Unveiling the Silent Epidemic: Understanding Fatty Liver Disease
In a world where lifestyle choices and dietary habits increasingly shape our health, a silent epidemic has been creeping into the lives of millions, often unnoticed until it’s too late. Fatty liver disease, once considered a condition confined to the shadows of medical textbooks, has emerged as a pressing health concern, affecting people across various ages and backgrounds. As we delve into the intricate world of this increasingly common ailment, we will explore its origins, risk factors, and the pathways to prevention and healing. Join us as we uncover the layers of fatty liver disease—a condition that may first seem innocuous but has the potential to impact not just the liver, but overall well-being. Understanding the nuances of this condition is the first step towards reclaiming our health in an era where knowledge is our greatest ally.
Understanding Fatty Liver: Causes and Risk Factors
Fatty liver disease, or hepatic steatosis, arises when excess fat builds up in the liver cells. This condition can be caused by a variety of factors that disrupt the normal metabolism of fats. Key contributors include:
- Obesity: Increased body weight significantly raises the likelihood of fat accumulation in the liver.
- Alcohol Consumption: Excessive drinking can lead to alcoholic fatty liver disease, where alcohol disrupts the liver’s ability to process fats.
- Insulin Resistance: Conditions such as type 2 diabetes can lead to a build-up of fats in the liver due to impaired glucose metabolism.
- Medications: Certain medications, like corticosteroids and some cancer drugs, can pose risks for developing fatty liver.
- Genetic Factors: Family history may predispose individuals to fatty liver disease.
Beyond the direct causes, various risk factors can exacerbate the likelihood of developing fatty liver disease. Some notable risk factors include:
- Age: Individuals over 50 are at higher risk due to metabolic changes.
- High Cholesterol: Elevated levels of bad cholesterol can lead to fat accumulation in the liver.
- Poor Diet: Diets high in sugar, refined carbohydrates, and unhealthy fats are significant contributors.
- Physical Inactivity: A sedentary lifestyle can hinder fat metabolism, increasing the risk.
- Metabolic Disorders: Conditions like metabolic syndrome synergize with lifestyle factors to heighten risk.
The Role of Diet in Managing Fatty Liver Disease
Diet plays a pivotal role in managing fatty liver disease, an increasingly prevalent condition often linked to lifestyle choices. A balanced and nutrient-rich diet can help reduce fat accumulation in the liver and improve overall liver function. Key dietary adjustments include:
- Increased fruits and vegetables: These are high in antioxidants and fiber, aiding in liver detoxification.
- Healthy fats: Incorporate sources of omega-3 fatty acids, such as fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, which can reduce liver fat levels.
- Whole grains: Choose whole grains over refined grains to maintain stable blood sugar levels and reduce insulin resistance.
- Lean proteins: Opt for poultry, beans, and legumes instead of fatty meats to support muscle maintenance without overloading the liver.
Additionally, it’s essential to limit certain foods that can exacerbate the condition. Avoiding the following can significantly impact liver health:
| Foods to Avoid | Reasons |
|---|---|
| Sugary beverages | They contribute to fat buildup and insulin resistance. |
| Processed foods | High in unhealthy fats and sugars, these can lead to weight gain. |
| Alcohol | It can cause further liver damage and impede recovery. |
| Refined carbohydrates | They can trigger spikes in blood sugar and fat accumulation. |
Effective Lifestyle Changes for Liver Health
Making thoughtful lifestyle adjustments is vital for enhancing liver health, particularly for those facing fatty liver issues. A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients can significantly impact liver function. Focus on incorporating a variety of whole foods, such as:
- Fruits and vegetables: Aim for a colorful plate filled with antioxidants.
- Whole grains: Choose brown rice, quinoa, and oats for sustained energy.
- Lean proteins: Opt for fish, poultry, and plant-based sources like beans and lentils.
- Healthy fats: Include sources like avocados, nuts, and olive oil while avoiding trans fats.
In addition to dietary changes, regular physical activity plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy liver. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise each week. This could include activities such as walking, cycling, or swimming. Furthermore, staying hydrated by drinking enough water daily can help flush toxins from the liver. Here’s a simple table summarizing some daily habits that promote liver health:
| Habit | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Regular Exercise | Boosts metabolism and helps maintain a healthy weight. |
| Hydration | Aids in detoxification and promotes overall health. |
| Sufficient Sleep | Supports the body’s recovery processes, including liver repair. |
| Limit Alcohol | Reduces the risk of liver damage and fatty liver progression. |
The Importance of Regular Exercise in Preventing Fatty Liver
Regular physical activity plays a crucial role in maintaining liver health and preventing conditions such as fatty liver disease. Engaging in exercise not only helps to manage body weight but also improves insulin sensitivity, which is vital for regulating fat storage in the liver. When you incorporate movement into your daily routine, you can significantly alter the course of your liver health. Here are some ways exercise contributes to a healthier liver:
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the risk of liver fat accumulation.
- Metabolism Boost: Physical activity enhances metabolic processes, preventing fat buildup in the liver.
- Improved Blood Circulation: Exercise increases blood flow, aiding in the liver’s detoxification processes.
In addition to these benefits, the type of exercise you choose can also play a significant role in liver health. Aerobic exercises, such as walking, jogging, and swimming, are especially effective in reducing liver fat. Strength training also offers advantages by building muscle mass, which helps in burning more calories and improving overall body composition. Consider the following activities to incorporate into your routine:
| Exercise Type | Frequency | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Aerobic Exercise | 150 minutes/week | Reduces liver fat, improves cardiovascular health |
| Strength Training | 2-3 times/week | Builds muscle, boosts metabolism |
| Flexibility & Balance | As needed | Improves overall body function, reduces injury risk |
Monitoring and Medical Guidance: When to Seek Help
Monitoring your health is crucial, especially when dealing with conditions like fatty liver. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help track liver function and assess the severity of the condition. Be vigilant for symptoms that may indicate a progression of the disease, such as:
- Fatigue: Unusual tiredness that interferes with daily activities
- Abdominal discomfort: Pain or discomfort in the upper right abdomen
- Unexplained weight loss: Losing weight without trying
- Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin and eyes
Knowing when to seek medical guidance can make a significant difference in managing fatty liver. Consult a doctor immediately if you experience any of the following:
- Severe abdominal pain: Sudden and intense pain that may indicate complications
- Swelling in the abdomen or legs: This could be a sign of fluid retention
- Confusion or difficulty thinking: Cognitive issues may suggest advanced liver disease
Keeping an open line of communication with your healthcare provider ensures that your treatment plan is effective and adjusted as needed. Regular blood tests and imaging can help in monitoring liver health and making necessary adjustments to lifestyle or medications.
Exploring Alternative Therapies and Supplements for Fatty Liver Management
As the prevalence of fatty liver disease continues to rise, many individuals are seeking alternative therapies and supplements to support liver health. These options can complement traditional treatments and help manage the condition more effectively. Some promising alternatives include:
- Milk Thistle: Known for its active compound, silymarin, which may promote liver regeneration and protect against damage.
- Turmeric: Contains curcumin, a powerful anti-inflammatory agent that may reduce liver inflammation.
- Artichoke Extract: Thought to enhance bile production and improve digestion, potentially benefiting liver function.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fish oil, these may help reduce liver fat levels and improve overall metabolic health.
In addition to herbal supplements, lifestyle changes play a critical role in managing fatty liver disease. Incorporating a balanced diet rich in antioxidants, fiber, and healthy fats can support liver health. Consider the following dietary tips:
| Food Group | Examples |
|---|---|
| Fruits and Vegetables | Berries, leafy greens, cruciferous vegetables |
| Whole Grains | Quinoa, brown rice, oats |
| Healthy Fats | Avocados, olive oil, nuts |
Q&A
Q&A: Understanding Fatty Liver Disease
Q1: What exactly is fatty liver disease?
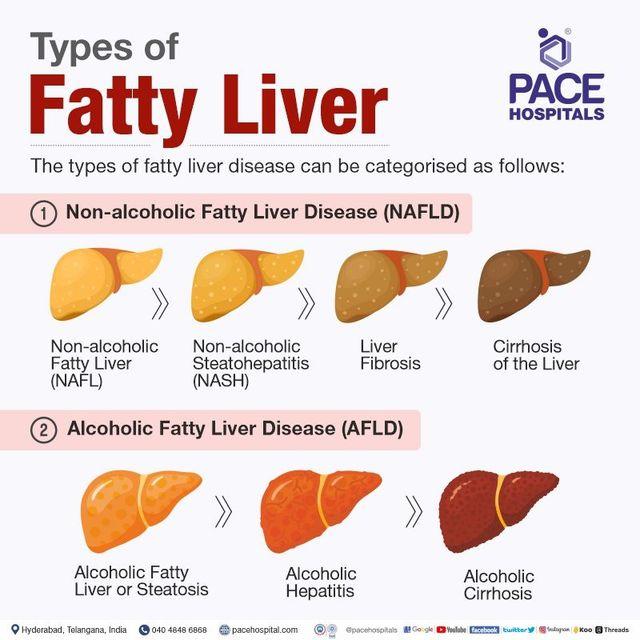
A1: Fatty liver disease, or hepatic steatosis, occurs when excess fat builds up in the liver. While it’s normal for the liver to contain some fat, the problem arises when fat makes up more than 5-10% of the liver’s weight. This condition can be classified into two main types: Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD) and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), the latter of which has become increasingly common in recent years.
Q2: What causes fatty liver disease?
A2: The causes of fatty liver disease can vary widely. In the case of AFLD, the primary culprit is excessive alcohol consumption. Meanwhile, NAFLD is often linked to factors such as obesity, insulin resistance, high blood sugar, and high cholesterol levels. Other risk factors include poor diet, sedentary lifestyle, certain medications, and genetic predispositions.
Q3: How do I know if I have fatty liver disease?
A3: Fatty liver disease can be tricky as it often presents with few or no symptoms in its early stages. Some individuals may experience fatigue, discomfort in the upper right abdomen, or unexplained weight loss. The most reliable way to diagnose it is through imaging tests such as ultrasounds, CT scans, or MRIs, or through liver function tests during routine blood work.
Q4: What are the potential complications of fatty liver disease?
A4: While many people with fatty liver disease may not experience severe health issues, it can progress to more serious conditions if left untreated. Complications can include inflammation of the liver (steatohepatitis), fibrosis (scarring), and eventually cirrhosis or liver cancer. Early intervention is crucial to prevent these severe outcomes.
Q5: Can fatty liver disease be reversed?
A5: The good news is, yes! Fatty liver disease is often reversible, especially in its early stages. Lifestyle changes, such as adopting a balanced diet, losing weight, increasing physical activity, and avoiding alcohol can make a significant difference. Regular monitoring and consultation with a healthcare professional can help tailor an effective management plan.
Q6: What dietary changes should I consider to combat fatty liver?
A6: Focusing on a nutrient-rich diet is key. Aim for whole foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats such as those found in nuts and olive oil. Reducing simple sugars, refined carbs, and saturated fats is also important. Incorporating foods high in fiber and antioxidants can further support liver health.
Q7: Is exercise important in managing fatty liver disease?
A7: Absolutely! Regular physical activity plays a fundamental role in managing and potentially reversing fatty liver disease. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise per week, combined with strength training. Exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity, aids in weight management, and can significantly reduce liver fat.
Q8: When should I see a doctor about fatty liver disease?
A8: It’s wise to consult a healthcare provider if you have risk factors for fatty liver disease, such as obesity or a family history of liver problems. If you notice any symptoms like persistent fatigue or abdominal discomfort, don’t hesitate to reach out. Early intervention can make all the difference in your liver health.
Q9: Are there any medications or treatments available for fatty liver disease?
A9: Currently, there are no specific medications approved solely for fatty liver disease. However, healthcare providers may recommend treatments targeting associated conditions, such as diabetes or high cholesterol. Lifestyle changes remain the cornerstone of managing the disease. In more severe cases, referral to a specialist may be necessary.
Q10: What’s the takeaway message about fatty liver disease?
A10: Fatty liver disease is a complex yet manageable condition. With awareness, lifestyle modifications, and proper medical guidance, individuals can take control of their liver health. Remember, the liver is a resilient organ; nurture it, and it will thank you in the long run!
To Conclude
the journey through the complexities of fatty liver disease reveals a landscape where awareness and proactive choices can forge a path toward better health. Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and embracing preventive measures empower us to take charge of our liver health. As we weave together lifestyle modifications, nutritional insights, and medical guidance, we can illuminate a brighter future, not just for ourselves but for those around us. Remember, the liver is not just an organ; it is a vital partner in our overall well-being. Let us honor it with the care and respect it deserves, embarking on a lifelong commitment to nurture and protect this essential pillar of our health. Together, we can turn the tide on fatty liver disease and cultivate a vibrant life filled with vitality and purpose.