Title: Understanding Bladder Infections: Navigating the Unseen Battle Within
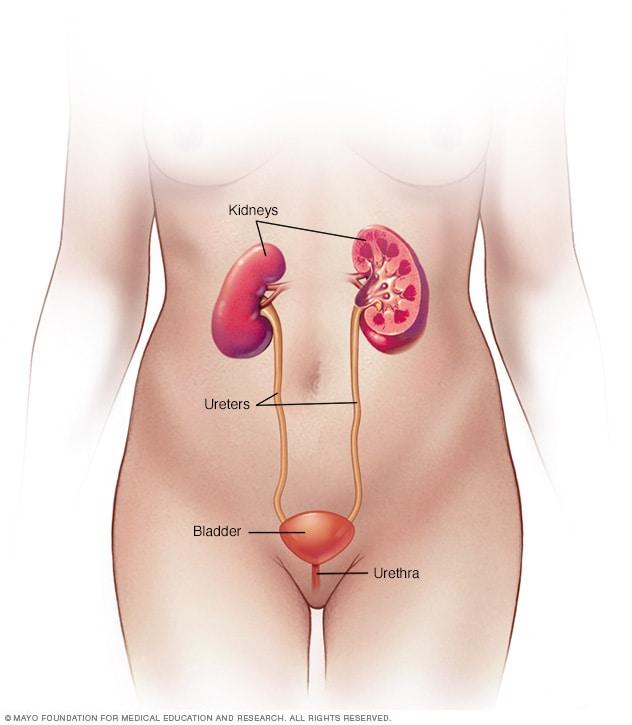
In the intricate landscape of our bodies, where countless processes harmonize to sustain life, the urinary system plays a vital yet often overlooked role. Among its myriad functions, it serves as a guardian, filtering out waste and maintaining a delicate balance of fluids. However, this essential system can sometimes become a battleground, particularly when faced with the unwelcome invasion of bacteria leading to bladder infections, or cystitis. This common yet often misunderstood condition can disrupt daily life, causing discomfort and distress. As we delve into the world of bladder infections, we aim to shed light on their causes, symptoms, and treatments, empowering readers with knowledge to recognize and address this prevalent health issue. By demystifying the complexities of bladder infections, we hope to foster a better understanding of how to protect this crucial aspect of our well-being.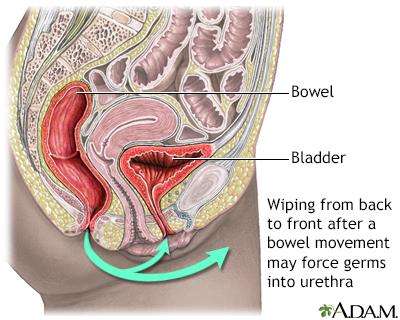
Understanding Bladder Infections: Causes and Symptoms
Bladder infections, also known as urinary tract infections (UTIs), occur when harmful bacteria invade the urinary system, leading to inflammation and discomfort. This condition can affect anyone, but certain factors can increase the likelihood of developing an infection. Common causes include:
- Poor hygiene practices: Insufficient cleanliness can allow bacteria to thrive.
- Sexual activity: Increased friction can introduce bacteria into the urethra.
- Dehydration: Not drinking enough fluids reduces urine flow, which helps flush out bacteria.
- Certain contraceptives: Products like spermicides can disrupt the natural balance of bacteria.
Recognizing the symptoms of a bladder infection is crucial for timely treatment. Individuals may experience a variety of signs indicating an infection, including:
- Frequent urge to urinate: A persistent feeling of needing to urinate even when little comes out.
- Burning sensation: Pain or discomfort during urination.
- Cloudy or strong-smelling urine: Changes in urine appearance can signal an infection.
- Pelvic pain: Discomfort in the lower abdomen can accompany other symptoms.
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Frequent urination | Feeling the need to urinate often, even if little is produced. |
| Painful urination | Experiencing burning or discomfort while urinating. |
| Pelvic discomfort | Feeling of pressure or pain in the lower abdomen. |
| Unusual urine odor | Urine may have a strong or unpleasant smell. |
The Role of Hydration in Preventing Bladder Infections
Staying adequately hydrated is one of the simplest yet most effective strategies for maintaining urinary tract health and minimizing the risk of bladder infections. When the body receives sufficient water, it promotes regular urination, which helps to flush out harmful bacteria that can lead to infection. This natural process acts as a defense mechanism, ensuring that pathogens do not have the opportunity to colonize within the bladder. Additionally, hydration aids in diluting the urine, which can reduce irritation within the bladder and lower the likelihood of discomfort or infection.
It’s important to recognize the signs of dehydration and adjust fluid intake accordingly, especially for individuals predisposed to urinary tract issues. Here are some benefits of proper hydration:
- Enhanced Urinary Flow: Regular urination eliminates bacteria more effectively.
- Improved Comfort: Well-hydrated individuals often experience less urinary tract irritation.
- Balanced pH Levels: Adequate water intake can help maintain a healthy urinary environment.
To illustrate the importance of hydration, consider the following table outlining daily water intake recommendations based on different lifestyles:
| Activity Level | Recommended Daily Intake (liters) |
|---|---|
| Sedentary | 2.0 - 2.5 |
| Moderate Activity | 2.5 - 3.0 |
| High Activity | 3.0 – 4.0 |
Effective Home Remedies for Managing Bladder Infections
When dealing with bladder infections, several natural remedies can provide relief and support your body’s healing process. One effective method is to increase your fluid intake, particularly water, as it helps flush out harmful bacteria. Additionally, consuming cranberry juice can prevent bacteria from adhering to the bladder wall, making it a popular choice among those seeking relief. Other helpful options include:
- Warm compresses on your abdomen to alleviate discomfort.
- Probiotics found in yogurt to restore healthy bacteria in your gut.
- D-mannose, a type of sugar that may help in preventing infections.
Incorporating these remedies into your daily routine can significantly enhance your ability to manage symptoms. A balanced diet rich in vitamin C can also boost your immune system, making it harder for infections to take hold. To further support your recovery, consider avoiding irritants such as caffeine, alcohol, and spicy foods. Here’s a simple table that outlines some beneficial foods and beverages for managing bladder infections:
| Food/Beverage | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Cranberry Juice | Prevents bacteria from sticking to the bladder |
| Yogurt | Restores beneficial gut bacteria |
| Water | Flushes out toxins and bacteria |
| Blueberries | Rich in antioxidants, supports immune health |
When to Seek Medical Attention for Bladder Infections
Recognizing the signs that warrant a visit to a healthcare professional is crucial for managing bladder infections effectively. If you experience symptoms such as persistent pain during urination, blood in urine, or fever, it’s essential to seek medical attention. These symptoms may indicate a more serious infection or complications that require prompt treatment. Additionally, if you find that over-the-counter remedies are not alleviating your discomfort, don’t hesitate to consult a doctor. Other indicators that should prompt a visit include:
- Severe abdominal pain
- Nausea or vomiting
- Frequent urination with little output
- Symptoms lasting longer than a few days
For individuals with underlying health conditions, such as diabetes or kidney issues, it is especially important to be vigilant. A bladder infection can escalate quickly in those populations, leading to more serious health concerns. Consider the following factors that may necessitate a medical consultation:
| Condition | Action Required |
|---|---|
| Pregnant | Immediate medical evaluation |
| Previous UTIs | Consult if symptoms recur |
| Compromised immune system | Seek help without delay |
Exploring Treatment Options: Antibiotics and Beyond
When it comes to treating a bladder infection, antibiotics are often the first line of defense. These medications work by targeting and eliminating the bacteria responsible for the infection. Common antibiotics prescribed include:
- Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole – A combination antibiotic that effectively combats various bacteria.
- Nitrofurantoin – Particularly effective for uncomplicated urinary tract infections.
- Ciprofloxacin – A broad-spectrum antibiotic that can treat more complicated cases.
However, the journey to recovery may extend beyond just antibiotics. Complementary treatments can enhance healing and alleviate symptoms. Consider integrating the following options:
- Hydration – Increasing water intake helps flush out bacteria.
- Probiotics – These beneficial bacteria support gut health and may reduce recurrence.
- Cranberry products – While evidence is mixed, some find that cranberry supplements or juice may prevent future infections.
Moreover, understanding how lifestyle modifications can impact bladder health is crucial. The table below outlines some effective strategies:
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Adequate Hydration | Drinking plenty of fluids helps dilute urine and prevent bacterial growth. |
| Regular Bathroom Breaks | Avoiding prolonged retention can help reduce infection risk. |
| Wearing Breathable Fabrics | Choosing cotton underwear can help maintain dryness and prevent irritation. |
Lifestyle Changes to Reduce the Risk of Recurrence
Making intentional lifestyle adjustments can play a pivotal role in minimizing the likelihood of bladder infection recurrence. Hydration is key; drinking plenty of water helps dilute the urine and flush out bacteria. Aim for at least eight 8-ounce glasses of water daily. Additionally, consider incorporating cranberry products into your diet, whether in juice form or as supplements, as they contain compounds that may prevent bacteria from adhering to the bladder wall. Maintaining proper hygiene practices, such as wiping from front to back after using the restroom, can also be beneficial in reducing risk factors.
Moreover, it is essential to evaluate and modify certain habits that may contribute to infections. Cotton underwear is preferable over synthetic fabrics, as it allows the area to remain dry and reduces bacterial growth. Try to avoid irritants like scented soaps or bubble baths that can disrupt the natural flora of the urinary tract. Regular exercise can enhance overall health, but be mindful of post-workout hygiene—changing out of damp clothing promptly can help maintain a healthy bladder environment. Lastly, consider scheduling regular check-ups with your healthcare provider to monitor your urinary health effectively.
Q&A
Q&A: Understanding Bladder Infections
Q1: What exactly is a bladder infection?
A1: A bladder infection, medically known as cystitis, occurs when bacteria invade the bladder, leading to inflammation and discomfort. It’s a common type of urinary tract infection (UTI) that can affect anyone, but women are more prone to experience it due to their anatomy.
Q2: What are the common symptoms of a bladder infection?
A2: Symptoms can include a persistent urge to urinate, a burning sensation during urination, cloudy or strong-smelling urine, and pelvic pain. Some might also experience fever or chills if the infection spreads to the kidneys.
Q3: What causes bladder infections?
A3: Bladder infections are typically caused by bacteria, most frequently Escherichia coli (E. coli), which normally live in the intestines. The infection can occur when bacteria enter the urinary tract through the urethra, often due to improper hygiene practices, sexual activity, or using certain types of birth control.
Q4: Who is most at risk for developing a bladder infection?
A4: While anyone can develop a bladder infection, certain groups are more susceptible. Women are at a higher risk due to their shorter urethra. Other risk factors include pregnancy, menopause, urinary tract abnormalities, and a weakened immune system.
Q5: How can bladder infections be diagnosed?
A5: Diagnosis typically involves a review of symptoms, a physical exam, and a urinalysis. A urine culture may also be performed to identify the specific bacteria causing the infection, which helps guide treatment.
Q6: What treatments are available for a bladder infection?
A6: The primary treatment for a bladder infection is a course of antibiotics tailored to the specific bacteria identified. Over-the-counter pain relievers can help alleviate discomfort. It’s important to complete the entire course of antibiotics, even if symptoms improve.
Q7: Are there any home remedies to help with bladder infections?
A7: While antibiotics are crucial for treating bladder infections, some home remedies may complement treatment. Drinking plenty of water can help flush out bacteria, while cranberry juice is often cited for its potential to prevent bacteria from adhering to the bladder wall. However, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider before relying solely on home remedies.
Q8: How can one prevent future bladder infections?
A8: Prevention strategies include staying well-hydrated, urinating after intercourse, practicing good hygiene, and avoiding irritating feminine products. For those who experience recurrent infections, consulting with a healthcare professional for personalized strategies is advisable.
Q9: When should someone seek medical attention for a bladder infection?
A9: If symptoms persist for more than a couple of days, worsen, or are accompanied by fever, chills, or back pain, it’s crucial to seek medical attention. Prompt treatment is essential to prevent complications, such as a kidney infection.
Q10: Can bladder infections have long-term effects?
A10: Most bladder infections are easily treatable without lasting effects. However, if recurrent or left untreated, they can lead to more serious conditions, including kidney infections or chronic bladder issues. Regular check-ups and communication with a healthcare provider can help manage and mitigate risks.
—
This Q&A aims to provide clear, concise information about bladder infections, promoting understanding and encouraging proactive health practices.
In Summary
navigating the complexities of bladder infections requires a combination of awareness, timely intervention, and informed care. While the discomfort and urgency that accompany this common ailment can be distressing, understanding the symptoms, treatment options, and preventive measures can empower individuals to take charge of their health. As we continue to unravel the mysteries of our bodies, fostering open dialogue with healthcare professionals remains essential in combating these infections effectively. With the right knowledge and resources, we can transform an uncomfortable experience into an opportunity for growth and resilience in our wellness journeys. Remember, your health matters—take the necessary steps to protect it.