Can lung infections be prevented?
Understanding Lung Infection: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Lung infections can be a serious health concern, affecting millions of individuals worldwide. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for lung infections is essential for maintaining respiratory health. This article delves into the various types of lung infections, how to recognize their symptoms, and the steps you can take to prevent and treat them.
What is a Lung Infection?
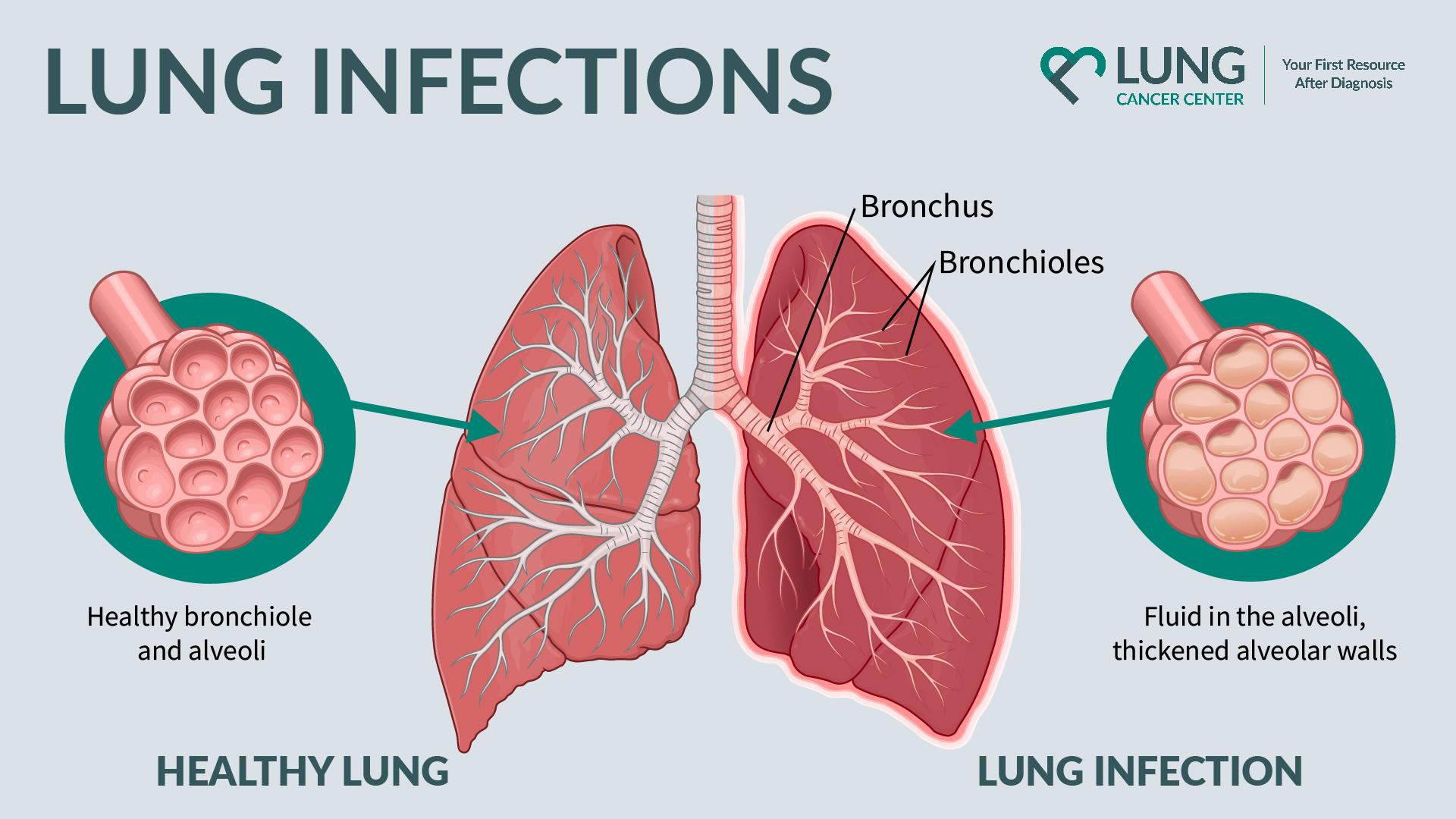
A lung infection, also known as pneumonia, occurs when the lung’s air sacs become inflamed due to bacteria, viruses, or fungi. This condition can lead to serious complications, especially in vulnerable populations such as the elderly, young children, and individuals with weakened immune systems.
Types of Lung Infections
Lung infections can be categorized into several types, each with unique causes and characteristics:
- Bacterial Pneumonia: Caused by bacteria, it is the most common type of lung infection.
- Viral Pneumonia: Often caused by the influenza virus, it tends to be milder than bacterial pneumonia.
- Fungal Pneumonia: Resulting from fungi, this type is more common in individuals with compromised immune systems.
- Aspiration Pneumonia: Occurs when food, liquid, or vomit is inhaled into the lungs.
Common Symptoms of Lung Infections
Recognizing the symptoms of a lung infection is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment. Common symptoms include:
- Coughing (with or without mucus)
- Fever and chills
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain, especially when breathing deeply
- Fatigue and weakness
Causes of Lung Infections
Lung infections can arise from various sources:
- Bacterial Invasion: Common bacteria include Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae.
- Viral Infections: Viruses such as the flu and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) can lead to pneumonia.
- Fungal Exposure: Fungi like Pneumocystis jirovecii can cause infections, particularly in immunocompromised individuals.
- Aspiration: Inhaling foreign materials can introduce pathogens into the lungs.
Risk Factors for Lung Infections
Certain factors can increase the likelihood of developing a lung infection:
- Age (young children and elderly)
- Chronic illnesses (like COPD or diabetes)
- Smoking and exposure to secondhand smoke
- Weakened immune system (due to medications or conditions)
- Hospitalization or living in nursing homes
Diagnosis of Lung Infections
If you suspect a lung infection, your healthcare provider may conduct several tests to confirm the diagnosis:
- Physical Examination: Checking for signs of infection, such as abnormal lung sounds.
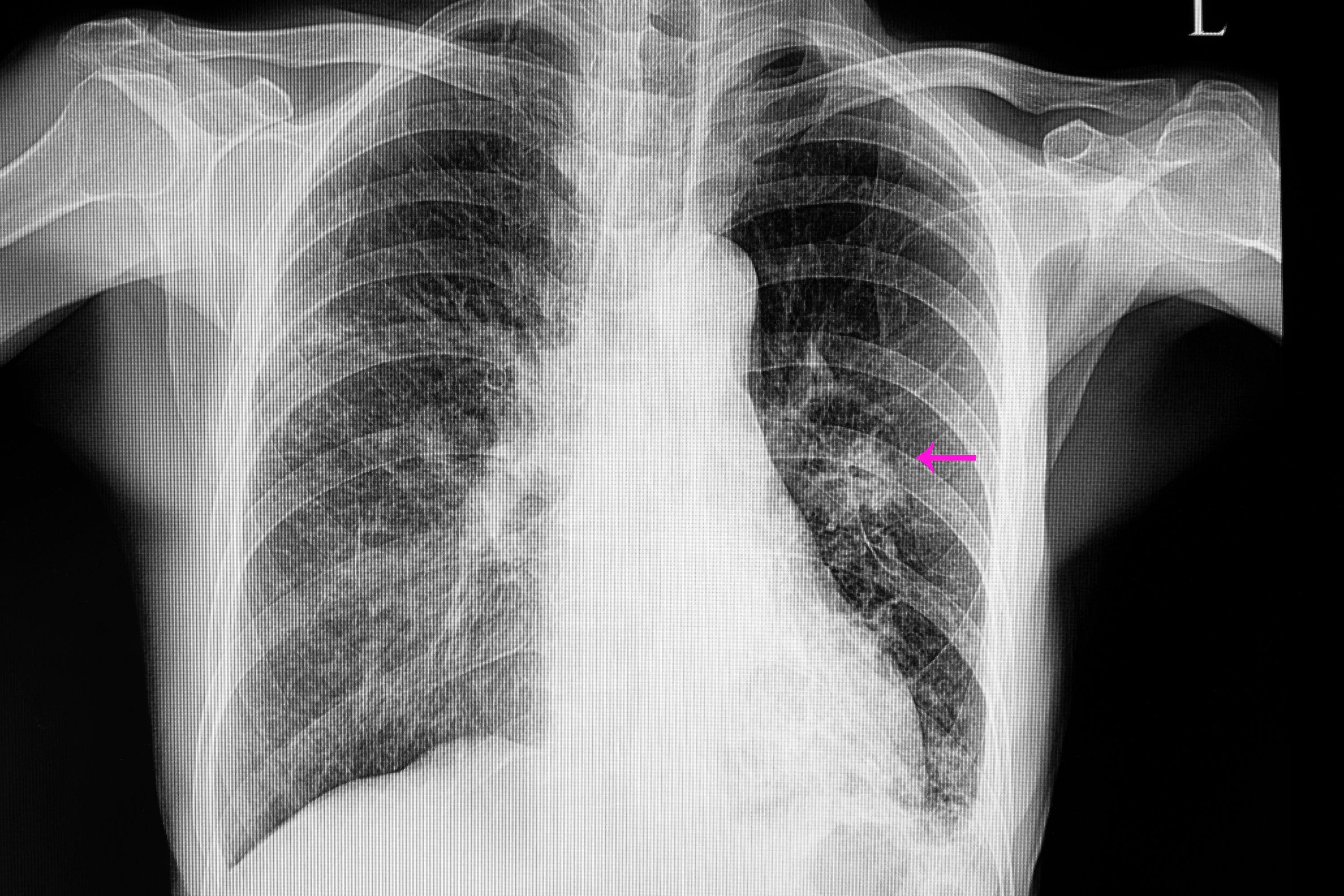
- Chest X-ray: Imaging to identify areas of inflammation or fluid in the lungs.
- Blood Tests: To detect the presence of infection or inflammation.
- Sputum Culture: Analyzing mucus from the lungs for pathogens.
Treatment Options for Lung Infections
Treatment for lung infections varies based on the underlying cause and severity:
- Antibiotics: Used for bacterial pneumonia.
- Antivirals: Prescribed for certain viral infections.
- Antifungal Medications: For fungal lung infections.
- Supportive Care: Includes rest, hydration, and over-the-counter medications for symptom relief.
Home Remedies and Management Tips
In addition to medical treatment, several home remedies and practical tips can help manage lung infections effectively:
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of fluids to help thin mucus.
- Use a Humidifier: Adding moisture to the air can ease breathing.
- Rest: Allow your body to recover by getting sufficient sleep.
- Warm Compresses: Applying warmth to the chest can relieve discomfort.
Benefits of Early Detection and Treatment
Early detection and treatment of lung infections can lead to:
- Reduced severity of symptoms
- Shorter duration of illness
- Lower risk of complications
- Improved overall recovery outcomes
Case Studies and First-Hand Experiences
Many individuals have faced lung infections, and their stories highlight the importance of awareness and timely medical intervention. For example:
- John’s Story: John, a 65-year-old man, ignored initial symptoms of coughing and fatigue. After a week, he was hospitalized with severe pneumonia. His experience underscores the necessity of seeking medical attention early.
- Maria’s Journey: Maria, a 30-year-old woman with asthma, recognized her symptoms early and sought treatment. With prompt care, her recovery was swift, showcasing the benefits of awareness in managing lung infections.
Prevention Strategies for Lung Infections
Preventing lung infections is crucial, especially for those at higher risk. Here are some effective strategies:
- Vaccinations: Get vaccinated against influenza and pneumonia.
- Practice Good Hygiene: Wash your hands frequently and avoid close contact with sick individuals.
- Avoid Smoking: Quit smoking and stay away from secondhand smoke.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Maintain a balanced diet, exercise regularly, and manage stress to boost your immune system.
Conclusion
Lung infections can have serious consequences, but understanding their causes, symptoms, and treatment options can empower you to take charge of your respiratory health. By recognizing early signs, seeking timely medical care, and implementing preventive measures, you can protect yourself and reduce the risk of lung infections. Always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and treatment options.