Understanding Relief: A Journey Through Medicines for Stomach Pain
Stomach pain is a universal experience, transcending age, culture, and lifestyle. Whether it strikes suddenly after a rich meal, lingers as a dull ache, or comes as a sharp reminder of an underlying condition, the discomfort can be both bewildering and debilitating. In a world where our diets and daily habits are constantly evolving, so too are the solutions we seek to alleviate this common affliction. From over-the-counter remedies to prescription medications and holistic approaches, the landscape of stomach pain relief is vast and varied. This article explores the myriad options available, shedding light on how these medicines work, their potential benefits, and when it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional. Join us on this informative journey as we navigate the intricate world of stomach pain relief, empowering you to make informed choices for your health and well-being.
Understanding the Causes of Stomach Pain
Stomach pain can stem from a variety of underlying issues, ranging from minor to serious conditions. One common cause is indigestion, which can occur after overeating or consuming spicy or fatty foods. Other potential triggers include gastritis, an inflammation of the stomach lining, and peptic ulcers, which are sores in the stomach or upper part of the small intestine. Additionally, food intolerances, such as lactose or gluten intolerance, can contribute to discomfort after eating certain foods.
Infections can also play a significant role in causing abdominal pain. For example, gastroenteritis, often referred to as the stomach flu, can lead to cramping and diarrhea. In more severe cases, conditions like appendicitis or pancreatitis can manifest as intense stomach pain that requires immediate medical attention. Understanding the underlying causes is crucial for effective treatment. Here’s a brief overview of some common causes:
| Cause | Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Indigestion | Bloating, heartburn, nausea |
| Gastritis | Stomach pain, loss of appetite |
| Peptic ulcer | Burning stomach pain, indigestion |
| Gastroenteritis | Diarrhea, vomiting, cramping |
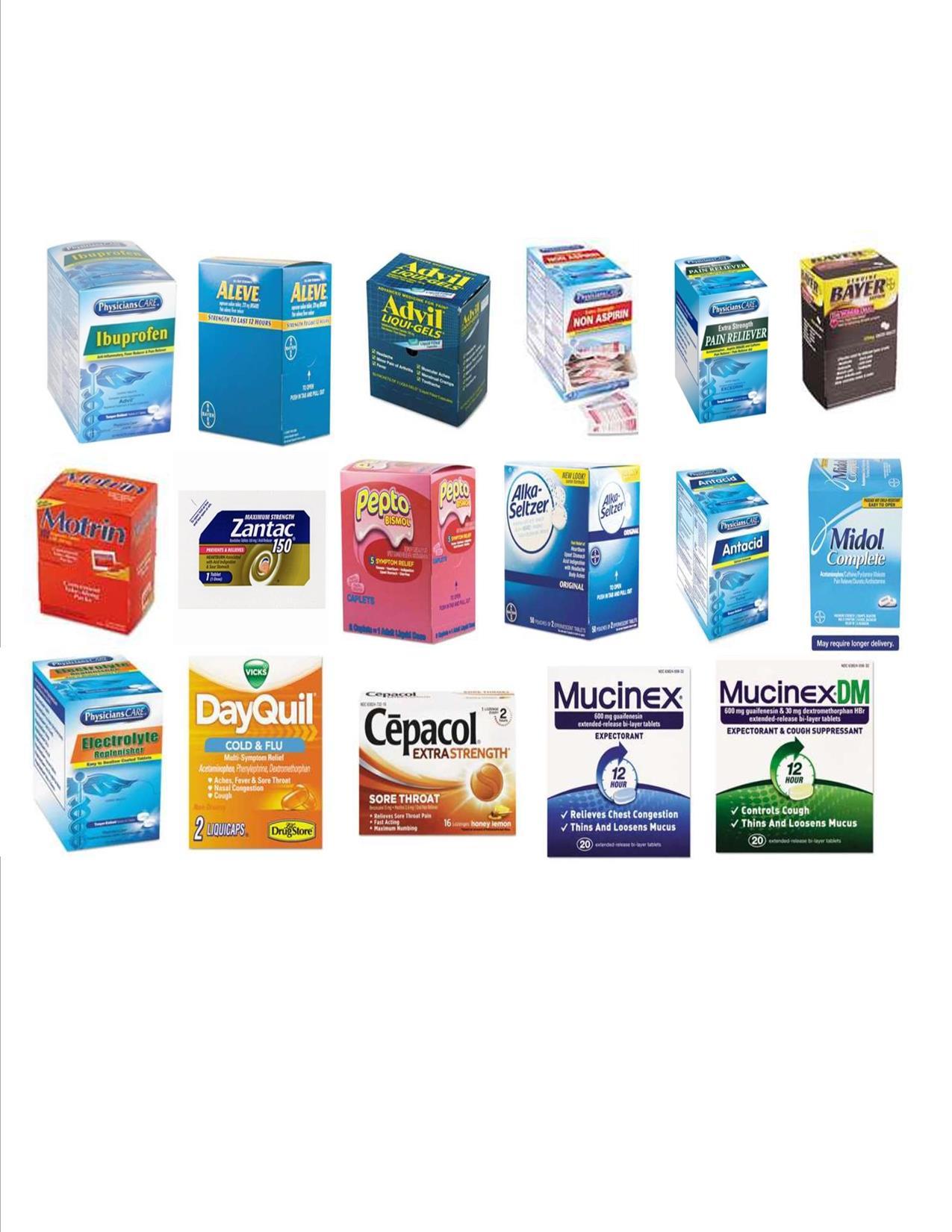
Exploring Over-the-Counter Medications for Relief
When dealing with stomach pain, many individuals turn to over-the-counter (OTC) medications for quick relief. These medications can be effective in addressing various types of stomach discomfort, whether it stems from indigestion, gas, or mild cramping. Some common OTC options include:
- Antacids: These neutralize stomach acid and provide fast relief from heartburn and acid indigestion.
- H2 Blockers: These reduce the amount of acid produced by the stomach, offering longer-lasting relief.
- Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs): These work to block acid production more effectively than H2 blockers, making them suitable for frequent discomfort.
- Simethicone: This helps relieve gas-related stomach pain by breaking up gas bubbles in the gut.
- Anti-diarrheal medications: These can help manage symptoms caused by diarrhea, providing comfort during an upset stomach.
While OTC medications can be beneficial, it’s essential to choose the right one for your specific symptoms. Below is a simple comparison table to help you identify which medication may be most suitable for your needs:
| Medication Type | Primary Use | Typical Relief Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Antacid | Heartburn, indigestion | Short-term |
| H2 Blocker | Acid reduction | Up to 12 hours |
| PPI | Frequent acid-related symptoms | 24 hours or more |
| Simethicone | Gas relief | As needed |
| Anti-diarrheal | Diarrhea management | Varies |
Natural Remedies to Soothe Digestive Discomfort
For those seeking relief from digestive discomfort, nature offers a variety of remedies that can soothe the stomach and promote overall gut health. One popular choice is ginger, known for its anti-inflammatory properties that help alleviate nausea and bloating. You can enjoy ginger in multiple forms: as a tea, in smoothies, or even as a spice in your meals. Another effective remedy is peppermint, which is often used to relax the muscles of the gastrointestinal tract, providing relief from cramps and bloating. Sipping on peppermint tea or chewing peppermint leaves can be particularly beneficial after meals.
In addition to these, consider incorporating probiotic-rich foods into your diet, such as yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut. These foods promote a healthy gut flora, essential for digestion. Another natural soother is chamomile tea, which has calming properties that can ease both the mind and digestive system. For quick reference, here’s a simple table highlighting these remedies and their benefits:
| Natural Remedy | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Ginger | Alleviates nausea and bloating |
| Peppermint | Relaxes gastrointestinal muscles |
| Probiotics | Promotes healthy gut flora |
| Chamomile Tea | Calms the digestive system |
When to Seek Professional Help for Stomach Pain
Stomach pain can range from mild discomfort to severe, debilitating agony, and understanding when to seek professional guidance is essential for your health. If you experience any of the following symptoms, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare provider:
- Persistent pain lasting more than a few days
- Severe or sudden onset of abdominal pain
- Accompanying symptoms such as fever, vomiting, or marked changes in bowel habits
- Unexplained weight loss or loss of appetite
- Signs of dehydration like excessive thirst or infrequent urination
Moreover, certain conditions may warrant immediate medical attention. Recognizing these can make a significant difference in treatment and recovery. Below is a summary of critical situations:
| Condition | Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Appendicitis | Sharp pain in the lower right abdomen, nausea, fever |
| Gallstones | Intense pain in the upper right abdomen, especially after meals |
| Pancreatitis | Severe abdominal pain radiating to the back, vomiting |
| Intestinal Obstruction | Severe cramping, inability to pass gas or stool |
Lifestyle Changes to Prevent Recurring Issues
Making certain lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the frequency of stomach pain and discomfort. Dietary adjustments play a crucial role in promoting digestive health. Incorporating more fiber-rich foods such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help regulate digestion. Additionally, avoiding spicy, fatty, or acidic foods can minimize irritation in the stomach lining. Staying hydrated is essential, so aim for at least 8 glasses of water a day. It’s also beneficial to establish a consistent eating schedule, which helps your body regulate its digestive processes more effectively.
Another vital aspect is managing stress, which can often exacerbate stomach issues. Relaxation techniques, such as yoga, meditation, or deep-breathing exercises, can help calm the mind and improve overall well-being. Regular physical activity is also beneficial not only for maintaining a healthy weight but for promoting better digestion. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week. To illustrate this, refer to the table below for tips on effective lifestyle changes that can help prevent recurrent stomach pain:
| Tip | Description |
|---|---|
| Eat Smaller Meals | Consume smaller, more frequent meals to ease digestion. |
| Limit Caffeine and Alcohol | Reduce intake of irritants that can trigger discomfort. |
| Keep a Food Diary | Track your food intake to identify triggers of stomach pain. |
| Prioritize Sleep | Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep for better overall health. |
Navigating Dietary Choices for Optimal Stomach Health
Maintaining optimal stomach health requires a thoughtful approach to dietary choices, focusing on foods that promote digestive well-being. A balanced diet rich in fiber can significantly ease the burden on your stomach by enhancing digestion and preventing issues such as bloating and constipation. Consider incorporating the following foods into your meals:
- Whole grains: Brown rice, quinoa, and whole grain bread help promote regular bowel movements.
- Fruits: Bananas, apples, and berries are high in fiber and can soothe your stomach.
- Vegetables: Leafy greens, carrots, and sweet potatoes provide essential nutrients and assist digestion.
- Probiotics: Yogurt, kefir, and fermented foods support a healthy gut microbiome.
In contrast, certain foods can exacerbate stomach discomfort and should be consumed in moderation or avoided altogether. It’s important to be mindful of your individual reactions to various foods. Here are some items that may trigger stomach issues:
- Spicy foods: Hot peppers and spicy sauces can irritate the stomach lining.
- Fatty foods: Fried and greasy foods can slow digestion and lead to discomfort.
- Dairy products: For those who are lactose intolerant, milk and cheese can cause bloating and gas.
- Caffeinated beverages: Coffee and certain teas may stimulate acid production and exacerbate symptoms.
By carefully selecting your food choices and listening to your body’s signals, you can significantly enhance your stomach health and alleviate pain. Below is a simple table summarizing the do’s and don’ts for optimal stomach health:
| Do’s | Don’ts |
|---|---|
| Eat fiber-rich foods | Avoid overly processed foods |
| Stay hydrated | Limit sugary beverages |
| Incorporate lean proteins | Skip heavy and fried foods |
| Practice portion control | Overeat during meals |
Q&A
Q&A: Understanding Medicine for Stomach Pain
Q1: What are the common causes of stomach pain that may require medication?
A1: Stomach pain can stem from a variety of causes, including indigestion, gas, gastritis, ulcers, and more serious conditions like appendicitis or gallstones. Lifestyle factors such as diet and stress can also contribute. Identifying the root cause is essential for effective treatment.
Q2: What types of over-the-counter medications are available for stomach pain?
A2: Over-the-counter (OTC) medications include antacids (like Tums and Maalox) for acid-related pain, H2 blockers (such as ranitidine and famotidine) for reducing stomach acid production, and proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) like omeprazole. Additionally, medications like simethicone can alleviate gas-related discomfort.
Q3: When should I consult a healthcare professional instead of self-medicating?
A3: If your stomach pain is severe, persistent, or accompanied by alarming symptoms such as fever, vomiting, or blood in stools, it’s crucial to seek medical attention. A healthcare professional can provide a proper diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment options tailored to your needs.
Q4: Are there any risks associated with taking medication for stomach pain?
A4: Yes, like all medications, those for stomach pain can have side effects. Long-term use of some OTC medications may lead to complications such as nutrient malabsorption or dependency. Additionally, not addressing the underlying cause of stomach pain can result in worsening health issues.
Q5: Can lifestyle changes help manage stomach pain alongside medication?
A5: Absolutely! Incorporating lifestyle changes can enhance the effectiveness of medication. This includes maintaining a balanced diet, managing stress through relaxation techniques, staying hydrated, and avoiding known irritants like spicy foods or caffeine. Keeping a food diary may also help identify triggers.
Q6: How can I differentiate between normal stomach pain and a more serious condition?
A6: Normal stomach discomfort often resolves with home remedies or OTC medications and is usually mild. However, if the pain is sudden, intense, or persists beyond a few days, it may indicate a more serious issue. Look for warning signs like swelling, localized pain, or changes in bowel habits, and consult a healthcare provider if in doubt.
Q7: Can herbal remedies be effective for stomach pain?
A7: Some people find relief from herbal remedies such as peppermint, ginger, or chamomile tea for mild digestive issues. While they can be soothing, it’s important to approach them with caution, as they can interact with other medications or may not be suitable for everyone.
Q8: How important is diagnosis in choosing the right medication for stomach pain?
A8: Diagnosis is key! Understanding the underlying cause of stomach pain ensures that you choose the most effective medication and avoid unnecessary side effects. A healthcare professional can help clarify the origin of your discomfort and guide you toward the most appropriate treatment plan.
Q9: What should I do if my medication isn’t alleviating my stomach pain?
A9: If your pain persists despite taking medication, it may be time to revisit your healthcare provider. They may adjust your treatment plan, perform additional tests, or investigate other potential causes of your discomfort.
Q10: Is it possible to prevent stomach pain with medication?
A10: While medications can help manage symptoms, prevention often lies in lifestyle modifications. A proactive approach that includes a healthy diet, regular exercise, and stress management can significantly reduce the likelihood of stomach pain, making medication less necessary in the long run.
Concluding Remarks
As we conclude our exploration of remedies for stomach pain, it becomes clear that while discomfort in the abdominal region is a common ailment, the path to relief is uniquely personal. From over-the-counter medications to lifestyle adjustments, understanding the root cause of your pain is paramount to finding effective treatment. As you navigate the myriad options available, remember that consulting a healthcare professional is always a wise choice, ensuring that your journey towards comfort is both safe and informed. Whether it’s a fleeting cramp or a more persistent issue, taking proactive steps can lead you to a healthier, more comfortable existence. Here’s to a future where stomach pain becomes a distant memory, and well-being takes center stage.
