In the intricate tapestry of human health, the immune system stands as a vigilant guardian, orchestrating a symphony of cells and molecules designed to protect our bodies from unseen invaders. Like a skilled conductor leading an orchestra, it harmonizes various components—white blood cells, antibodies, and signaling molecules—to fend off pathogens and maintain balance within. Yet, this complex system is not merely a defensive force; it embodies a delicate interplay of recognition, response, and memory. As we delve into the fascinating world of the immune system, we will explore its remarkable functions, the factors that influence its performance, and the cutting-edge advancements that continue to reshape our understanding of immunity. Join us on this journey to uncover the mysteries of the body’s innate protector and gain insights into the vital role it plays in our overall well-being.
Understanding the Immune System: The Bodys Defense Network
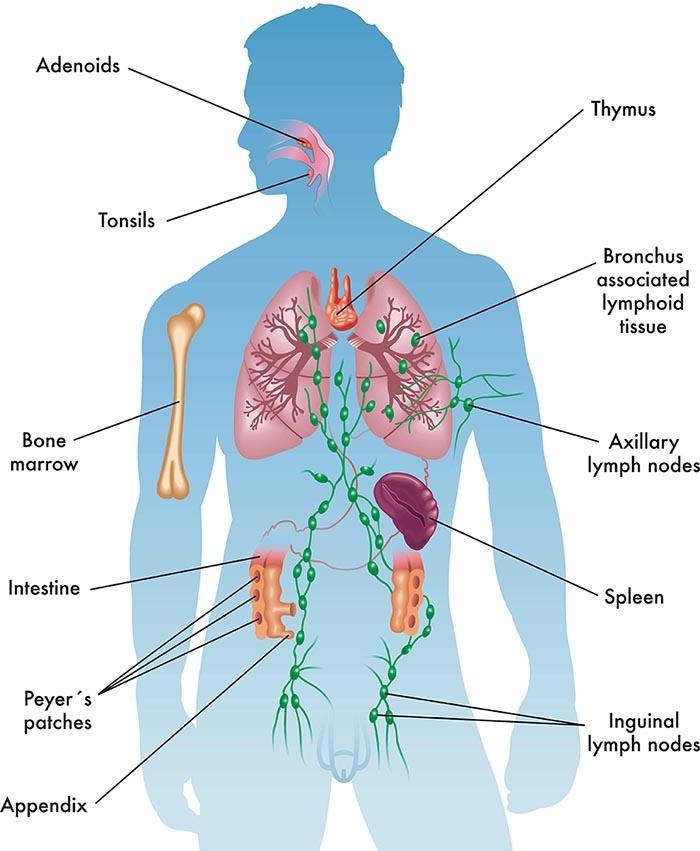
The immune system is a complex network of cells, tissues, and organs that work together to protect the body from harmful invaders. It identifies and neutralizes pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, and parasites, ensuring the body remains healthy and resilient. Key components include:
- White Blood Cells: The primary defenders that identify and destroy foreign bodies.
- Lymphatic System: A network of vessels that transports lymph, a fluid containing immune cells.
- Spleen: A vital organ that filters blood and helps fight infections.
- Bone Marrow: The birthplace of blood cells, including the crucial immune cells.
Additionally, the immune response can be categorized into two main types: innate and adaptive immunity. Innate immunity serves as the body’s first line of defense, acting quickly to provide a general response to pathogens. Adaptive immunity, on the other hand, develops over time and provides a targeted response to specific invaders. This sophisticated system also utilizes memory cells, which allow the body to respond more efficiently to previously encountered pathogens. The interaction between these two branches is essential for a well-functioning defense network.
Key Components of Immunity: Cells and Molecules at Work
The immune system is a complex network of cells and molecules that work in concert to defend the body against pathogens. Among the primary players are white blood cells, which include various types that each serve distinct functions. These cells can be categorized into two main groups: phagocytes, which engulf and destroy invaders, and lymphocytes, which are crucial for adaptive immunity. Key types of lymphocytes include:
- B cells: Responsible for producing antibodies to neutralize pathogens.
- T cells: Further divided into helper T cells that aid in orchestrating the immune response and cytotoxic T cells that directly kill infected cells.
- Natural killer (NK) cells: Provide a rapid response to virally infected cells and tumor formation.
In addition to these cells, a variety of molecules play essential roles in mounting an effective immune response. These include cytokines, which are signaling proteins that help regulate immunity, inflammation, and hematopoiesis. Furthermore, complement proteins enhance the ability of antibodies and phagocytic cells to clear microbes and damaged cells. Below is a simple overview of some key immune molecules:
| Molecule | Function |
|---|---|
| Cytokines | Mediate communication between cells during immune responses. |
| Antibodies | Bind to specific antigens on pathogens, marking them for destruction. |
| Complement proteins | Enhance opsonization and promote inflammation to eliminate pathogens. |
The Role of Nutrition: Fueling Your Immune System
Nutrition plays a paramount role in maintaining and enhancing the body’s natural defenses. A well-balanced diet rich in essential vitamins and minerals not only supports overall health but also fortifies the immune system against various pathogens. Key nutrients that should be part of your daily intake include:
- Vitamin C: Found in citrus fruits, strawberries, and bell peppers, it boosts the production of white blood cells.
- Vitamin D: Known for its role in immune regulation, sources include fatty fish, fortified foods, and sunlight exposure.
- Zinc: Essential for immune cell function, it can be obtained from meat, shellfish, legumes, and seeds.
- Probiotics: Beneficial bacteria found in yogurt and fermented foods that promote gut health and bolster immunity.
Furthermore, the timing and quality of your meals can influence immune responsiveness. Consuming a variety of whole foods ensures a diverse array of nutrients, which is crucial for the production of immune cells and antibodies. Below is a simple table highlighting some common foods and their immune-boosting properties:
| Food | Key Nutrient | Immune Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Oranges | Vitamin C | Enhances white blood cell function |
| Salmon | Vitamin D | Regulates immune responses |
| Spinach | Iron & Antioxidants | Supports overall immune health |
| Yogurt | Probiotics | Boosts gut immunity |
Lifestyle Factors: How Exercise and Sleep Influence Immunity
Engaging in regular physical activity has profound effects on the body’s defense mechanisms. Exercise not only enhances circulation but also promotes the efficient movement of immune cells throughout the body. This increased mobilization of cells, such as lymphocytes and macrophages, helps in identifying and combating pathogens more effectively. Additionally, moderate exercise is associated with lower levels of stress hormones, which can otherwise suppress immune function. It’s important to note that the type and duration of exercise matter; while moderate intensity is beneficial, excessive strenuous exercise can lead to temporary immune suppression.
Equally important is the role of sleep in maintaining a robust immune response. During sleep, the body undergoes crucial repair processes and the production of cytokines, which are proteins that help regulate immune responses. Lack of quality sleep can lead to a decrease in these protective proteins, making the body more susceptible to infections. Studies suggest that adults should aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night to optimize their immune function. The following table summarizes the key impacts of exercise and sleep on immunity:
| Factor | Positive Impact | Negative Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Exercise | Boosts circulation, mobilizes immune cells | Excessive intensity may hinder immune function |
| Sleep | Enhances cytokine production, repair processes | Insufficient sleep decreases immune defense |
Common Myths and Misconceptions: Debunking Immunity Fallacies
Many people hold misconceptions about the immune system that can lead to confusion and misinformation. One prevalent myth is that taking vitamin C can prevent colds. While vitamin C is essential for immune function and can help shorten the duration of illness, it does not provide guaranteed protection against respiratory infections. Furthermore, the idea that a stronger immune system will always lead to better health is misleading. In fact, an overly active immune response can result in autoimmune diseases, where the body mistakenly attacks its own tissues.
Another common misunderstanding is the belief that vaccines weaken the immune system. In reality, vaccines work by training the immune system to recognize and fight specific pathogens without causing the disease itself. This process not only strengthens the immune response but also promotes herd immunity, protecting those who cannot be vaccinated. Additionally, many think that stress always leads to a weakened immune response, but the relationship is more complex. While chronic stress can indeed harm immune function, short-term stress can sometimes enhance immunity, highlighting the need for a balanced perspective on the impacts of our lifestyle choices.
Practical Steps to Strengthen Your Immune System: Tips for Daily Wellness
To bolster your immune system effectively, consider integrating a few simple yet impactful habits into your daily routine. Nutrition plays a pivotal role; focus on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. These foods are packed with essential vitamins and minerals that support immune function. Additionally, stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day, as hydration is key for optimal cellular function.
Another significant factor is regular physical activity. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week, which can enhance circulation and help your body fight off illness. Don’t forget the importance of quality sleep; aim for 7-9 hours each night to allow your body to recover and regenerate. Lastly, consider incorporating mindfulness practices such as meditation or yoga to reduce stress levels, as chronic stress can negatively impact your immune system.
Q&A
Q&A: Understanding the Immune System
Q1: What exactly is the immune system?
A1: The immune system is like the body’s own superhero squad, tirelessly working to defend against harmful invaders such as bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens. Comprising a complex network of cells, tissues, and organs, it coordinates a response to identify and eliminate these threats while distinguishing them from the body’s own healthy cells.
Q2: How does the immune system recognize invaders?
A2: The immune system employs a high-tech recognition system. Specialized cells called antigen-presenting cells display pieces of pathogens, known as antigens, on their surfaces. When immune cells, like T-cells and B-cells, encounter these antigens, they spring into action, launching targeted attacks or producing antibodies to neutralize the intruders.
Q3: Are there different types of immunity?
A3: Absolutely! There are two primary types of immunity: innate and adaptive. Innate immunity is the body’s first line of defense, featuring barriers like skin and mucous membranes, along with immune cells that respond quickly to any threat. Adaptive immunity, on the other hand, develops over time, providing a tailored response to specific pathogens and creating a memory that enhances future defenses.
Q4: Can the immune system remember past infections?
A4: Yes! Think of the immune system as a librarian with a vast archive of past encounters. Once the immune system has successfully fought off an infection, it retains a memory of it through memory B-cells and T-cells. This memory allows for a faster and more efficient response if the same pathogen tries to invade again, which is why vaccines are so effective in preparing our immune defenses.
Q5: What factors can weaken the immune system?
A5: Several factors can compromise this intricate defense system. Chronic stress, poor nutrition, lack of sleep, and sedentary lifestyles can all take a toll on immune function. Additionally, certain medical conditions and age can also diminish the immune response, making individuals more susceptible to infections.
Q6: How can we boost our immune system?
A6: While there’s no magic potion for instant immunity, maintaining a healthy lifestyle is key. Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables, exercising regularly, staying hydrated, managing stress, and getting adequate sleep can all enhance immune function. Additionally, vaccines can provide essential protection against specific diseases, fortifying the body’s defenses.
Q7: Is it possible to have an overactive immune system?
A7: Yes! An overactive immune system can lead to allergic reactions and autoimmune disorders, where the body mistakenly attacks its own tissues as if they were foreign invaders. Conditions like asthma, rheumatoid arthritis, and lupus are examples of how the immune system can misinterpret the body’s signals, leading to inflammation and damage.
Q8: How does the immune system change as we age?
A8: As we age, the immune system undergoes a gradual decline in function, a phenomenon known as immunosenescence. This can result in a slower response to infections and a reduced ability to generate new immune cells. Consequently, older adults may face a higher risk of infections and may not respond as well to vaccines, emphasizing the importance of proactive health measures in maintaining immune resilience.
Q9: What role does the gut microbiome play in immunity?
A9: The gut microbiome is a bustling metropolis of microorganisms that plays a crucial role in supporting the immune system. These friendly microbes help train immune cells, modulate inflammatory responses, and even influence the production of antibodies. A balanced and diverse microbiome, often supported by a diet rich in fiber and fermented foods, can enhance overall immune health.
Q10: What’s the takeaway message about the immune system?
A10: The immune system is a remarkable and dynamic defense mechanism, continually adapting to protect the body from a myriad of threats. By understanding its functions and supporting it through healthy lifestyle choices, we can empower our immune defenses to keep us thriving in the face of challenges.
The Conclusion
As we draw the curtain on our exploration of the immune system, it becomes clear that this intricate network of cells and molecules is nothing short of a marvel. Like a well-orchestrated symphony, each component plays its part in the ongoing performance of protection and resilience. From the first line of defense offered by our skin to the sophisticated responses of antibodies, our immune system is a dynamic and adaptive fortress, tirelessly working to shield us from the unseen threats that surround us.
Understanding how this complex system operates not only deepens our appreciation for the human body but also highlights the importance of nurturing our immune health. Lifestyle choices, nutrition, and stress management play pivotal roles in ensuring that our defenses remain robust and responsive. As we navigate an ever-changing world, let us carry this knowledge with us, empowering ourselves to foster our well-being and embrace the vitality that a well-functioning immune system can provide.
In the grand tapestry of life, our immune system is the thread that binds our body’s defenses, reminding us that we are not just passive inhabitants of our own health, but active participants in the journey toward wellness. As we conclude this discussion, may we continue to seek understanding and cultivate the habits that support our immune resilience, ensuring that we can thrive in every season of life.