Title: Unraveling the Complex Tapestry of Manic Depression
In the intricate landscape of human emotions, few conditions evoke as much intrigue and misunderstanding as manic depression, more formally known as bipolar disorder. This mental health condition weaves a delicate thread between the peaks of euphoric highs and the depths of sorrowful lows, creating a tapestry rich with contrasting experiences. While the term “manic depression” may conjure images of wild swings in mood and energy, it also invites us to explore the profound complexities of the human psyche and the myriad factors that contribute to mental health. In this article, we will delve into the nature of manic depression, examine its symptoms and impacts, and shed light on the avenues available for understanding and treatment, revealing a story that is as multifaceted as the individuals it affects. Join us on this journey as we seek to illuminate the shadows and celebrate the resilience found within the spectrum of human emotion.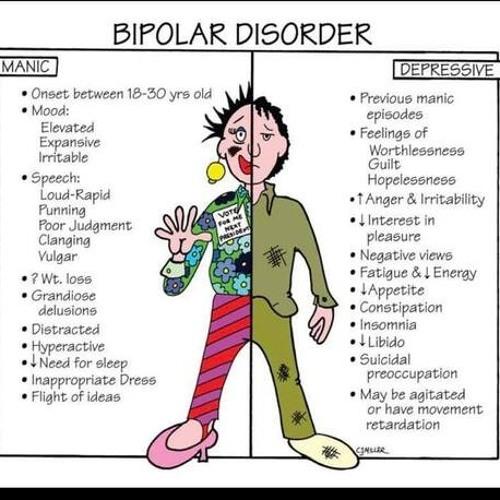
Understanding Manic Depression: A Comprehensive Overview of the Condition
Manic depression, also known as bipolar disorder, is a mental health condition characterized by extreme mood swings that include emotional highs (mania or hypomania) and lows (depression). Individuals experiencing this disorder may find themselves in a state of euphoria, high energy, and reduced need for sleep during manic phases, which can lead to impulsive and reckless behavior. Conversely, depressive episodes can plunge them into feelings of hopelessness, lethargy, and a lack of interest in previously enjoyed activities. Understanding these contrasting states is crucial for both those affected and their loved ones, as it can foster empathy and support during challenging times.
Effective management of manic depression often involves a combination of medication, therapy, and lifestyle adjustments. Here are some common approaches:
- Medications: Mood stabilizers, antipsychotics, and antidepressants.
- Therapy: Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and interpersonal therapy.
- Lifestyle Changes: Regular exercise, balanced diet, and sleep hygiene.
Additionally, support networks play a vital role in recovery. Family members and friends can help by recognizing warning signs and encouraging treatment adherence. The journey through manic depression varies for each individual, making tailored care essential for effective intervention.
The Emotional Rollercoaster: Exploring the Symptoms and Phases of Manic Depression
The experience of manic depression, more formally known as bipolar disorder, can feel like an unpredictable journey through a landscape of emotional extremes. Individuals may find themselves soaring to exhilarating heights during manic phases, characterized by an elevated mood, increased energy, and heightened creativity. However, this can swiftly transition into depressive episodes, where feelings of hopelessness, fatigue, and disinterest can dominate. Understanding the symptoms associated with these phases is crucial for both those affected and their loved ones. Here are some common signs:
- Manic Phase Symptoms:
- Racing thoughts
- Impulsive behavior
- Increased talkativeness
- Unusual or excessive happiness
- Depressive Phase Symptoms:
- Persistent sadness
- Difficulty concentrating
- Changes in sleep patterns
- Loss of interest in activities
The cyclical nature of manic depression can lead individuals and their families through a profound emotional landscape. A typical cycle may include various phases such as hypomania, full-blown mania, a transitional period, and then depressive episodes, which might vary in duration and intensity. To better illustrate this complexity, consider the following table that outlines the potential duration and characteristics of each phase:
| Phase | Duration | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Hypomania | Days to weeks | Mildly elevated mood, increased productivity |
| Mania | Days to weeks | Excessive energy, impulsivity, euphoria |
| Depression | Weeks to months | Low mood, fatigue, disinterest |
| Stable | Varies | Emotional balance, normal functioning |
Navigating Triggers: Identifying Factors That Influence Mood Swings
Understanding the subtle nuances that contribute to mood fluctuations is essential for anyone navigating the complexities of manic depression. Various internal and external factors can act as triggers, influencing emotional states and leading to significant changes in behavior. Among the most common triggers are:
- Sleep Patterns: Disrupted sleep can dramatically affect mood stability.
- Stress Levels: High-stress situations often precede episodes of mania or depression.
- Dietary Changes: Nutritional deficiencies or excesses can impact mental health.
- Seasonal Changes: Shifts in seasons can lead to variations in mood, commonly seen in seasonal affective disorder.
- Substance Use: Alcohol and drugs can exacerbate mood swings.
By becoming more aware of these influencing factors, individuals can better manage their mood swings and enhance their overall well-being. It’s also beneficial to track mood variations alongside potential triggers, creating a clearer picture of personal patterns. This can be effectively done using a simple table:
| Date | Mood Level | Possible Triggers |
|---|---|---|
| October 1 | 8 (High) | Good sleep, healthy meal |
| October 2 | 3 (Low) | Stressful meeting, missed sleep |
| October 3 | 5 (Neutral) | Regular exercise, social interaction |
Effective Treatment Approaches: Medications and Therapeutic Strategies
When addressing manic depression, a multifaceted approach often yields the best results. Medications play a crucial role in stabilizing mood and preventing the recurrence of episodes. Commonly prescribed medications include:
- Mood Stabilizers: Such as lithium, which helps maintain a balanced mood.
- Atypical Antipsychotics: Medications like quetiapine or olanzapine are used to manage severe symptoms.
- Antidepressants: They can be effective during depressive episodes but must be used cautiously to avoid triggering mania.
In addition to pharmacological interventions, therapeutic strategies are vital for long-term management. Psychotherapy offers individuals a safe space to explore their thoughts and feelings. Effective types of therapy include:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Helps in identifying and changing negative thought patterns.
- Interpersonal and Social Rhythm Therapy (IPSRT): Focuses on stabilizing daily routines and improving interpersonal relationships.
- Family Therapy: Involves family members in the treatment process to foster understanding and support.
| Medication Type | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Mood Stabilizers | Prevent mood swings |
| Atypical Antipsychotics | Manage severe symptoms |
| Antidepressants | Treat depressive episodes |
Building a Support System: The Role of Community and Relationships
Creating a network of supportive relationships is essential for anyone grappling with manic depression. Friends, family, and peers can offer a safe space where individuals can share their experiences and feelings without fear of judgment. Engaging in open conversations fosters understanding and empathy, transforming isolation into connection. It’s crucial to surround oneself with people who are not only willing to listen but also genuinely understand the complexities of mental health. Building this kind of community can include:
- Support groups: Finding local or online support groups can provide camaraderie and shared experiences.
- Therapists: Professional guidance can help navigate the emotional landscape of manic depression.
- Family involvement: Educating family members about the condition can enhance their support.
Within this supportive framework, relationships can serve as a lifeline. They encourage individuals to seek help when needed and remind them they are not alone in their struggles. The role of community extends beyond immediate family and friends; it encompasses mentors, colleagues, and even social media connections who share similar experiences. To illustrate the importance of these relationships, consider the following table that highlights various sources of support:
| Source of Support | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Friends | Emotional support and companionship |
| Family | Unconditional love and understanding |
| Support Groups | Shared experiences and encouragement |
| Therapists | Professional advice and coping strategies |
Coping Strategies for Daily Life: Practical Tips for Managing Manic Depression
Finding effective methods to manage manic depression can significantly enhance daily functioning and overall well-being. Establishing a consistent routine helps create a sense of stability and predictability. Incorporating activities such as regular exercise, healthy eating, and adequate sleep into your schedule can yield substantial benefits. Consider the following strategies:
- Mindfulness practices: Engage in meditation or yoga to foster a sense of calm.
- Social support: Stay connected with friends and family for emotional backing.
- Journaling: Write down thoughts and feelings to process emotions more clearly.
- Limit triggers: Identify and minimize exposure to stressors that exacerbate symptoms.
Incorporating creative outlets can also be a vital aspect of managing manic depression. Activities like painting, music, or writing can serve as powerful forms of expression and emotional release. Establishing a self-care routine is crucial; make time for hobbies that bring joy and relaxation. You might find it helpful to create a simple table to track your moods and activities to identify patterns or triggers:
| Date | Mood Level (1-10) | Activity | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10/01 | 8 | Painting | Felt relaxed and inspired. |
| 10/02 | 3 | Skipped exercise | Overslept, felt sluggish. |
| 10/03 | 7 | Yoga class | Improved mood after session. |
Q&A
Q&A on Manic Depression: Understanding the Spectrum of Mood Disorders
Q1: What is manic depression?
A1: Manic depression, more commonly known as bipolar disorder, is a mental health condition characterized by extreme mood swings that include emotional highs (mania or hypomania) and lows (depression). These mood episodes can affect energy levels, activity, judgment, and the ability to think clearly, making daily functioning challenging.
Q2: What are the different types of bipolar disorder?
A2: Bipolar disorder is classified into several types:
- Bipolar I Disorder: Defined by manic episodes lasting at least seven days, or by manic symptoms severe enough to require immediate hospital care, often accompanied by depressive episodes.
- Bipolar II Disorder: Characterized by a pattern of depressive episodes and hypomanic episodes, but without the full-blown manic episodes found in Bipolar I.
- Cyclothymic Disorder: Involves periods of hypomanic symptoms and periods of depressive symptoms lasting for at least two years (one year in children and adolescents), but the symptoms do not meet the criteria for a hypomanic episode or a depressive episode.
Q3: What are the common symptoms associated with manic episodes?
A3: During a manic episode, individuals may experience heightened energy levels, reduced need for sleep, inflated self-esteem, excessive talkativeness, racing thoughts, distractibility, and engaging in risky behaviors such as spending sprees or reckless driving.
Q4: How do depressive episodes manifest in bipolar disorder?
A4: Depressive episodes in bipolar disorder can include persistent feelings of sadness or hopelessness, loss of interest in most activities, significant weight loss or gain, insomnia or excessive sleeping, fatigue, difficulty concentrating, and thoughts of death or suicide.
Q5: What causes manic depression?
A5: The exact causes of bipolar disorder are not fully understood, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic, biochemical, and environmental factors. A family history of the disorder can increase risk, as can major life changes, trauma, or stress.
Q6: How is manic depression diagnosed?
A6: Diagnosis typically involves a thorough evaluation by a mental health professional, including a detailed history of mood changes, behavior patterns, and family history. Standardized questionnaires and criteria from the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) are often utilized to assist in the diagnosis.
Q7: What treatment options are available for manic depression?
A7: Treatment for bipolar disorder usually includes a combination of medication (such as mood stabilizers, antipsychotics, and antidepressants) and psychotherapy. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and psychoeducation can be particularly effective in helping individuals manage their symptoms and develop coping strategies.
Q8: Can lifestyle changes help manage manic depression?
A8: Yes, lifestyle changes can play a significant role in managing bipolar disorder. Regular exercise, a healthy diet, sufficient sleep, and stress reduction techniques—such as mindfulness and relaxation practices—can help stabilize mood and improve overall well-being.
Q9: What should someone do if they suspect they have manic depression?
A9: If someone suspects they have manic depression, it’s crucial to seek help from a healthcare professional. Early diagnosis and intervention can lead to more effective management of the disorder and significantly improve quality of life. Support from family and friends is also invaluable during this journey.
Q10: How can friends and family support someone with manic depression?
A10: Friends and family can be instrumental in supporting someone with bipolar disorder by educating themselves about the condition, maintaining open and non-judgmental communication, encouraging adherence to treatment plans, and being there during both the highs and lows. Empathy and understanding can foster a supportive environment that helps individuals feel less isolated in their experience.
Insights and Conclusions
As we reach the end of our exploration into manic depression, it becomes evident that this complex condition weaves a rich tapestry of human emotion and experience. From the exhilarating highs to the profound lows, those navigating this journey face a myriad of challenges that extend beyond the individual, touching families, communities, and societal perceptions at large.
Understanding manic depression is not merely an academic pursuit; it’s a call to empathy and awareness. By acknowledging the nuances of this mental health condition, we can foster a more compassionate dialogue that dismantles stigma and promotes support. As we continue to learn and grow in our understanding, let us remain vigilant in our efforts to ensure that those affected by manic depression receive the care, respect, and understanding they deserve.
In a world that often rushes to label and categorize, it is essential to remember that each person’s experience is unique. The spectrum of emotions within manic depression invites us to listen closely, to engage openly, and to advocate relentlessly for mental health awareness. So, as we close this chapter, let us carry forward the insights gained and the stories heard, weaving them into a broader narrative of hope and resilience. Together, may we nurture a future where understanding flourishes, and those affected find solace in the knowledge that they are not alone.
