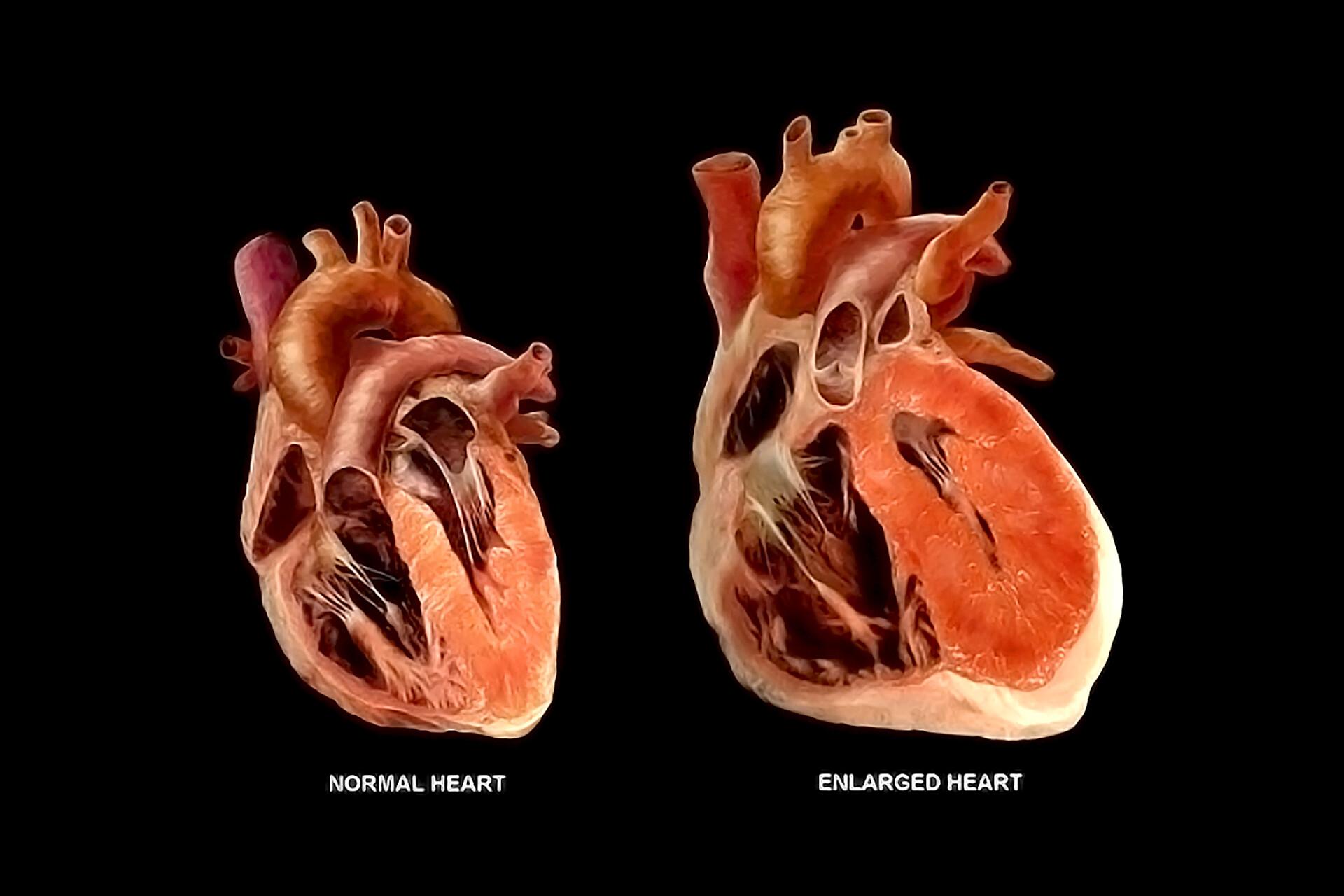
Understanding the Heart: Unraveling the Mystery of an Enlarged Heart
The heart, often poetically described as the seat of emotion, is also a marvel of biological engineering, tirelessly working to sustain life with each rhythmic beat. Yet, when the heart begins to grow larger than its intended size, it signals a shift from the norm—a phenomenon known as an enlarged heart, or cardiomegaly. This condition, which can stem from a myriad of causes ranging from hypertension to underlying heart disease, often raises questions and concerns about health and well-being. In this article, we will delve into the complexities of an enlarged heart, exploring its causes, symptoms, implications, and the pathways to effective management. Join us as we navigate this often-misunderstood condition and shed light on the vital role of the heart in our overall health.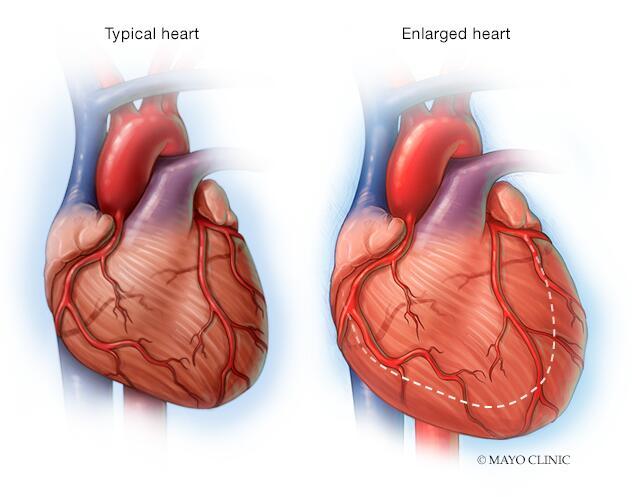
Understanding the Anatomy and Function of the Heart
The heart, a marvel of biological engineering, consists of four main chambers: the right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, and left ventricle. Each chamber plays a vital role in the circulatory process, ensuring that oxygen-rich blood is delivered to the body while carbon dioxide-laden blood is sent to the lungs for purification. The heart’s structure is reinforced by a network of valves, which maintain the unidirectional flow of blood, preventing any backflow. The myocardium, the muscular layer of the heart, enables the powerful contractions necessary for effective blood pumping, while the pericardium, a protective sac, shields the heart from infection and trauma.
When the heart becomes enlarged, a condition known as cardiomegaly, it signals underlying health issues that can disrupt its normal function. This enlargement can be attributed to various factors, including hypertension, heart valve disease, or cardiomyopathy. Common symptoms of an enlarged heart may include fatigue, shortness of breath, and irregular heartbeats. Understanding these changes is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment, as the ramifications of an enlarged heart can lead to severe complications. Below is a simple overview of potential causes and effects:
| Causes | Effects |
|---|---|
| Hypertension | Increased workload on the heart |
| Valve disease | Improper blood flow |
| Cardiomyopathy | Weakened heart muscle |
| Coronary artery disease | Decreased oxygen supply |
Recognizing the Symptoms and Risk Factors of an Enlarged Heart
An enlarged heart, medically known as cardiomegaly, can present a variety of symptoms that might indicate an underlying health issue. Common symptoms to watch for include:
- Shortness of breath, especially during physical activity
- Fatigue or weakness, often felt with minimal exertion
- Swelling in the legs, ankles, or feet due to fluid retention
- Palpitations, or a feeling of irregular heartbeats
- Chest pain, which can vary in intensity and frequency
Additionally, certain risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing this condition. Understanding these risk factors is crucial for preventive measures. Key factors include:
| Risk Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| High Blood Pressure | Excess pressure on heart arteries can lead to enlargement. |
| Coronary Artery Disease | Reduced blood flow can weaken heart muscle. |
| Obesity | Excess weight increases heart strain. |
| Diabetes | Can cause damage to blood vessels, affecting the heart. |
| Family History | Genetic predisposition may elevate risk levels. |
Exploring the Common Causes of Cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy, a term that encompasses a variety of heart muscle diseases, can arise from numerous underlying factors. Some of the most prevalent causes include genetic predispositions, chronic high blood pressure, and coronary artery disease. Each of these conditions contributes to the deterioration of heart function, leading to an enlarged heart. Genetic mutations can disrupt the normal structure and function of heart cells, while prolonged high blood pressure forces the heart to work harder, ultimately resulting in its enlargement. Additionally, coronary artery disease restricts blood flow to the heart muscle, causing it to weaken and expand over time.
Other significant contributors to cardiomyopathy include diabetes, alcohol use, and inflammatory conditions. Diabetes can lead to changes in the heart muscle, increasing the risk of heart failure, while excessive alcohol consumption can poison heart tissue and disrupt its normal function. Furthermore, inflammatory diseases, such as myocarditis, can damage the heart muscle, causing it to swell and impairing its ability to pump blood efficiently. Understanding these causes is crucial for effective management and treatment strategies.
Diagnostic Approaches to Assess Heart Enlargement
When evaluating an enlarged heart, healthcare professionals employ a variety of diagnostic approaches to gain a comprehensive understanding of the underlying causes and implications. These methods often begin with a thorough physical examination, during which doctors assess symptoms such as shortness of breath, fatigue, or palpitations. Following this initial assessment, several diagnostic tools are typically utilized, including:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) – An essential test that records the electrical activity of the heart, helping to identify irregularities.
- Echocardiogram – This ultrasound-based technique provides detailed images of the heart’s structure and function, enabling the observation of enlargement.
- Chest X-ray – A quick imaging test that can reveal heart size and any potential fluid accumulation in the lungs.
- Cardiac MRI – Often used for more detailed imaging, this test provides high-resolution pictures of the heart muscle and can assess any damage or abnormalities.
In addition to these primary evaluations, blood tests may be conducted to measure levels of natriuretic peptides, which can indicate heart stress. Furthermore, advanced methods such as cardiac catheterization may be utilized to assess blood flow and pressure within the heart chambers. For a clearer picture of patient health, the following table outlines the various tests and their respective benefits:
| Diagnostic Test | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Electrocardiogram (ECG) | Detects electrical activity and irregularities. |
| Echocardiogram | Visualizes heart structure and function. |
| Chest X-ray | Assesses heart size and detects fluid in the lungs. |
| Cardiac MRI | Provides detailed images of heart muscle. |
Treatment Options and Lifestyle Changes for Heart Health
Managing an enlarged heart involves a combination of medical treatment and lifestyle adjustments that can significantly improve heart function and overall health. Depending on the underlying cause, treatment options may include medications such as ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, and diuretics, which help reduce the workload on the heart and improve its efficiency. In more severe cases, surgical interventions like coronary bypass surgery or heart valve repair may be necessary. Regular follow-ups with a healthcare provider are essential to monitor the condition and make any necessary adjustments to the treatment plan.
In addition to medical treatments, adopting heart-healthy lifestyle changes can play a crucial role in managing an enlarged heart. Consider implementing the following practices:
- Heart-healthy diet: Focus on whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats while reducing sodium and processed foods.
- Regular exercise: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity each week, as approved by your healthcare provider.
- Weight management: Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce stress on the heart.
- Avoid tobacco: Quitting smoking and avoiding secondhand smoke is vital for heart health.
- Stress reduction: Engage in relaxation techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep-breathing exercises.
Preventive Measures for Maintaining a Healthy Heart Size
Maintaining a healthy heart size requires a proactive approach to lifestyle choices and regular health monitoring. A balanced diet plays a crucial role in heart health. Focus on incorporating a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats into your meals. Additionally, it’s essential to limit the intake of sodium, saturated fats, and added sugars. Here are some dietary tips to consider:
- Increase fiber: Choose high-fiber foods like legumes, oats, and barley.
- Stay hydrated: Aim for at least 8 glasses of water daily.
- Control portion sizes: Be mindful of serving sizes to avoid overeating.
Regular physical activity is another critical element in preventing an enlarged heart. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise each week, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming. Additionally, incorporating strength training exercises into your routine can help improve overall cardiovascular health. Below is a simple exercise plan:
| Activity | Duration | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Brisk Walking | 30 minutes | 5 days a week |
| Strength Training | 20 minutes | 2-3 days a week |
| Yoga or Stretching | 15 minutes | Daily |
Q&A
Q&A: Understanding Enlarged Heart
Q1: What exactly is an enlarged heart?
A1: An enlarged heart, medically known as cardiomegaly, refers to a condition where the heart’s size is larger than normal. This can be due to various factors, including high blood pressure, heart valve disease, or cardiomyopathy. The increase in size could be a response to stress or damage, indicating that the heart is working harder than it should.
Q2: What are the common symptoms of an enlarged heart?
A2: Individuals might experience a range of symptoms, though some may not show any at all. Common signs include shortness of breath, fatigue, palpitations, and swelling in the legs or abdomen. If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation.
Q3: What causes an enlarged heart?
A3: There are several potential causes of an enlarged heart, including:
- High Blood Pressure: This increases the workload on the heart, leading to enlargement over time.
- Heart Valve Disease: Malfunctioning valves may cause the heart to pump harder.
- Cardiomyopathy: This disease of the heart muscle can result in thickened or enlarged walls.
- Coronary Artery Disease: Reduced blood flow can weaken the heart, prompting it to enlarge.
- Other Factors: Conditions like thyroid disorders, anemia, or chronic lung diseases can also contribute.
Q4: How is an enlarged heart diagnosed?
A4: Diagnosis typically begins with a physical examination and a review of medical history. Healthcare providers may use imaging tests such as an echocardiogram, MRI, or a chest X-ray to visualize the heart’s size and function. Additional tests like blood tests or electrocardiograms (ECGs) can provide further insight.
Q5: What treatment options are available for an enlarged heart?
A5: Treatment for an enlarged heart focuses on addressing the underlying causes. This may involve medication to manage symptoms, lifestyle changes such as a heart-healthy diet and regular exercise, or surgical interventions for more severe cases. It’s essential to work closely with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan.
Q6: Can lifestyle changes help in managing an enlarged heart?
A6: Absolutely! Lifestyle changes can play a significant role in managing the condition. Adopting a balanced diet low in sodium and rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, engaging in regular physical activity, quitting smoking, and limiting alcohol intake can all contribute to better heart health and potentially reduce the heart’s size.
Q7: Is there a risk of complications from an enlarged heart?
A7: Yes, an enlarged heart can lead to serious complications if left untreated. Possible risks include heart failure, arrhythmias (irregular heartbeats), blood clots, and even sudden cardiac arrest. Regular monitoring and adhering to treatment plans can help mitigate these risks.
Q8: Can an enlarged heart be reversed?
A8: In some cases, if caught early and managed effectively, the enlargement of the heart can be reversed or improved. This often depends on the underlying cause and how well an individual responds to treatment and lifestyle modifications. However, it’s crucial to maintain ongoing medical supervision.
Q9: When should someone seek medical advice regarding an enlarged heart?
A9: Anyone experiencing symptoms associated with heart issues, such as persistent shortness of breath, unusual tiredness, or swelling in the extremities, should seek medical advice promptly. Early detection and intervention can significantly improve outcomes.
Q10: What is the outlook for individuals diagnosed with an enlarged heart?
A10: The outlook varies based on the cause, severity, and the individual’s overall health. With appropriate treatment and lifestyle changes, many people can manage their condition effectively and maintain a good quality of life. Regular follow-up with healthcare providers is essential for monitoring and adjusting treatment as necessary.
—
By understanding the complexities of an enlarged heart, individuals can take proactive steps towards better heart health and well-being. Always consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and care.
Key Takeaways
an enlarged heart, while a concerning medical condition, serves as a reminder of the intricate complexity of our bodies and the vital importance of cardiovascular health. Whether resulting from hypertension, heart disease, or other underlying factors, understanding the nuances of this condition can empower individuals to seek timely medical advice and adopt healthier lifestyles. As we navigate the path toward better heart health, let us remain vigilant and proactive, turning knowledge into action. Ultimately, by prioritizing our wellbeing and fostering open conversations about heart health, we can ensure that our hearts continue to beat strong for years to come.