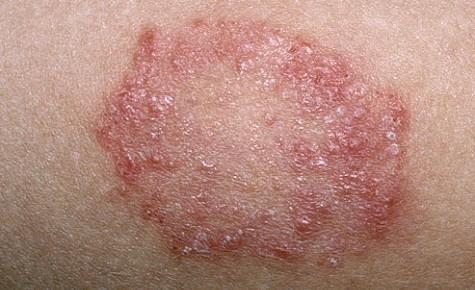
In a world teeming with diverse forms of life, fungi often dwell in the shadows, unseen yet omnipresent. From the forest floor to the walls of our homes, these organisms play a crucial role in ecosystems, decomposing organic matter and recycling nutrients. However, lurking beneath their seemingly innocuous facade lies a darker side: fungal infections. These opportunistic invaders can wreak havoc on human health, targeting individuals with weakened immune systems and sparking a growing concern in the medical community. As we delve into the realm of fungal infections, we will explore their causes, symptoms, and the latest advancements in treatment, shedding light on an often-overlooked aspect of our biological world. Join us on this journey to understand how these tiny organisms can have a profound impact on our lives, urging us to take heed of the delicate balance between nature and human health.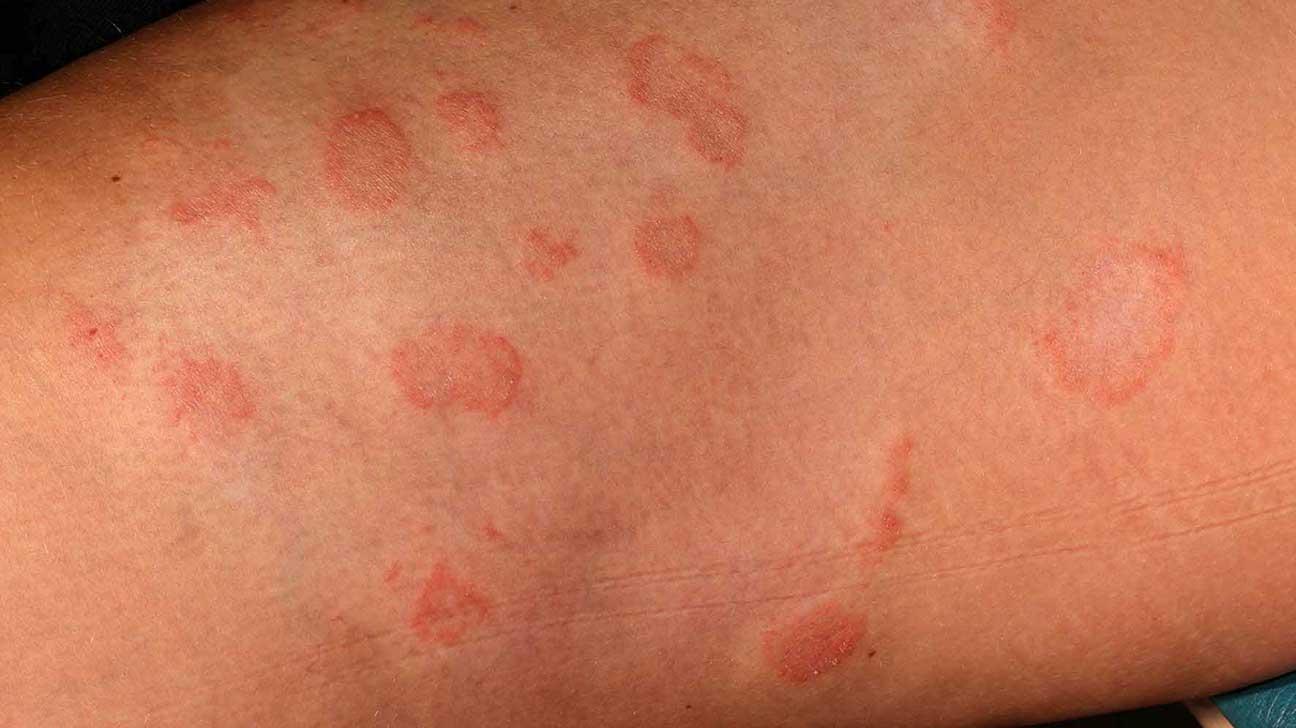
Understanding Fungal Infections and Their Causes
Fungal infections are caused by a variety of fungi that can thrive in moist, warm environments. These microorganisms are ubiquitous in nature, existing in soil, air, and even on human skin. There are several factors that can contribute to the development of fungal infections, including:
- Weakened Immune System: Individuals with compromised immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or undergoing chemotherapy, are more susceptible.
- Antibiotic Use: Prolonged use of antibiotics can disrupt the balance of normal flora, allowing fungi to overgrow.
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels can create a conducive environment for fungal growth.
- Moisture: Areas of the body that remain damp, such as between toes or under breasts, are prime targets for fungal infections.
Common types of fungal infections include athlete’s foot, ringworm, and candidiasis. Each of these infections is caused by different species of fungi and presents unique symptoms. Understanding the specific fungi involved can aid in effective treatment. A simple overview of some common fungal infections, their causes, and symptoms is illustrated in the table below:
| Fungal Infection | Caused By | Common Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Athlete’s Foot | Trichophyton rubrum | Itching, burning, peeling skin |
| Ringworm | Microsporum canis | Red, itchy, circular rash |
| Candidiasis | Candida albicans | White patches, itching, discomfort |
Identifying Symptoms: Signs That Should Not Be Ignored
Fungal infections can manifest in various ways, and some signs are more indicative of a serious problem than others. It’s essential to pay attention to these symptoms, as early detection can prevent complications. Common warning signs include:
- Persistent itching – An unrelenting itch, especially in warm, moist areas of the body, can signal a fungal infection.
- Redness and inflammation – Noticeable redness or swelling around the infected area often points to a fungal issue.
- Patches of dry or flaky skin – These patches may appear white, red, or discolored and can be a sign of a dermatophyte infection.
- Unusual odor – Foul-smelling infections, particularly in skin folds, may indicate a yeast infection.
If symptoms progress, they can lead to more severe complications, making it crucial to seek medical advice. In some cases, additional symptoms might arise, indicating a more systemic issue:
| Symptom | Possible Implication |
|---|---|
| Fever | Signs of systemic infection |
| Fatigue | Possible widespread fungal presence |
| Joint pain | Fungal arthritis or systemic spread |
Diagnosis Techniques: From Visual Examination to Laboratory Tests
Diagnosing a fungal infection involves a combination of visual examination and more advanced techniques to confirm the presence and type of fungus. Initial assessments often include a thorough inspection of the affected area, where practitioners look for characteristic signs such as redness, swelling, and scaling. Common visual indicators can include:
- Red rash or patches
- Itchiness or discomfort
- Flaking or peeling skin
- Discoloration of nails or hair
Once a visual inspection raises suspicion, laboratory tests become critical for an accurate diagnosis. These tests can range from microscopic examination of skin scrapings to culture tests that identify the specific fungal species involved. In some cases, blood tests may be necessary to detect disseminated fungal infections. Key laboratory techniques include:
| Test Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Direct visualization of fungal hyphae or spores. |
| Culture | Growing the fungus in a controlled environment to identify it. |
| Serology | Blood tests to detect immune responses to fungal antigens. |
Treatment Options: Navigating Antifungal Medications and Home Remedies
When it comes to combating fungal infections, a variety of treatment options are available, ranging from prescription antifungal medications to natural home remedies. Antifungal medications are often the frontline defense, categorized into several classes based on their mechanism of action. Commonly prescribed options include:
- Azoles: Effective for skin and systemic infections, they inhibit fungal growth.
- Echinocandins: Primarily used for severe candidiasis and invasive fungal infections, they disrupt cell wall synthesis.
- Polyene antibiotics: Target the cell membrane, commonly used for serious infections like cryptococcosis.
In addition to pharmaceuticals, some individuals may seek out home remedies to alleviate symptoms or support recovery. While these alternatives can be comforting, it’s essential to approach them with caution. Some popular home remedies include:
- Tea Tree Oil: Known for its antifungal properties, it’s often applied topically.
- Apple Cider Vinegar: A natural disinfectant that may help restore skin pH.
- Garlic: Believed to possess antifungal activity, it can be consumed or applied in oil form.
However, it’s crucial to remember that while home remedies can provide relief, they should not replace professional medical advice or treatment. Combining conventional medications with supportive home therapies may enhance recovery and promote overall well-being.
Preventive Measures: Protecting Yourself from Future Infections
To effectively shield yourself from future fungal infections, it is essential to adopt a holistic approach to hygiene and lifestyle choices. Start by maintaining a clean and dry environment, as fungi thrive in moist conditions. Consider these preventive measures:
- Wear breathable fabrics: Opt for cotton or moisture-wicking materials to reduce sweat accumulation.
- Avoid tight footwear: Choose shoes that allow air circulation to keep your feet dry.
- Practice good personal hygiene: Regularly wash and thoroughly dry areas prone to moisture, such as armpits, groin, and between toes.
- Limit exposure to communal areas: Use sandals in locker rooms, pools, and shared showers to minimize contact with fungal spores.
In addition to personal care, enhancing your immune system plays a pivotal role in preventing infections. A balanced diet rich in antioxidants and probiotics can boost your body’s defenses against fungal threats. Consider incorporating a variety of foods into your meals:
| Food Group | Examples |
|---|---|
| Fruits & Vegetables | Blueberries, Spinach, Garlic |
| Probiotic-rich Foods | Yogurt, Sauerkraut, Kimchi |
| Nuts & Seeds | Almonds, Chia seeds, Walnuts |
By integrating these practices into your daily routine, you can significantly lower your risk of fungal infections and promote overall well-being.
Living with Fungal Infections: Managing Symptoms and Finding Support
Living with a fungal infection can be challenging, as it often brings a host of uncomfortable symptoms that can interfere with daily life. To manage these symptoms effectively, it’s essential to adopt a proactive approach. Start by maintaining good hygiene, as keeping affected areas clean and dry can significantly reduce irritation. Incorporating antifungal powders or creams into your routine can also provide relief. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Wear breathable fabrics: Opt for loose-fitting clothing made from natural fibers to help keep moisture at bay.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can aid in flushing out toxins from your body.
- Limit sugar intake: Reducing sugar can help starve the fungi, as they thrive on sugar and yeast.
Support is crucial when dealing with fungal infections, both emotionally and physically. Connecting with others who share similar experiences can provide a sense of community and encouragement. Consider joining support groups, whether online or in-person, where you can share your journey and learn from others. Additionally, consulting with healthcare professionals can help you explore various treatment options tailored to your specific needs. Below is a simple table outlining potential support options:
| Support Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Online Forums | Discussion boards where individuals can share experiences and advice. |
| Local Support Groups | Meetings where people can connect in person and discuss coping strategies. |
| Healthcare Consultations | Regular check-ins with doctors to ensure proper management of the infection. |
Q&A
Q&A: Understanding Fungal Infections
Q: What exactly is a fungal infection?
A: A fungal infection occurs when fungi, which are microscopic organisms, invade the body and begin to multiply. These infections can affect various parts of the body, including the skin, nails, and internal organs. While not all fungi are harmful, some can lead to serious health concerns, especially in individuals with weakened immune systems.
Q: What are the common types of fungal infections?
A: Fungal infections can be classified into several categories: superficial, cutaneous, subcutaneous, and systemic. Common examples include athlete’s foot (a superficial infection), ringworm (cutaneous), and more severe conditions like candidiasis (which can be systemic). Each type varies in severity and location, requiring different approaches for treatment.
Q: Who is at risk for developing fungal infections?
A: Anyone can develop a fungal infection, but certain groups are more susceptible. This includes individuals with compromised immune systems, those who take antibiotics frequently, and people with chronic health conditions such as diabetes. Additionally, warm, humid environments can create a breeding ground for fungi, increasing risk.
Q: How can one recognize a fungal infection?
A: Symptoms of a fungal infection can vary widely depending on the type and location. Common signs include itching, redness, swelling, and peeling skin. In cases of nail infections, nails may become discolored or thickened. Systemic infections can lead to more serious symptoms such as fever and fatigue, making timely diagnosis crucial.
Q: What are the common treatments for fungal infections?
A: Treatment typically involves antifungal medications, which can be topical (applied directly to the affected area) or systemic (taken orally or intravenously). Over-the-counter creams can suffice for mild infections, while more severe cases may require prescription medication. It’s always advisable to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan.
Q: Can fungal infections be prevented?
A: Yes, many fungal infections can be prevented with simple hygiene practices. Keeping skin dry and clean, using antifungal powders in warm, moist areas, and wearing breathable footwear can help reduce risk. Additionally, avoiding close contact with infected individuals and not sharing personal items like towels or nail clippers can also minimize chances of infection.
Q: Are there any myths about fungal infections that need to be addressed?
A: Absolutely! One common myth is that fungal infections only occur in dirty or unhygienic conditions. In reality, fungi are ubiquitous in our environment, and anyone can be affected regardless of cleanliness. Another myth is that fungal infections are not serious; however, untreated infections can lead to severe health issues, particularly for those with weakened immune systems.
Q: When should someone seek medical attention for a fungal infection?
A: It’s important to see a healthcare provider if you notice persistent or worsening symptoms of a fungal infection. Additionally, if you have a weakened immune system or underlying health issues, seeking prompt medical attention at the first sign of infection is vital to prevent complications.
Q: What is the future of fungal infection treatment?
A: Research is ongoing to improve the treatment and understanding of fungal infections. Scientists are exploring new antifungal drugs, vaccines, and alternative therapies to combat resistant strains and enhance prevention strategies. As our knowledge of fungi increases, so too does our ability to effectively manage these infections.
In Retrospect
In the intricate tapestry of human health, fungal infections weave a complex thread, often overlooked yet profoundly impactful. As we journey through the microscopic realms of these organisms, we uncover the delicate balance between cohabitation and conflict within our bodies. Such infections remind us of the resilience of life in all its forms, prompting us to remain vigilant, informed, and proactive in our health choices. While the world continues to evolve with emerging pathogens and treatments alike, understanding fungal infections equips us with the knowledge to better navigate the challenges they present. As we close this chapter, let us foster a deeper awareness of our microbial companions, appreciating their roles while remaining cautious of their potential to disrupt. In our quest for wellness, knowledge truly is our greatest ally.