management of hyperthyroidism can lead to:
- Restored energy levels
- Improved mental health and mood stability
- Weight stabilization
- Better cardiovascular health
Managing an Overactive Thyroid: Practical Tips
For those living with hyperthyroidism, lifestyle adjustments can help manage symptoms:
- Diet: Focus on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to aid in regulating body temperature and metabolism.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in low-impact activities like walking or yoga to boost mood and energy levels.
- Stress Management: Incorporate relaxation techniques such as meditation and deep breathing exercises.
Case Study: Living with Hyperthyroidism
Consider the case of Sarah, a 35-year-old teacher who was diagnosed with Graves’ disease. Initially overwhelmed by fatigue and anxiety, she sought help from an endocrinologist. Through a combination of medication and lifestyle changes, Sarah regained her energy and learned to manage her symptoms effectively. Today, she leads a fulfilling life while keeping her hyperthyroidism in check.
First-Hand Experience: A Patient’s Journey
John, a 42-year-old man, shares his experience with hyperthyroidism:
“At first, I attributed my weight loss and anxiety to stress. After being diagnosed with hyperthyroidism, I realized the importance of self-care and medication adherence. With support from my healthcare team, I learned to embrace a healthier lifestyle, and it has made a world of difference.”
Conclusion
Overactive thyroid, or hyperthyroidism, can significantly impact your quality of life if left untreated. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options is essential for effective management. With the right approach—including medications, lifestyle changes, and ongoing support—you can lead a healthy, fulfilling life despite this condition. If you suspect you have an overactive thyroid, consult a healthcare professional for evaluation and personalized treatment options.