Understanding Hernias: Unraveling the Mystery of a Common Condition
Imagine your body’s sturdy walls, crafted to protect and support your vital organs. Now, picture a small, unexpected breach in that fortress—this is the essence of a hernia. While often overlooked or misunderstood, hernias are more common than many realize, affecting millions of people worldwide. This article aims to demystify this condition, exploring its various types, potential causes, and available treatment options. Whether you’re seeking knowledge for yourself or someone you care about, join us as we journey through the anatomy of hernias, shedding light on their impact on health and well-being.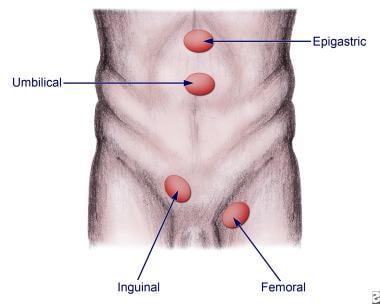
Understanding the Basics of Hernias and Their Types
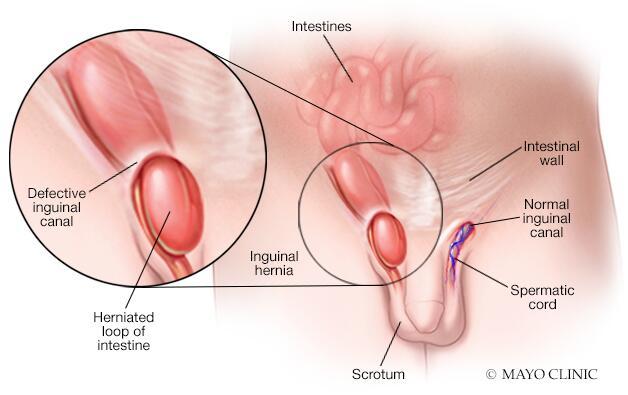
A hernia occurs when an internal organ or tissue pushes through a weak spot in the surrounding muscle or connective tissue. This condition can manifest in various parts of the body and is often exacerbated by factors such as heavy lifting, obesity, or chronic coughing. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of a hernia is crucial for early detection and treatment. Common symptoms may include:
- A noticeable bulge in the affected area
- Pain or discomfort, especially when bending, coughing, or lifting
- Weakness in the abdomen or groin
- Possible gastrointestinal issues like constipation or nausea
There are several types of hernias, each with unique characteristics. The most prevalent include:
| Type of Hernia | Description |
|---|---|
| Inguinal Hernia | Occurs in the groin area, most common in men. |
| Femoral Hernia | Develops when tissue pushes through a weak spot in the femoral canal, more common in women. |
| Umbilical Hernia | Appears near the belly button, often seen in infants. |
| Hiatal Hernia | Occurs when part of the stomach pushes through the diaphragm into the chest cavity. |
Recognizing the Symptoms: When to Seek Medical Attention
Understanding when to seek medical attention for a hernia is crucial for your health and well-being. Some symptoms may indicate that immediate care is required, including:
- Severe pain at the site of the hernia
- Swelling or a noticeable bulge that becomes larger
- Nausea or vomiting accompanying the discomfort
- Inability to pass gas or have a bowel movement
Additionally, if the bulge becomes tender, discolored, or feels firm to the touch, these signs suggest a potential complication known as strangulation. In such cases, blood supply to the affected area can be compromised, leading to serious health risks. Consider the following table for easy reference on symptoms that warrant urgent intervention:
| Symptom | Action |
|---|---|
| Severe pain | Visit the emergency room immediately |
| Bulge grows larger | Schedule a consultation with a surgeon |
| Nausea or vomiting | Seek medical attention |
| Inability to pass gas | Contact your healthcare provider |
The Diagnostic Journey: Tests and Procedures Explained
Diagnosing a hernia typically begins with a thorough physical examination conducted by a healthcare professional. During this assessment, the doctor will check for visible bulges or swelling, particularly in the abdomen or groin area. In some cases, the patient may be asked to perform specific maneuvers, such as coughing, to help reveal the hernia. If the diagnosis remains unclear, further tests may be recommended to provide a clearer picture of the underlying issue.
Common diagnostic procedures include:
- Ultrasound: This imaging technique uses sound waves to create images of the internal structures, helping to identify the presence and type of hernia.
- X-rays: If complications like bowel obstruction are suspected, X-rays can be useful in visualizing the affected areas.
- CT scans: A computed tomography scan provides detailed cross-sectional images, offering more precise information on the size and location of the hernia.
| Test/Procedure | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Physical Examination | Initial assessment and detection of hernia. |
| Ultrasound | Visualize soft tissues and assess hernia type. |
| CT Scan | Detailed imaging for size and complications. |
Treatment Options: From Lifestyle Changes to Surgical Solutions
When it comes to addressing a hernia, the approach often begins with lifestyle changes that can alleviate discomfort and prevent further complications. These modifications may include:
- Dietary Adjustments: Incorporating high-fiber foods to prevent constipation, which can exacerbate hernias.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce pressure on the abdominal wall.
- Exercise: Engaging in low-impact activities to strengthen core muscles without straining them.
- Avoiding Heavy Lifting: Being mindful of physical strain that can aggravate the condition.
For more severe cases, surgical interventions may be necessary to repair the hernia effectively. The most common surgical options include:
| Procedure | Description |
|---|---|
| Open Surgery | A traditional method involving a larger incision to access the hernia directly. |
| Laparoscopic Surgery | A minimally invasive technique using small incisions and a camera for guidance. |
| Robotic Surgery | An advanced form of laparoscopic surgery providing enhanced precision through robotic assistance. |
Preventive Strategies: Reducing Your Risk of Developing a Hernia
Taking proactive measures can significantly lower your chances of developing a hernia. Incorporating exercise into your daily routine is essential. Focus on strengthening your core and abdominal muscles, as a strong core can help support your internal organs. Consider the following activities:
- Weight training: Build your strength progressively to avoid straining your muscles.
- Pilates or yoga: These practices enhance flexibility and core stability.
- Aerobic exercises: Improve overall fitness and help maintain a healthy weight.
In addition to physical activity, maintaining a healthy lifestyle plays a crucial role in hernia prevention. Proper nutrition and weight management can alleviate excess pressure on your abdomen. Consider the following dietary strategies:
| Food Group | Recommended Foods |
|---|---|
| Fruits & Vegetables | Berries, leafy greens, carrots |
| Whole Grains | Quinoa, brown rice, oats |
| Lean Proteins | Chicken, fish, legumes |
| Healthy Fats | Avocados, nuts, olive oil |
Furthermore, staying hydrated and avoiding heavy lifting or straining during physical activities can also prevent hernias. Remember, little changes in your daily habits can lead to significant improvements in your overall health and well-being.
Navigating Recovery: Tips for Post-Surgery Care and Rehabilitation
Recovering from hernia surgery requires a thoughtful approach to ensure a smooth healing process and minimize the risk of complications. After the procedure, it is essential to prioritize rest and allow your body the time it needs to recover. Listening to your body is crucial; if you feel pain or discomfort, don’t shy away from taking a step back. Here are some tips to keep in mind during your recovery:
- Follow your surgeon’s instructions: Adhering to the guidelines provided by your healthcare team is vital for a successful recovery.
- Manage pain effectively: Use prescribed medications as directed and discuss any concerns about pain management with your doctor.
- Gradually increase activity: Start with light activities and slowly incorporate more strenuous tasks as your body heals.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of fluids can help with digestion and overall well-being.
Nutrition also plays a significant role in your recovery journey. A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals can support healing and boost your energy levels. Consider incorporating foods that promote recovery into your meals, such as:
| Food | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Lean Proteins | Support muscle repair and recovery. |
| Fruits & Vegetables | Rich in antioxidants and vitamins for healing. |
| Whole Grains | Provide energy and fiber for digestion. |
| Healthy Fats | Support cell regeneration and overall health. |
Q&A
Q&A: Understanding Hernias
Q1: What exactly is a hernia?
A1: A hernia occurs when an organ or tissue protrudes through a weak spot in the surrounding muscle or connective tissue. This can create a noticeable bulge, often accompanied by discomfort or pain. Common types include inguinal (groin), umbilical (belly button), and hiatal hernias.
Q2: What causes a hernia to develop?
A2: Hernias can develop due to a variety of factors. These include congenital weaknesses in the abdominal wall, increased pressure within the abdomen from heavy lifting, straining during bowel movements, obesity, or even chronic coughing. Aging also plays a role, as muscles can weaken over time.
Q3: Are there any symptoms I should be aware of?
A3: Yes! Common symptoms of a hernia include a visible bulge, discomfort or pain at the site, especially when lifting or bending, and sometimes nausea or vomiting in cases of a strangulated hernia. In some instances, hernias can be asymptomatic, only becoming noticeable during physical activity.
Q4: How is a hernia diagnosed?
A4: Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination by a healthcare professional, who may ask you to cough or strain to observe the bulge. Imaging tests, such as ultrasound or CT scans, can also be used to confirm the diagnosis, especially in ambiguous cases.
Q5: What treatment options are available?
A5: Treatment for a hernia depends on its size and severity. Sometimes, lifestyle changes and watchful waiting are all that’s needed. However, surgery is often recommended to repair the hernia, especially if it causes pain or complications. Surgical options may include open surgery or minimally invasive laparoscopic techniques.
Q6: Can I prevent a hernia from occurring?
A6: While not all hernias can be prevented, certain strategies can help reduce the risk. Strengthening core muscles through exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, using proper lifting techniques, and avoiding prolonged coughing or straining can all be beneficial.
Q7: What should I do if I suspect I have a hernia?
A7: If you suspect you have a hernia, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management. Early intervention can help prevent complications, such as strangulation, where the blood supply to the herniated tissue is cut off.
Q8: Are hernias common?
A8: Yes, hernias are quite common, affecting millions of people worldwide. They can occur at any age, but certain types, like inguinal hernias, are more prevalent in men. Understanding the risks and being aware of symptoms can help in timely diagnosis and treatment.
Q9: What is the recovery process after hernia surgery?
A9: Recovery after hernia surgery varies based on the type of procedure, but most people experience a relatively quick return to normal activities. Pain management, rest, and gradually increasing light activity are key to a smooth recovery. It’s important to follow your surgeon’s post-operative instructions closely.
Q10: Can hernias recur after surgery?
A10: While hernia repairs are generally successful, there is a possibility of recurrence. Factors such as infection, strain on the surgical site, or underlying medical conditions can contribute to this. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and following medical advice post-surgery can help reduce this risk.
Whether for understanding or prevention, knowing more about hernias can empower you to take proactive steps for your health!
In Conclusion
As we draw the curtain on our exploration of hernias, it becomes clear that this common yet often misunderstood medical condition can affect anyone, regardless of age or lifestyle. Whether it’s the result of heavy lifting, natural wear and tear, or a genetic predisposition, understanding the nuances of hernias empowers us to approach our health with greater awareness.
The journey from symptoms to diagnosis and treatment is a path best navigated with the guidance of healthcare professionals. As we continue to advance in medical science, new techniques and interventions offer hope to those affected, transforming lives and restoring comfort.
Ultimately, knowledge is our most potent ally in the battle against hernias. By recognizing the signs, seeking timely medical advice, and embracing preventive measures, we can take proactive steps to safeguard our well-being. Let this article serve as a starting point for further inquiry and dialogue, fostering a community that prioritizes health and education. In a world where our bodies are our most valuable assets, understanding conditions like hernias is not just beneficial; it’s essential.