Are there any vaccines available for malaria?
Understanding Malaria: Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention
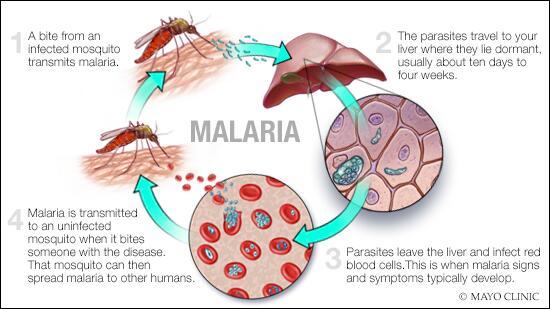
Malaria is a serious and sometimes fatal disease caused by parasites that are transmitted to humans through the bites of infected female Anopheles mosquitoes. With over 200 million cases reported annually, malaria is a significant global health problem, particularly in tropical and subtropical regions. In this article, we will dive deep into the world of malaria, exploring its symptoms, treatments, and prevention methods, while also discussing its global impact and personal experiences.
What is Malaria?
Malaria is caused by Plasmodium parasites, with five species known to infect humans:
- Plasmodium falciparum: The most deadly form, responsible for the majority of malaria-related deaths.
- Plasmodium vivax: Common in Asia and South America and can remain dormant in the liver.
- Plasmodium ovale: Similar to P. vivax but less common.
- Plasmodium malariae: Generally causes a milder form of malaria.
- Plasmodium knowlesi: A simian malaria found in Southeast Asia.
Symptoms of Malaria
Symptoms of malaria typically appear between 10 to 15 days after being bitten by an infected mosquito and can range from mild to severe. Common symptoms include:
- Fever and chills
- Headaches
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fatigue
- Muscle and joint pain
If left untreated, malaria can lead to severe complications, including:
- Cerebral malaria (affecting the brain)
- Respiratory distress
- Organ failure
- Death
Treatment for Malaria
Treatment for malaria typically involves the use of antimalarial medications. The choice of drug depends on the type of malaria, the severity of the disease, and the geographic region where the infection was contracted. Common treatment options include:
- Artemisinin-based combination therapies (ACTs): Recommended as first-line treatments for uncomplicated malaria.
- Chloroquine: Effective against P. vivax and P. malariae but resistance has developed in some areas.
- Quinine: Often used for severe cases of malaria.
- Primaquine: Used to eliminate dormant liver stages of P. vivax.
Prevention Methods
Preventing malaria is crucial, especially in high-risk areas. Here are some effective prevention methods:
1. Mosquito Control
Controlling mosquito populations is critical. This can include:
- Eliminating standing water where mosquitoes breed.
- Using insecticide-treated bed nets (ITNs).
- Indoor residual spraying (IRS) with insecticides.
2. Personal Protection
Individuals can protect themselves by:
- Wearing long-sleeved clothing and long pants.
- Using insect repellent on exposed skin.
- Avoiding outdoor activities during peak mosquito hours (dusk and dawn).
3. Medications
Travelers to high-risk areas may consider taking prophylactic medications, such as:
- Mefloquine
- Doxycycline
- Atovaquone-proguanil
Global Impact of Malaria
Malaria remains a significant public health challenge, particularly in sub-Saharan Africa, where it poses a high burden on health systems. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), there were an estimated 627,000 malaria deaths globally in 2020, with children under five years old disproportionately affected.
Case Studies: Successes and Challenges
Success: The Roll Back Malaria Partnership
Initiated in 1998, this global partnership aimed to halve malaria deaths by 2010. Significant progress was made through increased funding, distribution of ITNs, and improved access to treatment.
Challenge: Drug Resistance
The emergence of drug-resistant malaria has complicated treatment efforts. Regions facing resistance require ongoing surveillance and adaptation of treatment guidelines.
Personal Experience: A Survivor’s Journey
Meet James, a 32-year-old traveler who contracted malaria during a trip to Tanzania. Experiencing severe chills and fever, he sought medical attention promptly. Thanks to a swift diagnosis and treatment with ACTs, James fully recovered. His experience emphasizes the importance of prompt action and awareness when traveling to endemic regions.
Benefits of Awareness and Education
Increasing awareness about malaria can significantly reduce its impact. Communities that are well-informed about prevention methods tend to have fewer cases. Here are some benefits of malaria education:
- Increased understanding of symptoms leads to quicker diagnosis.
- Empowerment of individuals to take preventive measures.
- Reduction in stigma associated with the disease.
Conclusion
Malaria is a serious disease that poses significant health risks, especially in certain regions of the world. Understanding its symptoms, treatment options, and prevention methods is essential in combating this public health challenge. By educating ourselves and others, we can contribute to reducing malaria’s impact and improving health outcomes for vulnerable populations. Remember, awareness and action are our strongest allies in the fight against malaria.