Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, commonly known as COPD, is a condition that quietly yet significantly alters the rhythm of daily life for millions around the globe. As the airways become inflamed and obstructed, simple actions like climbing stairs or enjoying a leisurely walk can transform into daunting challenges. With its roots often buried in years of exposure to harmful substances, such as tobacco smoke and air pollution, COPD is not just a respiratory ailment; it is a complex interplay of genetics, environment, and lifestyle choices. In this article, we will explore the nuances of COPD—its causes, symptoms, and the latest advancements in management and treatment—shedding light on a condition that often goes unnoticed until it has made its presence felt. Join us as we navigate the landscape of COPD, aiming to inform and empower those affected by this chronic illness.
Understanding COPD: A Comprehensive Overview of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
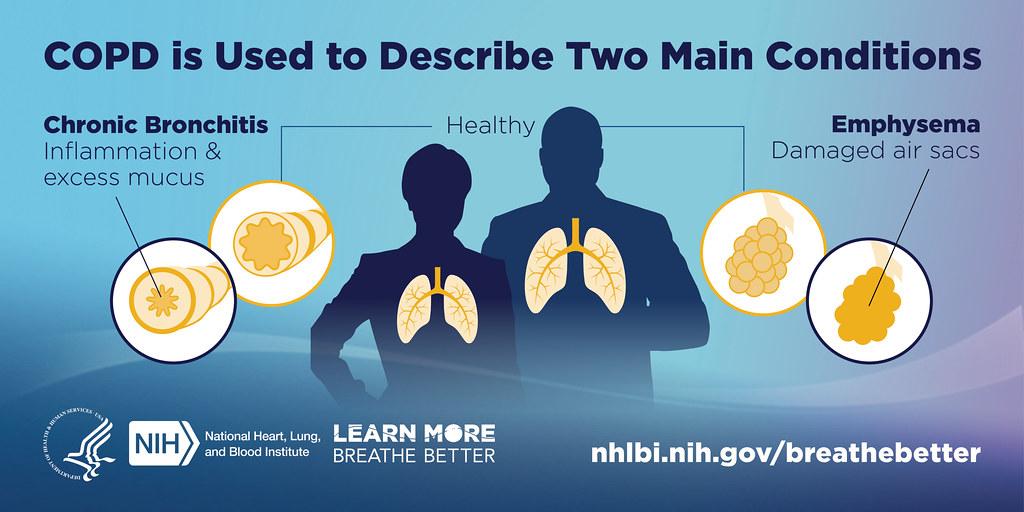
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) encompasses a group of progressive lung diseases that obstruct airflow and make breathing difficult. The primary conditions that fall under this umbrella include emphysema and chronic bronchitis. Common symptoms of COPD can significantly impair the quality of life, such as:
- Shortness of breath: Often exacerbated by physical activity.
- Chronic cough: A persistent cough that produces mucus.
- Wheezing: A whistling sound during breathing.
- Chest tightness: A sensation of pressure or discomfort in the chest.
The primary cause of COPD is long-term exposure to irritating gases or particulate matter, most commonly from cigarette smoke. Additionally, environmental pollutants and occupational dust can contribute to the development of this disease. Understanding risk factors is crucial for prevention and management. Here’s a brief overview of common risk factors:
| Risk Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Smoking | The leading cause of COPD; both active and passive exposure is harmful. |
| Age | Most commonly diagnosed in individuals over 40. |
| Genetic Factors | A rare genetic condition known as Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency can lead to COPD. |
| Environmental Exposure | Long-term exposure to air pollution, chemical fumes, and dust. |
Recognizing Symptoms: Early Detection and Its Importance in COPD Management
Understanding the early signs of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is crucial for effective management and improved quality of life. Recognizing symptoms such as chronic cough, shortness of breath, and frequent respiratory infections can lead to timely medical intervention. Early detection allows patients to implement lifestyle changes and receive appropriate treatments that can slow the progression of the disease. Some of the primary symptoms to be aware of include:
- Increased mucus production: This can lead to discomfort and difficulty breathing.
- Wheezing: A whistling sound during breathing can indicate airway obstruction.
- Fatigue: Persistent tiredness can be a sign of compromised lung function.
- Chest tightness: This sensation may indicate bronchoconstriction.
Monitoring these symptoms is essential for patients with risk factors such as smoking or a history of lung infections. Regular check-ups and lung function tests can facilitate early diagnosis, potentially preventing serious complications. The following table summarizes key actions for early detection:
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
| Self-monitoring | Keep track of symptoms and their frequency. |
| Consulting a physician | Seek medical advice if symptoms worsen or new symptoms arise. |
| Lung function tests | Regular tests can assess lung capacity and airflow. |
Lifestyle Modifications: Practical Strategies for Living Well with COPD
Living with COPD requires a proactive approach to managing symptoms and maintaining quality of life. Adopting certain lifestyle changes can significantly enhance daily functioning and well-being. Consider incorporating the following strategies:
- Regular Exercise: Engage in low-impact activities such as walking, swimming, or cycling. Aim for at least 30 minutes a day to strengthen your lungs and improve endurance.
- Healthy Nutrition: Focus on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Staying hydrated is equally important to keep mucus thin.
- Controlled Breathing Techniques: Practices like pursed-lip breathing can help reduce shortness of breath and enhance oxygen intake.
- Stress Management: Incorporate mindfulness, yoga, or meditation to reduce stress levels, which can exacerbate breathing difficulties.
Additionally, it’s essential to create an environment that supports respiratory health. Simple changes in your living space can make a significant difference. Consider the following:
| Modification | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Eliminate Smoking | Reduces irritation and improves lung function. |
| Use Air Purifiers | Helps remove allergens and pollutants from the air. |
| Maintain a Clean Home | Minimizes dust and molds that could trigger symptoms. |
| Control Temperature and Humidity | Ensures optimal air quality for easier breathing. |
Treatment Options: Exploring Medications and Therapy for Better Respiratory Health
The Role of Nutrition: How a Balanced Diet Can Support Lung Function
Nutrition plays a pivotal role in maintaining overall health, particularly in supporting respiratory function for those with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients can help strengthen lung capacity and improve overall well-being. Key dietary components include:
- Fruits and Vegetables: Packed with antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals that combat oxidative stress.
- Whole Grains: Provide fiber which aids in digestion and may reduce inflammation.
- Lean Proteins: Essential for muscle repair and maintenance, critical for breathing muscles.
- Healthy Fats: Sources like olive oil and avocados support heart health, which is closely linked to lung function.
Incorporating a variety of foods ensures a wide range of nutrients. Additionally, certain vitamins and minerals are particularly beneficial for lung health:
| Nutrient | Benefits for Lung Health |
|---|---|
| Vitamin C | May reduce airway inflammation and improve lung function. |
| Vitamin D | Supports immune function and may decrease susceptibility to respiratory infections. |
| Magnesium | Helps regulate bronchial muscle function and can alleviate asthma symptoms. |
By focusing on a nutrient-dense diet, individuals with COPD can enhance their lung capacity and potentially improve their quality of life. Making informed dietary choices is a proactive step towards better respiratory health.
Emotional Well-being: Addressing Mental Health Challenges in COPD Patients
Living with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) not only affects physical health but also takes a toll on emotional well-being. Patients frequently encounter feelings of anxiety and depression, which can exacerbate their symptoms and hinder their ability to manage the disease effectively. It’s crucial for caregivers and healthcare professionals to recognize these emotional challenges and provide support through various means such as:
- Emotional Counseling: Professional support can help patients process their feelings and develop coping strategies.
- Support Groups: Sharing experiences with others facing similar challenges can foster a sense of community and belonging.
- Mindfulness Practices: Techniques such as meditation and breathing exercises can reduce stress and enhance emotional resilience.
Moreover, addressing emotional health can significantly improve the quality of life for COPD patients. Implementing a holistic approach that incorporates both physical and mental health strategies is essential. Consider the following supportive measures tailored for COPD patients:
| Support Measure | Description |
|---|---|
| Physical Activity | Engaging in regular, manageable exercises to boost mood and improve overall health. |
| Nutritional Guidance | A balanced diet can have a positive impact on mental health and energy levels. |
| Education | Understanding COPD can empower patients and reduce feelings of helplessness. |
Q&A
Q&A on COPD: Understanding Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Q1: What is COPD?
A1: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a progressive lung condition that makes it difficult to breathe due to obstruction of airflow. It encompasses two main diseases: chronic bronchitis and emphysema, both of which can significantly impact daily life.
Q2: What are the primary causes of COPD?
A2: The leading cause of COPD is long-term exposure to harmful substances, particularly cigarette smoke. Other factors include exposure to air pollution, occupational dust and chemicals, and genetic factors, such as Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency.
Q3: What are the common symptoms of COPD?
A3: Individuals with COPD often experience chronic cough, wheezing, shortness of breath, and the production of mucus. These symptoms may worsen over time, especially during physical exertion or respiratory infections.
Q4: How is COPD diagnosed?
A4: Diagnosis typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and lung function tests like spirometry. Imaging tests, such as chest X-rays or CT scans, may also be utilized to assess lung damage.
Q5: Can COPD be prevented?
A5: While not all cases of COPD can be prevented, reducing exposure to risk factors can significantly lower the likelihood of developing the disease. Quitting smoking, avoiding secondhand smoke, and minimizing exposure to air pollutants can make a substantial difference.
Q6: What treatment options are available for COPD?
A6: Although there is no cure for COPD, various treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. These may include bronchodilators, corticosteroids, pulmonary rehabilitation, oxygen therapy, and, in severe cases, surgery.
Q7: How does lifestyle impact COPD management?
A7: Lifestyle choices play a crucial role in managing COPD. Regular exercise, maintaining a healthy diet, and staying hydrated can enhance lung function and overall health. Additionally, avoiding respiratory irritants and participating in support groups can be beneficial.
Q8: What should someone diagnosed with COPD do next?
A8: If diagnosed with COPD, it’s essential to work closely with healthcare providers to develop a personalized management plan. This may include regular check-ups, medication adherence, and lifestyle modifications tailored to individual needs.
Q9: Is there hope for those living with COPD?
A9: Yes, while COPD is a chronic condition, many people lead fulfilling lives with the right treatment and support. Ongoing research continues to explore new therapies and interventions aimed at improving outcomes for those affected by the disease.
Q10: Where can I find more information about COPD?
A10: For more information, consider visiting reputable health organizations such as the American Lung Association or the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. They provide valuable resources, support networks, and educational materials to help individuals navigate life with COPD.
To Wrap It Up
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) presents a complex challenge that extends beyond the individual to touch families, communities, and healthcare systems. As we have explored, the interplay between prevention, early detection, and effective management can significantly alter the trajectory of this condition. Understanding COPD isn’t merely about recognizing symptoms or adhering to treatment; it’s about fostering a culture of awareness and support. By prioritizing lung health, advocating for better resources, and embracing advancements in medical research, we can contribute to a future where those affected by COPD can breathe a little easier. Let us move forward with knowledge and compassion, ensuring that every breath counts.