Hepatitis, a term that often evokes concern and curiosity, is more than just a medical condition; it is a complex tapestry woven from various viral strains, modes of transmission, and global health implications. As we delve into the world of this multifaceted disease, we uncover the intricacies of its types—A, B, C, D, and E—each with its own story and set of challenges. From the bustling streets of urban centers to remote villages across continents, hepatitis poses a silent threat, often going unnoticed until it reaches advanced stages. This article aims to illuminate the nuances of hepatitis, exploring its causes, symptoms, prevention, and the ongoing efforts to combat its spread. Join us on this informative journey to understand a condition that affects millions worldwide, shedding light on its impact on both individual lives and public health.
Understanding Hepatitis: Types, Transmission, and Global Impact
Hepatitis encompasses a range of viral infections that cause inflammation of the liver, leading to significant health challenges worldwide. The most common types are Hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E, each with distinct modes of transmission and varying impacts on health. Hepatitis A and E are primarily transmitted through contaminated food and water, making hygiene practices critical in preventing outbreaks. In contrast, Hepatitis B and C are spread through exposure to infected bodily fluids, such as blood, making safe practices in healthcare and personal behaviors essential. Hepatitis D is a unique virus that can only infect individuals already infected with Hepatitis B, illustrating the complexity of viral interactions within the body.
The global impact of hepatitis is profound, with millions of individuals affected and a significant burden on healthcare systems. According to the World Health Organization, approximately 325 million people are living with chronic hepatitis B and C infections, leading to 1.4 million deaths each year, primarily from cirrhosis and liver cancer. Prevention strategies, including vaccination for Hepatitis A and B, safe injection practices, and public health initiatives, are vital in reducing transmission rates. Below is a table summarizing the key differences among the types of hepatitis:
| Type | Transmission | Prevention |
|---|---|---|
| A | Fecal-oral route | Vaccination, hygiene |
| B | Blood, sexual contact | Vaccination, safe practices |
| C | Blood | Safe injections, treatment |
| D | Requires Hepatitis B | Vaccination against B |
| E | Fecal-oral route | Improved sanitation |
Recognizing Symptoms: Early Warning Signs of Hepatitis Infection
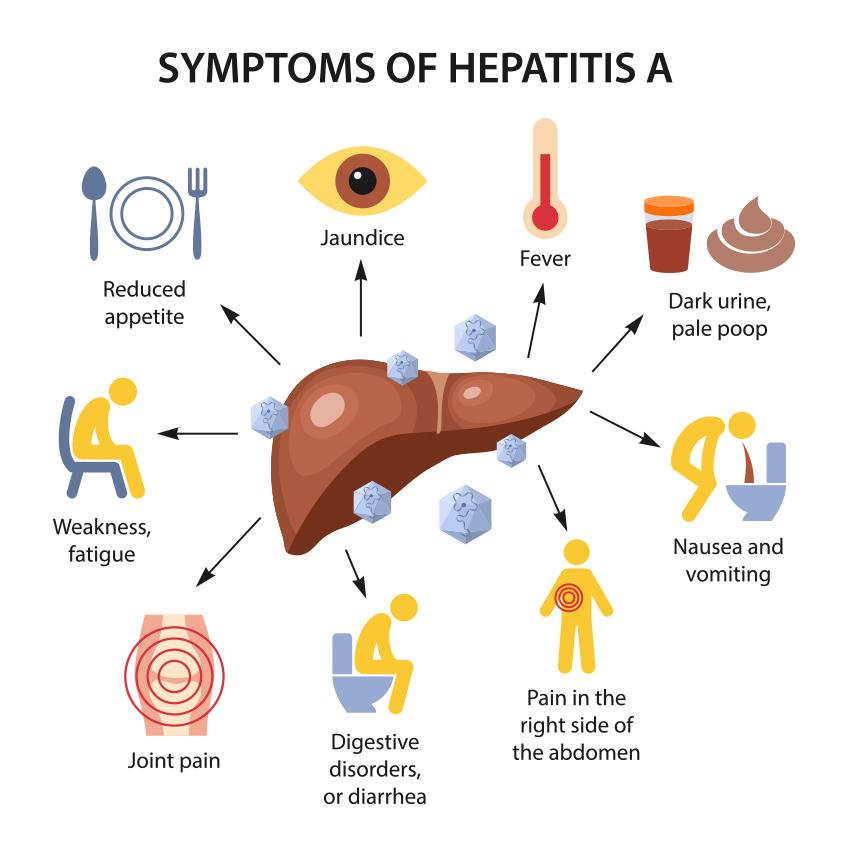
Hepatitis can manifest in various forms, and recognizing its early warning signs is crucial for timely intervention. Individuals may experience symptoms that can easily be mistaken for common illnesses. Fatigue, often profound and persistent, is one of the first indicators. Alongside this, many report loss of appetite and nausea, which can lead to significant weight loss over time. Other signs to be aware of include:
- Dark urine: A noticeable change in urine color can indicate liver dysfunction.
- Jaundice: The yellowing of skin and eyes is a classic sign of liver issues.
- Abdominal discomfort: Pain or discomfort in the upper right abdomen may signal liver inflammation.
Though these symptoms can vary by individual and the type of hepatitis, understanding them can lead to earlier diagnosis and treatment. To further clarify, the following table illustrates the symptoms commonly associated with different hepatitis types:
| Hepatitis Type | Common Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Hepatitis A | Fatigue, nausea, abdominal pain, jaundice |
| Hepatitis B | Loss of appetite, dark urine, joint pain |
| Hepatitis C | Fatigue, jaundice, chronic pain |
Diagnosis and Testing: Navigating the Path to Accurate Detection
Accurate detection of hepatitis hinges on a multifaceted approach involving both clinical evaluation and laboratory testing. Typically, healthcare providers begin by assessing the patient’s medical history and conducting a physical examination. This process may unveil crucial signs and symptoms, such as jaundice, fatigue, or abdominal pain. Following this, a series of tests are employed to confirm the diagnosis and determine the specific type of hepatitis—be it A, B, C, or another variant. These tests generally include:
- Blood tests: To measure liver enzymes, assess liver function, and identify specific viral markers.
- Imaging tests: Such as ultrasounds, to visualize any liver damage or abnormalities.
- Liver biopsy: In certain cases, to evaluate the extent of liver inflammation or scarring.
Understanding the results of these tests is crucial for effective treatment planning. The following table summarizes the common types of hepatitis and their diagnostic tests:
| Type of Hepatitis | Key Diagnostic Tests |
|---|---|
| Hepatitis A | Anti-HAV antibody test |
| Hepatitis B | HBsAg, Anti-HBs, and Anti-HBc tests |
| Hepatitis C | Anti-HCV antibody test and HCV RNA test |
This comprehensive diagnostic process not only aids in identifying the presence of the virus but also helps clinicians understand the stage of infection, guiding them towards the most appropriate therapeutic interventions. By effectively navigating these diagnostic steps, patients can receive timely treatment, improving their chances of recovery and reducing the risk of liver complications.
Treatment Options: Exploring Therapies and Management Strategies
When it comes to managing hepatitis, a tailored approach is essential. Treatment options vary significantly depending on the type of hepatitis (A, B, C, D, or E) and the particular needs of the patient. For chronic hepatitis B and C, antiviral medications have become a cornerstone of therapy, aiming to reduce viral load and prevent liver damage. Some of the commonly prescribed antiviral treatments include:
- Tenofovir – often used for chronic hepatitis B.
- Entecavir – another effective option for hepatitis B.
- Ledipasvir/Sofosbuvir – a combination therapy for hepatitis C.
- Glecaprevir/Pibrentasvir – used for various genotypes of hepatitis C.
In addition to antiviral drugs, lifestyle changes play a crucial role in the management of hepatitis. Patients are encouraged to adopt a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, maintain regular exercise, and avoid substances that could further harm the liver such as alcohol and certain medications. Supportive therapies may also be beneficial:
| Therapy | Description |
|---|---|
| Nutritional Counseling | Guidance on diet to support liver health. |
| Psycho-social Support | Counseling to cope with emotional aspects of the disease. |
| Regular Monitoring | Frequent check-ups to assess liver function and treatment efficacy. |
Prevention Strategies: How to Reduce Your Risk of Hepatitis
To effectively safeguard yourself against hepatitis, consider adopting a multifaceted approach that emphasizes hygiene and lifestyle choices. Maintaining proper hand hygiene is crucial; wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water after using the restroom and before handling food. Additionally, be cautious with food and drink, especially when traveling to areas with low sanitation standards. Opt for bottled water and avoid raw or undercooked foods to diminish your risk. Ensure that any tattoos or piercings are done in reputable establishments that follow strict hygiene protocols.
Vaccination is a powerful tool in hepatitis prevention. For example, vaccines are available for hepatitis A and B, and getting vaccinated can significantly lower your risk. Moreover, practicing safe sex by using condoms can help prevent the spread of hepatitis B and C, particularly among individuals with multiple partners. It is also wise to avoid sharing personal items such as razors or toothbrushes, which can carry infectious blood. By integrating these strategies into your daily life, you can greatly reduce your vulnerability to hepatitis.
Living with Hepatitis: Support Systems and Lifestyle Adjustments
Living with hepatitis can be a complex journey, but the right support systems can make a significant difference in managing the condition. Building a strong network of support is essential. Consider reaching out to:
- Healthcare Professionals: Regular check-ups and consultations with specialists can help monitor your health.
- Support Groups: Connecting with others who share similar experiences can provide emotional relief and practical advice.
- Friends and Family: Having a reliable support system at home can help you navigate daily challenges.
Adapting your lifestyle is equally important to manage hepatitis effectively. Small changes can lead to significant improvements in your overall well-being. Here are some lifestyle adjustments to consider:
- Balanced Diet: Focus on a nutrient-rich diet that includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Limiting alcohol and processed foods is crucial.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in physical activity can boost your immune system and improve your mood. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise each week.
- Stress Management: Practices such as yoga, meditation, or deep-breathing exercises can help reduce stress levels.
Q&A
Q&A: Understanding Hepatitis
Q1: What is hepatitis?
A1: Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver, a vital organ responsible for various bodily functions, including detoxification and metabolism. This condition can result from viral infections, toxins, alcohol consumption, autoimmune diseases, or certain medications. The term “hepatitis” encompasses several forms, with the most common being hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E, each differing in transmission, severity, and treatment.
Q2: How is hepatitis transmitted?
A2: Transmission varies depending on the type of hepatitis. Hepatitis A and E are typically spread through the consumption of contaminated food or water. In contrast, hepatitis B and C are primarily transmitted through blood and other bodily fluids, such as sharing needles or unprotected sex. Hepatitis D, an unusual player, only exists in conjunction with hepatitis B, thus sharing similar routes of transmission.
Q3: What are the symptoms of hepatitis?
A3: Symptoms can range from mild to severe and may vary based on the type of hepatitis. Common signs include fatigue, jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), abdominal pain, dark urine, light-colored stool, and nausea. Some individuals may be asymptomatic, particularly in the early stages, making regular screenings essential for high-risk groups.
Q4: How is hepatitis diagnosed?
A4: Diagnosis begins with a thorough medical history and physical examination. Blood tests play a crucial role, revealing the presence of specific antibodies or viral genetic material. These tests help determine the type of hepatitis and the extent of liver damage, guiding appropriate treatment options.
Q5: Is there a cure for hepatitis?
A5: The answer varies. Hepatitis A and E typically resolve on their own without specific treatment. Hepatitis B can be managed with antiviral medications, though it may not be completely eradicated. Hepatitis C has seen significant advancements with direct-acting antiviral drugs that can cure the infection in many cases. Hepatitis D, however, remains challenging, as treatments are limited and often rely on effective management of hepatitis B.
Q6: How can hepatitis be prevented?
A6: Prevention strategies differ for each type. Vaccination is available for hepatitis A and B, providing robust protection. Practicing good hygiene, such as proper handwashing and safe food handling, can help combat hepatitis A and E. For hepatitis B and C, avoiding sharing needles and engaging in safe sex are crucial preventive measures. Regular screenings for at-risk individuals can also play a pivotal role in early detection and management.
Q7: What is the impact of hepatitis on public health?
A7: Hepatitis is a significant global health concern, affecting millions and contributing to liver disease, cirrhosis, and liver cancer. Public health initiatives focus on vaccination, education, and treatment accessibility to reduce the prevalence and impact of the disease. Awareness campaigns aim to destigmatize hepatitis, encouraging individuals to seek testing and treatment without fear.
Q8: What should someone do if they suspect they have hepatitis?
A8: If you suspect you have hepatitis, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional promptly. Early diagnosis and intervention can prevent complications and improve outcomes. A healthcare provider can guide you through testing, explain the results, and develop a personalized treatment plan if needed, ensuring you’re not navigating this journey alone.
By unraveling the complexities of hepatitis, we empower ourselves and others with the knowledge to foster better health and well-being.
In Summary
the journey through the intricate landscape of hepatitis reveals a complex interplay of viral behaviors, human resilience, and the ongoing quest for effective treatment and prevention. As we navigate the waters of awareness, it becomes increasingly clear that education, early detection, and compassionate care are our best allies in combating this silent adversary. Whether through vaccination, lifestyle choices, or medical breakthroughs, we hold the power to transform the narrative surrounding hepatitis. By fostering a culture of understanding and support, we can empower individuals and communities to take charge of their health. Together, let us illuminate the shadows of this disease, turning knowledge into action and hope into healing.