Understanding Bipolar II: The Subtle Spectrum of Mood Disorders
In the intricate tapestry of mental health, few conditions weave a narrative as complex and often misunderstood as Bipolar II Disorder. While the term “bipolar” may evoke images of dramatic mood swings and stark contrasts, Bipolar II offers a more nuanced experience—one characterized by the delicate interplay between periods of depression and episodes of hypomania. This lesser-known sibling of Bipolar I can easily slip under the radar, frequently misdiagnosed or overshadowed by its more conspicuous counterpart. Yet, it holds profound implications for those who navigate its ebbs and flows. In this article, we will delve into the defining features of Bipolar II, explore its impact on daily life, and illuminate the importance of understanding this condition in fostering compassion and effective support. Join us as we unravel the layers of Bipolar II, shedding light on the often-overlooked experiences of those living with this unique mood disorder.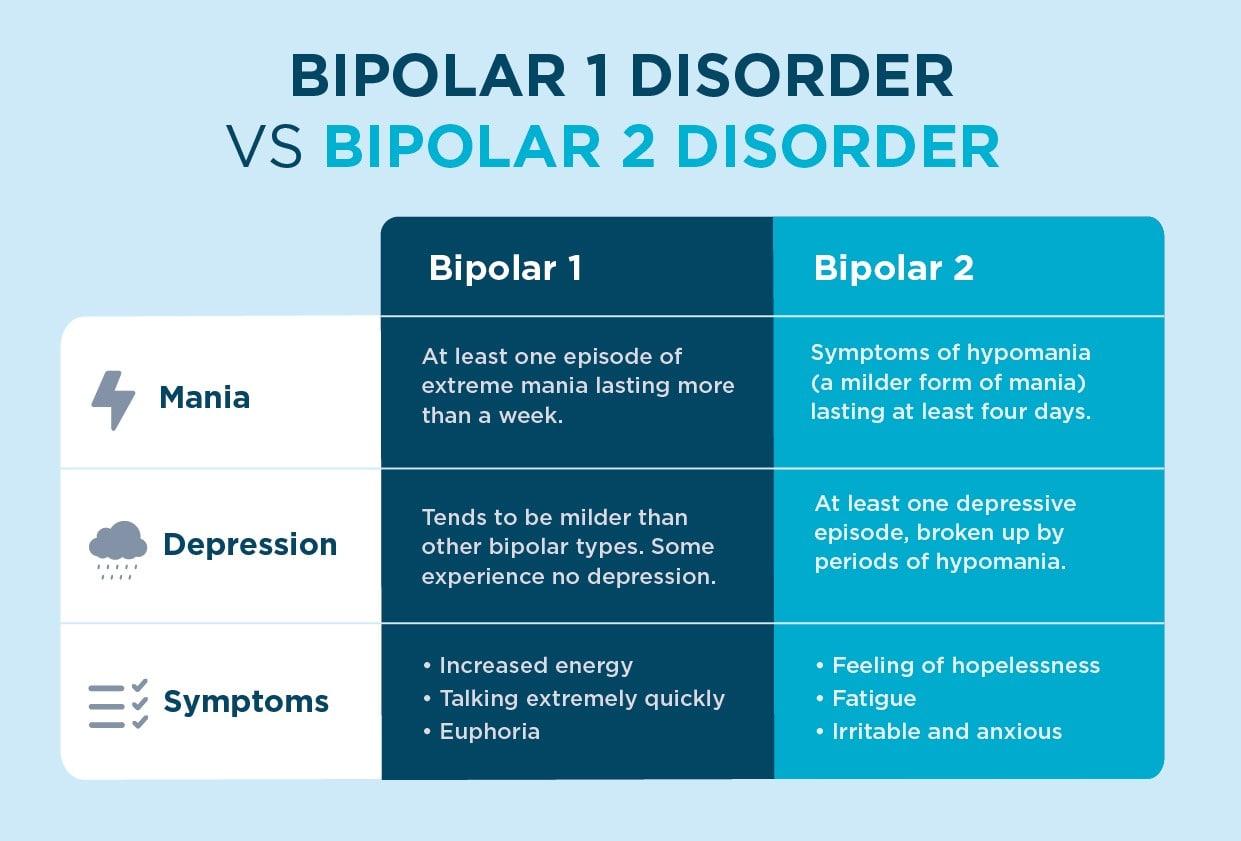
Understanding Bipolar 2 and Its Distinct Symptoms
Bipolar II Disorder is often misunderstood, as it differs significantly from its more severe counterpart, Bipolar I. In this condition, individuals experience episodes of hypomania—a milder form of mania—alongside major depressive episodes. Hypomanic episodes may include heightened energy levels, increased productivity, and a sense of euphoria, yet they typically do not escalate to the extreme highs seen in full-blown manic episodes. This nuanced presentation can lead to challenges in diagnosis, as the subtle symptoms may be dismissed or attributed to other conditions.
Understanding the distinct symptoms of Bipolar II is crucial for effective management and support. Common signs include:
- Hypomanic Symptoms: Elevated mood, decreased need for sleep, and racing thoughts.
- Major Depressive Episodes: Feelings of hopelessness, fatigue, and loss of interest in daily activities.
- Emotional Instability: Rapid mood swings that may not align with external circumstances.
- Difficulty in Functioning: Struggles with maintaining relationships and fulfilling responsibilities.
Recognizing these patterns is essential, as they can significantly impact an individual’s daily life and relationships. With appropriate treatment and support, individuals with Bipolar II can find a balance that allows them to thrive.
The Emotional Spectrum: Recognizing Hypomania and Depression
Understanding the nuances of emotional states in bipolar II disorder is crucial for effective management and support. Hypomania, a milder form of mania, often presents with elevated mood, increased energy, and heightened creativity. Individuals may experience a surge of productivity, but this state can evolve into impulsivity and poor decision-making. Recognizing these key characteristics can help in distinguishing hypomania from the more severe manic episodes seen in other forms of bipolar disorder. Some notable signs include:
- Increased talkativeness or pressure to keep talking
- Heightened self-esteem or grandiosity
- Decreased need for sleep
- Engagement in risky behavior
On the opposite end of the emotional spectrum, depression in bipolar II can be profoundly debilitating. Individuals may find themselves engulfed in overwhelming sadness, fatigue, and a sense of hopelessness. This phase can severely impact daily functioning and quality of life. Identifying these common symptoms is important for timely intervention. The following traits often accompany depressive episodes:
- Persistent feelings of worthlessness or guilt
- Loss of interest in previously enjoyed activities
- Significant changes in appetite or sleep patterns
- Difficulty concentrating or making decisions
Navigating the Diagnosis: Steps to Seek Professional Help
Understanding the complexities of bipolar II disorder often begins with recognizing the symptoms and their impact on daily life. If you suspect you or someone you know may be experiencing this condition, it is essential to take structured steps towards obtaining a professional diagnosis. Start by documenting your experiences, focusing on mood variations, energy levels, and any episodes of depression or hypomania. Keeping a mood journal can be particularly beneficial, as it provides healthcare professionals with valuable insights into your emotional patterns. Engaging in open conversations with trusted friends or family members can also help build a supportive network that encourages seeking help.
Once you’ve gathered your observations, the next step is to consult a qualified mental health professional. Look for specialists who have experience with mood disorders, such as psychiatrists or clinical psychologists. In your initial consultation, you might consider discussing the following:
- Your mood history: Describe fluctuations in mood, energy, and behavior.
- Impact on daily life: Explain how symptoms affect work, relationships, and overall functioning.
- Family history: Share any known mental health issues within your family.
After your consultation, if a diagnosis is made, it’s crucial to collaborate with your healthcare provider on a treatment plan tailored to your needs. Treatment options may include therapy, medication, lifestyle changes, or a combination of these approaches. To help you better understand potential treatment methods, consider the following:
| Treatment Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Therapy | Engaging in cognitive-behavioral therapy or other therapeutic modalities. |
| Medication | Using mood stabilizers or antidepressants as prescribed by a psychiatrist. |
| Lifestyle Changes | Implementing regular exercise, a balanced diet, and sufficient sleep. |
Effective Treatment Options for Managing Bipolar 2
Managing Bipolar 2 requires a multifaceted approach that often combines medication, therapy, and lifestyle changes. Mood stabilizers are commonly prescribed to help regulate mood swings, while antidepressants may be used cautiously to treat depressive episodes. Alongside these medications, atypical antipsychotics can also play a vital role in stabilizing mood. It’s essential for individuals to work closely with their healthcare providers to find the right combination and dosage tailored to their specific needs.
Therapeutic interventions can significantly enhance the management of Bipolar 2. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) can help individuals identify and modify negative thought patterns, while Interpersonal and Social Rhythm Therapy (IPSRT) focuses on stabilizing daily routines and improving interpersonal relationships. Additionally, incorporating mindfulness practices such as meditation and yoga can be beneficial for emotional regulation. Creating a supportive environment through peer support groups can also foster a sense of community and understanding among those living with the condition.
Building a Support System: Engaging Friends and Family
Creating a robust support system is essential for managing Bipolar II disorder, and engaging friends and family plays a pivotal role in this journey. By sharing your experiences and educating loved ones about the condition, you can foster understanding and empathy. Consider discussing the following key points with your support network:
- Symptoms and Triggers: Help them recognize the signs of mood changes and what might provoke them.
- Communication Preferences: Explain how you prefer to talk about your feelings and what language is most supportive.
- Encouragement Techniques: Suggest ways they can offer encouragement during challenging times.
Moreover, it can be beneficial to establish a communication plan that outlines when you might need extra support. A simple table can help illustrate how to respond during different phases of your experience:
| Phase | Recommended Responses |
|---|---|
| Hypomania | Encourage creativity and activity, but remind to stay grounded. |
| Stable | Engage in regular check-ins and maintain open dialogue. |
| Depression | Provide reassurance, offer help with daily tasks, and listen without judgment. |
By proactively sharing this information with your loved ones, you empower them to become proactive and supportive allies in your mental health journey. Building a collaborative approach to understanding and managing your condition will not only strengthen your relationships but also enhance your overall well-being.
Practical Strategies for Daily Life and Self-Care
Living with bipolar II disorder can present unique challenges, but incorporating practical strategies into your daily routine can significantly improve your quality of life. Establishing a consistent daily schedule is key; it helps to regulate sleep patterns and manage mood fluctuations. Consider the following tips:
- Set regular sleep hours: Prioritize 7-9 hours of sleep each night to stabilize your mood.
- Maintain a balanced diet: Incorporate a variety of nutrients to support brain health.
- Engage in regular exercise: Physical activity can improve mood and reduce anxiety.
- Practice mindfulness: Techniques such as meditation or deep breathing can help manage stress.
Additionally, it’s important to foster connections and seek support. Building a reliable support network can create a sense of belonging and understanding. Here are some strategies to consider:
| Support Strategies | Description |
|---|---|
| Join a support group | Connecting with others who have similar experiences can provide comfort and insights. |
| Communicate openly | Share your feelings with trusted friends or family to foster understanding. |
| Seek professional help | Therapists or counselors can offer strategies tailored to your individual needs. |
Q&A
Q&A on Bipolar II Disorder
Q1: What is Bipolar II Disorder?
A: Bipolar II Disorder is a mental health condition characterized by recurring episodes of depression and hypomania. Unlike its counterpart, Bipolar I, individuals with Bipolar II do not experience full-blown manic episodes. Instead, they may experience elevated moods, increased energy, and heightened creativity during hypomanic phases, but these episodes are less intense and shorter in duration.
Q2: How does Bipolar II differ from Bipolar I?
A: The key difference lies in the severity of manic episodes. In Bipolar I Disorder, individuals experience manic episodes that last at least seven days or are so severe that they require hospitalization. In contrast, Bipolar II Disorder involves at least one major depressive episode and at least one hypomanic episode, but no full manic episodes. This distinction is important for diagnosis and treatment.
Q3: What are the common symptoms of Bipolar II Disorder?
A: Symptoms of Bipolar II Disorder can vary widely but typically include:
- Depressive Episodes: Feelings of sadness, hopelessness, fatigue, and loss of interest in daily activities.
- Hypomanic Episodes: Increased energy, elevated mood, irritability, racing thoughts, and a decreased need for sleep, lasting at least four consecutive days.
- Changes in sleep patterns, appetite, and concentration may also be observed, affecting day-to-day life.
Q4: How is Bipolar II Disorder diagnosed?
A: Diagnosis is typically made by a qualified mental health professional through a comprehensive assessment that includes a detailed clinical interview, patient history, and standardized diagnostic criteria. It is crucial to differentiate it from other mood disorders, as well as to rule out any physiological causes for the symptoms.
Q5: What treatment options are available?
A: Treatment for Bipolar II Disorder usually includes a combination of medication and psychotherapy. Mood stabilizers, antipsychotics, and antidepressants may be prescribed. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and other therapeutic approaches can help individuals manage their symptoms, develop coping strategies, and improve overall functioning.
Q6: Can Bipolar II Disorder be managed effectively?
A: Yes, many people with Bipolar II Disorder can lead fulfilling lives with proper treatment and support. Regular monitoring by a healthcare professional, adherence to prescribed treatment, and a strong support system are essential components in managing the condition. Education about the disorder can also empower individuals to recognize warning signs and seek help when needed.
Q7: What should someone do if they suspect they have Bipolar II Disorder?
A: If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms consistent with Bipolar II Disorder, it’s important to seek professional help. A mental health professional can provide an accurate diagnosis and tailor a treatment plan that suits individual needs. Reaching out for support from friends and family can also make a significant difference in navigating the journey toward wellness.
Q8: Is there a stigma associated with Bipolar II Disorder?
A: Unfortunately, mental health conditions, including Bipolar II Disorder, often carry stigma, which can discourage individuals from seeking help. It’s important to foster open conversations about mental health, promote understanding, and encourage empathy in society. By breaking down these barriers, we can create a more supportive environment for those affected by bipolar disorders.
Bipolar II Disorder is a complex condition, but with knowledge, understanding, and the right treatment approach, individuals can manage their symptoms and thrive.
In Summary
In the intricate tapestry of mental health, Bipolar II stands out as a complex yet often misunderstood thread. As we’ve explored, the nuances of this condition stretch far beyond the traditional highs and lows commonly associated with bipolar disorders. It invites us to engage in a deeper conversation about emotional resilience, the importance of understanding, and the significance of adequate support systems.
As we draw this exploration to a close, it’s vital to remember that living with Bipolar II is not merely defined by the challenges it presents, but also by the unique strengths and perspectives it fosters. Each individual’s experience is distinct, colored by personal stories of struggle and triumph.
In illuminating the realities of Bipolar II, we not only pave the way for greater awareness but also encourage compassion and empathy. With continued dialogue and education, we can dismantle the stigmas that still cling to mental health conditions, fostering a world where those affected feel seen, heard, and understood.
The journey toward mental wellness is rarely a straight path, yet it is one that holds the potential for profound growth and understanding. As we move forward, let us carry these insights with us, championing a future where every individual, regardless of their mental health journey, is empowered to thrive.
