In the intricate landscape of human health, blood glucose levels serve as a vital compass, guiding our bodies through the daily ebb and flow of energy and well-being. Much like the delicate balance of a finely tuned instrument, these levels fluctuate in response to the foods we eat, the activities we engage in, and the myriad of metabolic processes at play. Understanding the nuances of blood glucose not only sheds light on our immediate physical state but also unveils the larger narrative of chronic conditions such as diabetes that affect millions worldwide. This article invites you to explore the science behind blood glucose levels, their significance in our daily lives, and the practical steps we can take to maintain a harmonious balance, empowering us to navigate our health with greater awareness and intention.
Understanding Blood Glucose Levels and Their Importance
Blood glucose levels are an essential aspect of our overall health, acting as a primary source of energy for our bodies. Understanding how these levels fluctuate can provide vital insights into our metabolic status. Maintaining balanced blood sugar is crucial for numerous bodily functions, including brain activity, muscle performance, and overall energy levels. Factors influencing these levels include:
- Diet: The types and amounts of food consumed directly affect blood glucose.
- Physical Activity: Exercise can lower blood sugar levels, as muscles utilize glucose for energy.
- Hormones: Insulin and glucagon play significant roles in regulating blood glucose levels.
- Stress: Psychological stress can elevate blood sugar levels through hormonal changes.
Monitoring blood glucose levels can help prevent various health complications, particularly for individuals with diabetes or those at risk. Regular checks can allow for the early detection of irregularities, enabling timely interventions. Consider the following range of blood glucose levels:
| Status | Fasting Blood Glucose (mg/dL) | Postprandial Blood Glucose (mg/dL) |
|---|---|---|
| Normal | 70-99 | Less than 140 |
| Prediabetes | 100-125 | 140-199 |
| Diabetes | 126 or higher | 200 or higher |
The Science Behind Blood Glucose Regulation
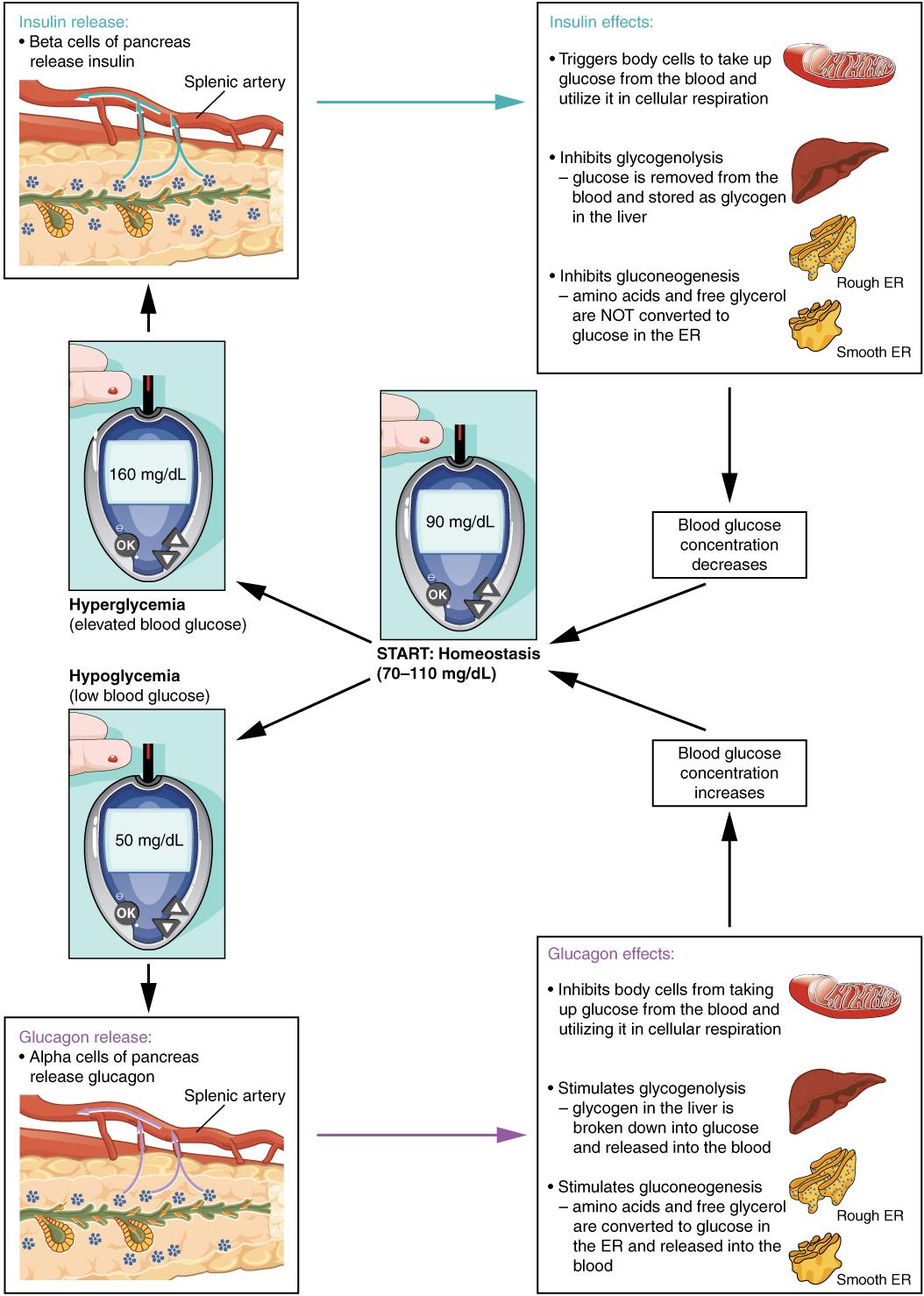
Understanding how blood glucose levels are regulated involves delving into the complex interplay of hormones, diet, and physical activity. The body primarily relies on insulin and glucagon to maintain glucose homeostasis. When you consume carbohydrates, they are broken down into glucose, leading to an increase in blood sugar levels. In response, the pancreas releases insulin, which facilitates the uptake of glucose by cells for energy or storage. Conversely, when blood sugar levels drop, glucagon is released to prompt the liver to convert stored glycogen back into glucose, ensuring a steady supply of energy. This dynamic regulation is crucial for energy balance and overall metabolic health.
The regulation of blood glucose can be influenced by various factors, including lifestyle choices. Consider the following aspects that play a significant role in maintaining healthy blood sugar levels:
- Diet: Consuming a balanced diet rich in fiber, healthy fats, and lean proteins can help manage glucose spikes.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise enhances insulin sensitivity, allowing cells to utilize glucose more effectively.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can lead to elevated cortisol levels, which may disrupt glucose regulation.
In addition to these factors, individual metabolic responses can vary based on genetics, age, and pre-existing health conditions. Understanding and monitoring these variables can empower individuals to take proactive steps in managing their blood glucose levels effectively.
Daily Habits for Maintaining Optimal Blood Glucose
Implementing consistent daily habits can significantly influence blood glucose levels, paving the way for a healthier lifestyle. Balanced meals are essential; aim for a combination of carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats. This not only helps in stabilizing blood sugar spikes but also provides sustained energy throughout the day. Hydration is equally crucial; drinking enough water can assist in regulating blood sugar levels. Consider integrating fiber-rich foods into your diet, as they can slow down glucose absorption, promoting a gradual increase in blood sugar.
Physical activity should be a staple in your daily routine, as even moderate exercise can enhance insulin sensitivity. Try engaging in 30 minutes of activity most days of the week, whether it’s walking, cycling, or yoga. Additionally, managing stress levels is vital; high stress can lead to elevated blood sugar. Incorporate mindfulness practices, such as meditation or deep-breathing exercises, to help keep stress in check. Below is a simple table highlighting daily habits that can contribute to optimal blood glucose management:
| Habit | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Eat Balanced Meals | Stabilizes blood sugar levels |
| Stay Hydrated | Supports metabolic functions |
| Get Regular Exercise | Improves insulin sensitivity |
| Practice Mindfulness | Reduces stress-induced spikes |
Dietary Choices That Influence Blood Sugar Levels
Understanding how specific foods impact blood glucose levels is crucial for maintaining overall health. By choosing the right dietary options, individuals can effectively manage their glucose levels. Whole grains, for instance, are an excellent choice because they are high in fiber, which helps stabilize blood sugar. Foods such as brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread release glucose slowly into the bloodstream, preventing spikes. On the other hand, refined carbohydrates, like white bread and sugary snacks, can lead to rapid increases in blood sugar, making it essential to minimize their consumption.
In addition to grains, the inclusion of protein and healthy fats in meals can further regulate blood sugar levels. Foods rich in protein, such as lean meats, fish, and legumes, promote satiety and lead to a more gradual absorption of carbohydrates. Similarly, avocados, nuts, and olive oil are sources of healthy fats that can slow the digestion of carbohydrates, thereby aiding in blood sugar management. To make informed dietary choices, here’s a simple table illustrating some helpful foods and their effects on blood glucose:
| Food Type | Effect on Blood Sugar |
|---|---|
| Whole Grains | Stable, slow release |
| Refined Carbs | Rapid spike |
| Lean Protein | Gradual absorption |
| Healthy Fats | Slower digestion |
Recognizing the Signs of Imbalanced Blood Glucose
Understanding the fluctuations in blood glucose levels is crucial for maintaining overall health. Individuals experiencing an imbalance may notice a range of symptoms that can significantly impact daily life. Common indicators include:
- Frequent fatigue: A sudden drop in energy can leave you feeling drained.
- Unexplained weight changes: Rapid weight loss or gain may suggest underlying issues.
- Frequent urination: An increase in urination can be a sign of elevated blood sugar levels.
- Increased thirst: Persistent thirst, even after adequate hydration, can indicate a problem.
- Mood swings: Irritability and anxiety could signal blood sugar irregularities.
Being mindful of these signs can lead to timely intervention and better management. Monitoring your body’s responses is essential, particularly if you have a history of metabolic conditions. Here’s a quick reference table of symptoms and potential causes:
| Symptom | Possible Cause |
|---|---|
| Fatigue | Low blood sugar or insulin resistance |
| Increased Thirst | Dehydration from high blood sugar |
| Weight Changes | Hormonal imbalances or metabolic issues |
| Mood Swings | Fluctuating glucose levels affecting brain function |
Managing Stress and Its Impact on Blood Sugar Control
Stress is a natural physiological response, but when it becomes chronic, it can wreak havoc on your body, particularly on blood sugar levels. During stressful moments, the body releases hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, which are designed to help us respond to immediate threats. However, these hormones can lead to increased blood sugar levels as the body prepares for a “fight-or-flight” response. This elevated state of glucose can be particularly concerning for individuals managing diabetes or those susceptible to blood sugar fluctuations. By recognizing the signs of stress and its potential impact, individuals can take proactive steps to mitigate its effects, ensuring a more stable blood glucose level.
To effectively manage stress and support optimal blood sugar control, consider the following strategies:
- Mindfulness Practices: Engage in meditation or deep-breathing exercises to reduce anxiety levels.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise can help lower stress hormones and improve insulin sensitivity.
- Nutrition: Consuming balanced meals rich in whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can stabilize blood sugar levels.
- Sleep Hygiene: Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night to support overall health and stress management.
Consider incorporating these practices into your daily routine. Below is a simple table summarizing the impact of stress on blood sugar levels:
| Type of Stress | Immediate Blood Sugar Response | Long-term Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Acute Stress | Temporary increase | May normalize after stressor is removed |
| Chronic Stress | Consistent elevation | Potential insulin resistance |
Q&A
Q&A: Understanding Blood Glucose Levels
Q1: What are blood glucose levels, and why are they important?
A1: Blood glucose levels refer to the amount of sugar (glucose) present in your bloodstream. Glucose serves as a primary energy source for our bodies. Maintaining balanced blood glucose levels is crucial because fluctuations can lead to various health issues, including diabetes, fatigue, and long-term complications affecting the heart, kidneys, and eyes.
Q2: How are blood glucose levels measured?
A2: Blood glucose levels can be measured using a few different methods. The most common is a fingerstick test using a glucometer, which provides a quick snapshot of your blood sugar at that moment. For a more comprehensive view, healthcare providers may order a fasting blood glucose test or an A1C test, which indicates average glucose levels over the past two to three months.
Q3: What factors can influence blood glucose levels?
A3: Several factors can impact blood glucose levels, including diet, physical activity, stress, medications, and hormonal changes. Foods high in carbohydrates, particularly sugars, can cause spikes in glucose levels, while regular exercise can help regulate them. Emotional stress can also lead to temporary increases in blood sugar due to hormonal responses.
Q4: What is considered a normal blood glucose level?
A4: Normal blood glucose levels generally range from 70 to 99 mg/dL (milligrams per deciliter) when fasting. After meals, levels can rise but should ideally remain below 140 mg/dL. Levels consistently outside these ranges may indicate prediabetes or diabetes, and it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for guidance.
Q5: How can one maintain healthy blood glucose levels?
A5: Maintaining healthy blood glucose levels involves a balanced approach to nutrition and lifestyle. Eating a diet rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins while limiting processed sugars is key. Regular physical activity, adequate hydration, and stress management techniques, like mindfulness or yoga, are also effective strategies. For individuals with diabetes, monitoring blood sugar and following a personalized care plan is crucial.
Q6: What should I do if my blood glucose levels are too high or too low?
A6: If your blood glucose levels are too high (hyperglycemia), it’s important to stay hydrated, adjust your diet, and consult with a healthcare professional for potential medication adjustments. Symptoms may include frequent urination, excessive thirst, or fatigue. Conversely, if you experience low blood glucose levels (hypoglycemia), consuming fast-acting carbohydrates, like fruit juice or glucose tablets, can help raise your levels quickly. Symptoms of hypoglycemia include dizziness, sweating, and confusion.
Q7: Can technology help in managing blood glucose levels?
A7: Absolutely! Advances in technology, such as continuous glucose monitors (CGMs), allow individuals to track their blood glucose levels in real-time. These devices provide valuable insights and alerts about fluctuations, helping users make informed decisions about their diet and activity. Smartphone apps also support tracking and managing glucose levels, making it easier for individuals to maintain control.
Q8: What’s the future of blood glucose management?
A8: The future of blood glucose management is bright, with ongoing research into innovative treatments, technologies, and even artificial pancreas systems that automate insulin delivery. Personalized medicine approaches are gaining traction as well, tailoring strategies based on individual genetic and lifestyle factors to optimize blood glucose control. The goal is to create a world where managing blood glucose is seamless and effective, promoting overall health and well-being.
understanding blood glucose levels is essential for everyone, not just those with diabetes. By being informed and proactive, individuals can take charge of their health and enhance their quality of life.
Closing Remarks
As we draw the curtain on this exploration of blood glucose levels, it’s clear that understanding this vital aspect of our health is more than just a scientific endeavor; it’s a gateway to a healthier, more balanced life. By keeping a vigilant eye on our glucose levels, we empower ourselves to make informed choices that can enhance our well-being and longevity. Whether through diet, exercise, or regular monitoring, the journey towards optimal blood sugar management is a collective effort, grounded in knowledge and proactive living. As you step into your day, remember that each choice you make is a stitch in the fabric of your health. So, embrace the path of awareness and let your blood glucose levels guide you toward a brighter, healthier future.