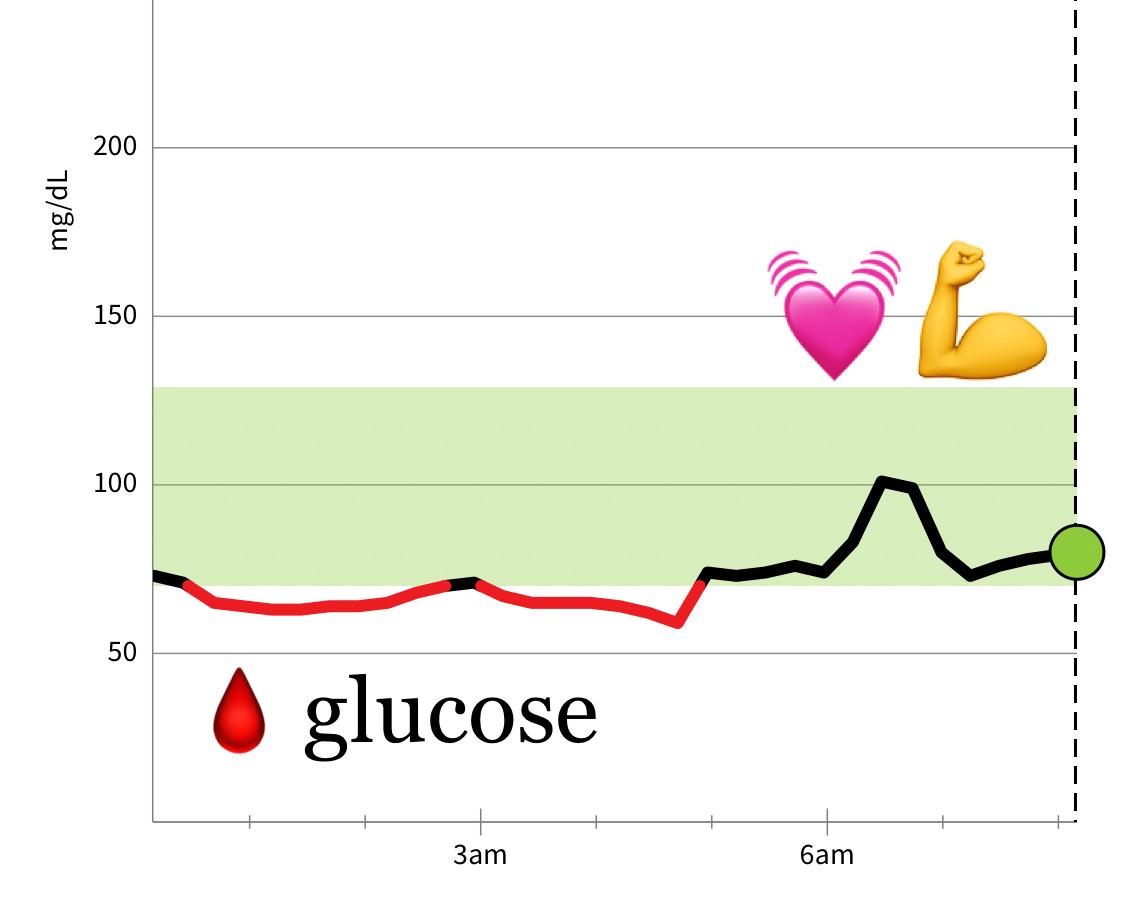
In the intricate tapestry of human health, few threads are as vital as the balance of blood sugar. Among the myriad factors that contribute to our well-being, fasting blood sugar levels stand out as a crucial marker, offering insights into how our bodies regulate energy and respond to dietary choices. This seemingly simple measurement can unveil a wealth of information about our metabolic state, signaling everything from the efficiency of our insulin response to the potential risk of chronic conditions. As we explore the concept of fasting blood sugar, we will delve into its significance, the science behind it, and the implications for our daily lives, illuminating the path toward better understanding our bodies and optimizing our health.
Understanding Fasting Blood Sugar and Its Importance for Health
Fasting blood sugar is a critical indicator of how well your body is managing glucose levels when it’s in a resting state. Typically measured after an overnight fast, this test helps to evaluate how effectively insulin works in the body. Understanding these levels is paramount, as they can provide insights into your risk for developing conditions such as diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and even cardiovascular diseases. Regular monitoring can lead to early detection and management, allowing individuals to make informed lifestyle choices. Some key factors influencing fasting blood sugar include:
- Diet: The composition of your meals can significantly affect blood sugar levels.
- Exercise: Physical activity can improve insulin sensitivity and help regulate blood sugar.
- Stress Levels: Chronic stress can lead to hormonal changes that raise blood sugar.
- Medications: Certain drugs can also impact glucose metabolism.
When fasting blood sugar levels exceed normal ranges, it often indicates a need for lifestyle adjustments or medical intervention. Understanding the classification of these levels can help in assessing your health more clearly. Here’s a simple table illustrating the different categories of fasting blood sugar:
| Category | Fasting Blood Sugar Level (mg/dL) |
|---|---|
| Normal | 70 – 99 |
| Prediabetes | 100 – 125 |
| Diabetes | 126 and above |
The Science Behind Fasting Blood Sugar Levels
Fasting blood sugar levels serve as a critical indicator of metabolic health, highlighting the body’s ability to manage glucose effectively. During a fasting state, typically defined as no caloric intake for at least eight hours, the body relies on stored glucose and fatty acids for energy. This process involves the liver releasing glucose into the bloodstream, while insulin levels remain low to facilitate fat burning. Various factors influence these fasting levels, including:
- Dietary Choices: The types of food consumed before the fasting period can significantly impact glucose levels.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise enhances insulin sensitivity, leading to improved glucose management.
- Stress Levels: High stress can lead to increased cortisol levels, which may elevate blood sugar.
Understanding the typical ranges for fasting blood sugar is essential for assessing overall health. A fasting blood sugar level under 100 mg/dL is generally considered normal, while levels between 100-125 mg/dL suggest prediabetes. Anything above 126 mg/dL on two separate tests usually indicates diabetes. The following table summarizes these ranges:
| Range | Status |
|---|---|
| Under 100 mg/dL | Normal |
| 100-125 mg/dL | Prediabetes |
| 126 mg/dL and above | Diabetes |
Interpreting Your Fasting Blood Sugar Results
Understanding your fasting blood sugar levels is crucial for evaluating your overall health and managing potential risks associated with diabetes. Typically, fasting blood sugar is measured after an overnight fast and can help indicate how well your body is processing glucose. Results are generally categorized as follows:
- Normal: 70-99 mg/dL
- Prediabetes: 100-125 mg/dL
- Diabetes: 126 mg/dL and above
When interpreting your results, consider factors that may affect your blood sugar levels. These can include the time of day, recent meals, medications, and even stress. It’s important to monitor trends over time rather than focusing solely on a single reading. Regular testing can provide a clearer picture of your metabolic health, and discussing your results with a healthcare professional can help you understand the implications for your lifestyle and treatment options.
| Category | Blood Sugar Level (mg/dL) | Implications |
|---|---|---|
| Normal | 70-99 | No immediate concerns |
| Prediabetes | 100-125 | Increased risk; lifestyle changes recommended |
| Diabetes | 126+ | Requires medical intervention |
Strategies to Maintain Healthy Fasting Blood Sugar Levels
Maintaining healthy fasting blood sugar levels is essential for overall well-being, particularly for those at risk of diabetes. One effective strategy is to focus on a balanced diet rich in complex carbohydrates, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Incorporating foods like whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds can help stabilize blood sugar levels. Additionally, including plenty of fiber-rich vegetables in your meals can slow the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream, preventing spikes in blood glucose. Here are some key dietary choices to consider:
- Whole grains: Brown rice, quinoa, and oats
- Healthy fats: Avocados, olive oil, and fatty fish
- Lean proteins: Chicken, turkey, tofu, and legumes
- Fruits: Berries, apples, and pears
In addition to dietary changes, incorporating regular physical activity can significantly impact fasting blood sugar levels. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise per week, such as brisk walking or cycling. Engaging in strength training exercises two or more days a week can also enhance insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism. Here’s a simple weekly exercise plan to consider:
| Day | Activity |
|---|---|
| Monday | Brisk walking (30 minutes) |
| Wednesday | Strength training (30 minutes) |
| Friday | Cycling (30 minutes) |
| Saturday | Yoga or Stretching (30 minutes) |
The Role of Diet and Lifestyle in Fasting Blood Sugar Control
Maintaining optimal fasting blood sugar levels is not solely reliant on medical interventions; rather, diet and lifestyle choices play a pivotal role in this balance. A diet rich in whole foods, with an emphasis on fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins, can significantly impact glucose levels. Foods that are high in fiber, such as legumes and whole grains, help to slow down the absorption of sugar, preventing spikes in blood glucose levels. Additionally, incorporating healthy fats from sources like avocados and nuts can improve insulin sensitivity, making it easier for the body to manage blood sugar effectively.
Lifestyle factors are equally influential. Regular physical activity—whether it’s brisk walking, cycling, or yoga—can enhance glucose metabolism and promote better fasting blood sugar control. Implementing stress management techniques such as meditation or mindfulness can also be beneficial, as stress hormones can elevate blood sugar levels. Adequate sleep is another critical component; poor sleep patterns have been associated with insulin resistance. To summarize the combined effects of diet and lifestyle on fasting blood sugar control, refer to the table below:
| Factor | Impact on Fasting Blood Sugar |
|---|---|
| Fiber-rich Foods | Helps stabilize blood sugar levels |
| Healthy Fats | Improves insulin sensitivity |
| Physical Activity | Enhances glucose metabolism |
| Stress Management | Reduces cortisol-related blood sugar spikes |
| Adequate Sleep | Supports insulin sensitivity |
When to Seek Medical Advice for Fasting Blood Sugar Concerns
Monitoring fasting blood sugar levels is essential for maintaining overall health, particularly for individuals at risk of diabetes or those already diagnosed. It’s crucial to recognize when changes in your readings warrant professional attention. If you experience consistent fasting blood sugar levels above 126 mg/dL, it may indicate prediabetes or diabetes, prompting a discussion with your healthcare provider. Additionally, if your levels drop below 70 mg/dL, this may signal hypoglycemia, requiring immediate evaluation and intervention.
Other symptoms that should not be ignored include:
- Frequent urination
- Excessive thirst
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue or weakness
- Blurry vision
Consulting a healthcare professional can provide clarity and guidance on lifestyle modifications, further testing, or potential treatments. Keeping a detailed record of your fasting blood sugar readings and associated symptoms can also be beneficial during your consultations.
Q&A
Q&A on Fasting Blood Sugar
Q1: What is fasting blood sugar, and why is it important?
A1: Fasting blood sugar refers to the level of glucose in your bloodstream after you haven’t eaten for at least 8 hours. This measurement is crucial because it gives insight into how your body manages glucose, which is a key factor in diagnosing and monitoring diabetes and prediabetes.
Q2: How is fasting blood sugar tested?
A2: The test is typically conducted in a healthcare setting. After fasting overnight, a healthcare professional will draw a small sample of your blood, which is then analyzed in a lab. Some at-home testing kits are also available for those who prefer to monitor their levels privately.
Q3: What are the normal ranges for fasting blood sugar?
A3: Normal fasting blood sugar levels are generally considered to be between 70 and 99 mg/dL (milligrams per deciliter). If your level falls between 100 and 125 mg/dL, you may be classified as having prediabetes, while a reading of 126 mg/dL or higher can indicate diabetes.
Q4: What factors can affect fasting blood sugar levels?
A4: Several factors can influence your fasting blood sugar, including stress, illness, hormonal changes, medications, and even the quality of your overnight sleep. Lifestyle choices, such as diet and exercise, also play significant roles in managing blood sugar levels.
Q5: How can one maintain healthy fasting blood sugar levels?
A5: Maintaining healthy fasting blood sugar levels can often be achieved through a balanced diet, regular physical activity, adequate hydration, and sufficient sleep. Monitoring your carbohydrate intake and opting for whole, unprocessed foods can also be beneficial. If you have diabetes or prediabetes, working with a healthcare provider to develop a tailored plan is essential.
Q6: What symptoms might indicate abnormal fasting blood sugar levels?
A6: Symptoms of high fasting blood sugar can include excessive thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, and blurred vision. On the other hand, low fasting blood sugar may lead to dizziness, confusion, sweating, or irritability. If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional.
Q7: Can fasting blood sugar levels fluctuate, and if so, why?
A7: Yes, fasting blood sugar levels can fluctuate due to various reasons, such as dietary choices, physical activity, and hormonal changes. For instance, consuming a heavy meal close to bedtime can result in elevated levels the next morning. Regular monitoring can help identify patterns and triggers for these fluctuations.
Q8: Is it necessary for everyone to test their fasting blood sugar levels?
A8: Not everyone needs to test their fasting blood sugar levels regularly; it is primarily recommended for those at high risk for diabetes or those already diagnosed. However, maintaining awareness of your blood sugar levels can encourage healthier lifestyle choices for anyone, regardless of risk.
Q9: Are there any emerging trends or technologies related to fasting blood sugar monitoring?
A9: Yes! Recent advancements in continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) technology allow individuals to track their blood sugar levels in real time without the need for frequent finger pricks. These devices can provide valuable insights into how daily activities and food choices affect blood sugar levels.
Q10: What should someone do if they discover their fasting blood sugar is outside the normal range?
A10: If your fasting blood sugar is outside the normal range, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional. They can provide guidance based on your individual health history, recommend further testing if necessary, and help devise a management plan tailored to your needs.
—
This Q&A aims to shed light on fasting blood sugar, providing a foundation for understanding its significance and implications for health.
In Conclusion
understanding fasting blood sugar is crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being. As we’ve explored, the levels of glucose in our blood can reveal much about our metabolic health and risk for conditions like diabetes. By incorporating regular monitoring and being mindful of dietary choices and lifestyle habits, we can take proactive steps towards better health. Remember, knowledge is power, and awareness of our blood sugar levels can empower us to make informed decisions that enhance our quality of life. Whether you’re managing an existing condition or simply aiming to optimize your health, staying attuned to your body’s signals is a journey worth taking. So, as you move forward, let this understanding guide your choices and inspire a more balanced approach to your health.