Type 1 diabetes is a condition that transforms the everyday landscape of life into a careful balance of vigilance and adaptability. Unlike its counterpart, type 2 diabetes, which is often linked to lifestyle factors, type 1 diabetes emerges as an autoimmune intruder, striking typically in childhood or adolescence, but sometimes later in life. This complex disorder requires individuals to navigate a world where their bodies no longer produce insulin, the hormone essential for regulating blood sugar levels. In this article, we will explore the nuances of type 1 diabetes—its causes, symptoms, and the profound impact it has on those affected. Through understanding, we can foster a greater awareness of the resilience and ingenuity that shines through in the daily lives of individuals managing this condition. Join us as we delve into the science, stories, and ongoing advancements in the quest for better treatment and, ultimately, a cure.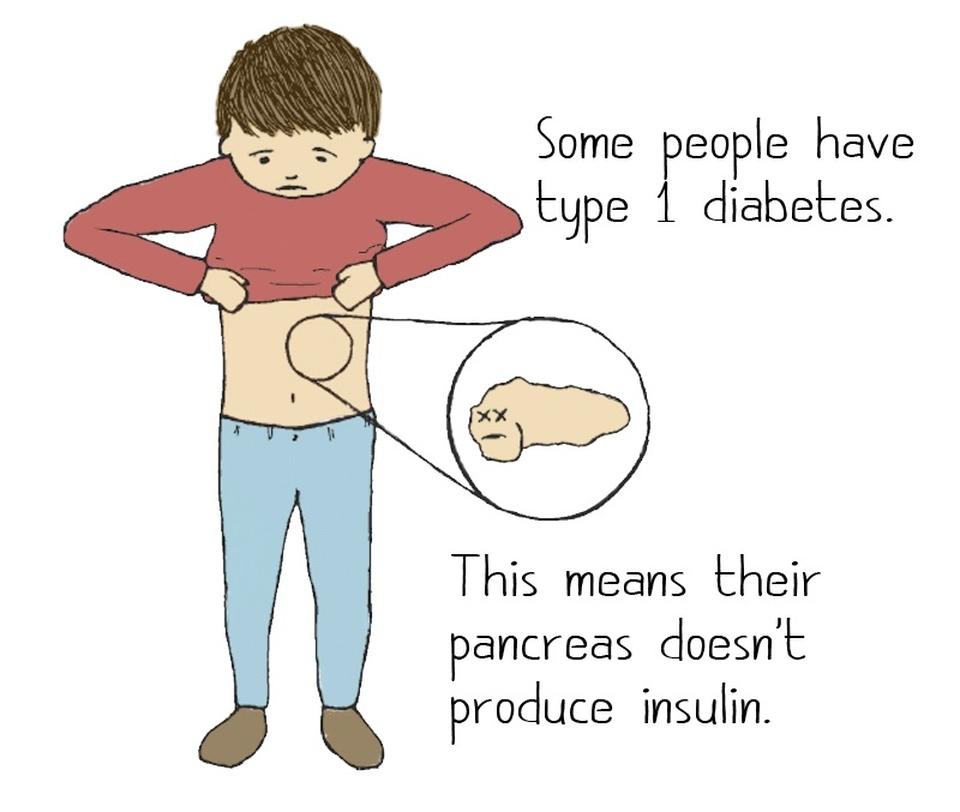
Understanding Type 1 Diabetes: The Immune Systems Role
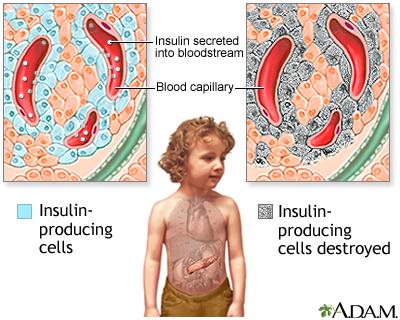
Type 1 diabetes is fundamentally an autoimmune condition, where the immune system mistakenly identifies insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas as foreign invaders. This misidentification leads to the destruction of these vital cells, resulting in little to no insulin production. Insulin is crucial for converting glucose into energy, and without it, blood sugar levels can rise to dangerous levels. The exact cause of this immune response is still not fully understood, but several factors could contribute, including genetic predisposition and environmental triggers. Some potential factors include:
- Genetic Factors: Family history may increase the risk.
- Viral Infections: Some viruses might trigger the immune response.
- Dietary Factors: Early exposure to certain proteins may influence immune function.
Research into the immune system’s role in Type 1 diabetes has opened pathways for potential therapies aimed at modulating immune responses. Understanding the specific immune mechanisms involved can lead to innovative treatments that aim to preserve beta cell function or protect them from immune attack. Current studies focus on identifying biomarkers that predict the onset of the disease, which could eventually lead to preventative measures. Here’s a brief overview of some immune components involved:
| Immune Component | Role in Type 1 Diabetes |
|---|---|
| T-cells | Attack and destroy beta cells. |
| B-cells | Produce antibodies that may target pancreatic cells. |
| Cytokines | Signaling molecules that mediate inflammation. |
Navigating Daily Life: Managing Blood Sugar Levels Effectively
Managing blood sugar levels is an essential part of daily life for those with type 1 diabetes. Achieving balance involves a combination of careful monitoring, dietary choices, and appropriate physical activity. Here are some key strategies to consider:
- Regular Monitoring: Frequent blood glucose checks help you understand how your body responds to food, exercise, and stress.
- Balanced Diet: Incorporate a variety of foods, focusing on complex carbohydrates, lean proteins, and healthy fats to maintain steady glucose levels.
- Carbohydrate Counting: Learn how to count carbs to adjust your insulin doses accordingly, allowing for more precise control.
- Physical Activity: Engage in regular exercise, which can improve insulin sensitivity and overall health.
- Stress Management: Practice techniques such as meditation or yoga to mitigate stress, which can affect blood sugar levels.
Planning meals and snacks is crucial for maintaining stable blood sugar levels throughout the day. A structured eating schedule can be beneficial:
| Time | Food/Activity | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Breakfast | Oatmeal with berries | High fiber, low glycemic |
| Mid-Morning Snack | Greek yogurt | Protein-rich |
| Lunch | Grilled chicken salad | Lean protein and greens |
| Afternoon Snack | Apple with almond butter | Healthy fats |
| Dinner | Baked salmon and quinoa | Balanced meal |
Nutrition Essentials: Crafting a Balanced Meal Plan
Creating a well-balanced meal plan is essential for managing type 1 diabetes effectively. This involves incorporating a variety of foods to ensure you receive all necessary nutrients while maintaining stable blood glucose levels. Focus on including the following food groups in your meals:
- Whole Grains: Opt for brown rice, quinoa, and whole grain bread to provide sustained energy.
- Lean Proteins: Include sources like chicken, turkey, beans, and fish for muscle repair and growth.
- Healthy Fats: Avocados, nuts, and olive oil can help with heart health.
- Fruits and Vegetables: Aim for a colorful variety to ensure a wide range of vitamins and minerals.
Monitoring carbohydrate intake is crucial for those with type 1 diabetes. A well-structured meal plan should include a balance of carbohydrates throughout the day. Utilize a simple table to help outline your daily carbohydrate goals:
| Meal | Carbohydrates (g) | Example Foods |
|---|---|---|
| Breakfast | 30-45 | Oatmeal, Greek yogurt with berries |
| Lunch | 45-60 | Quinoa salad with chickpeas and veggies |
| Dinner | 45-60 | Grilled chicken with sweet potatoes |
| Snacks | 15-30 | Apple with almond butter, carrots with hummus |
Exercise and Activity: Finding the Right Routine for You
Finding the right exercise routine when managing type 1 diabetes requires careful consideration of your individual needs and lifestyle. It’s essential to integrate activities that not only keep you physically fit but also help in maintaining stable blood glucose levels. Start by identifying exercises that you enjoy, as this increases the likelihood of sticking with your routine. Here are some effective options to consider:
- Aerobic Activities: Walking, cycling, swimming, and dancing
- Strength Training: Bodyweight exercises, resistance bands, or weights
- Flexibility Exercises: Yoga or Pilates for balance and stretching
It’s also important to monitor your blood sugar levels before, during, and after exercise to understand how your body responds. In addition, consider the timing and intensity of your workouts; some individuals may find that moderate-intensity exercise for 30 minutes a day works best, while others might prefer shorter, high-intensity sessions. Below is a simple table outlining some tips to help you establish a balanced routine:
| Tip | Description |
|---|---|
| Stay Hydrated | Drink water before, during, and after exercising. |
| Monitor Blood Sugar | Check levels before and after workouts to prevent hypoglycemia. |
| Warm-Up and Cool Down | Incorporate gentle stretches to reduce injury risk. |
Supporting Mental Health: Coping Strategies for Living with Type 1 Diabetes
Living with Type 1 diabetes can pose unique challenges that extend beyond physical health, impacting mental well-being as well. It’s essential to cultivate coping strategies that not only manage blood glucose levels but also support emotional resilience. Here are some effective methods to help navigate the emotional landscape:
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Practicing mindfulness can help ground you in the present moment, reducing anxiety and promoting a balanced mindset.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise releases endorphins, which can elevate mood and provide a sense of achievement.
- Connect with Others: Joining support groups or connecting with friends who understand your journey can foster a sense of community and belonging.
- Structured Routine: Creating a daily routine for managing diabetes can reduce feelings of chaos and help in establishing a sense of control.
Incorporating these strategies into daily life can significantly enhance your emotional health. Additionally, consider tracking your feelings and symptoms in a simple table to develop insights into your mental health over time:
| Date | Blood Sugar Level | Mood Rating (1-10) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2023-10-01 | 150 mg/dL | 8 | Feeling optimistic |
| 2023-10-02 | 180 mg/dL | 5 | Stressed about work |
| 2023-10-03 | 130 mg/dL | 9 | Great day, went for a run |
Innovations in Treatment: Exploring Advances in Diabetes Management
In recent years, the landscape of diabetes management has evolved dramatically, particularly for those living with type 1 diabetes. One of the most significant advancements is the innovation of continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems, which allow users to track their blood glucose levels in real-time. These devices not only provide instant feedback but also help in identifying trends and patterns. Coupled with smart insulin pens, which automatically calculate the required insulin dosage based on real-time data, individuals can achieve more precise control over their blood sugar levels. The integration of these technologies into daily life helps to reduce the risk of complications and enhances the quality of life for those managing the condition.
Furthermore, the advent of artificial pancreas systems represents a groundbreaking step in automating diabetes management. These systems combine insulin pump technology with CGM to automatically adjust insulin delivery based on blood glucose readings. This seamless interaction mimics the natural function of a healthy pancreas, significantly lowering the burden of constant monitoring. Ongoing research into closed-loop systems is also promising, with potential advancements including the use of machine learning algorithms to predict blood glucose fluctuations. As these technologies evolve, they empower individuals to take control of their health, fostering independence and reducing the anxiety often associated with diabetes management.
Q&A
Q&A: Understanding Type 1 Diabetes
Q1: What is Type 1 Diabetes?
A1: Type 1 diabetes is a chronic condition in which the pancreas produces little to no insulin, a hormone essential for converting sugar, starches, and other food into energy. Unlike Type 2 diabetes, which is often related to lifestyle and can be managed with diet and exercise, Type 1 diabetes is typically diagnosed in children and young adults and is considered an autoimmune disease.
Q2: What causes Type 1 Diabetes?
A2: The exact cause of Type 1 diabetes remains a mystery, although it is believed to involve a combination of genetic predisposition and environmental triggers. In this condition, the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas, leading to an insulin deficiency.
Q3: How is Type 1 Diabetes diagnosed?
A3: Diagnosis usually involves a series of blood tests. Healthcare professionals look for elevated blood sugar levels, as well as the presence of autoantibodies that indicate the immune system’s attack on insulin-producing cells. Common tests include the A1C test, fasting blood sugar test, and oral glucose tolerance test.
Q4: What are the symptoms of Type 1 Diabetes?
A4: Symptoms can develop rapidly and may include excessive thirst, frequent urination, extreme fatigue, blurred vision, and unexpected weight loss. If left untreated, it can lead to a life-threatening condition known as diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), characterized by nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and confusion.
Q5: How is Type 1 Diabetes managed?
A5: Management of Type 1 diabetes primarily involves lifelong insulin therapy, which can be administered through injections or an insulin pump. Regular blood glucose monitoring, a balanced diet, and exercise are also crucial components of managing the condition effectively. Continuous glucose monitors and advanced technologies are improving management for many individuals.
Q6: Can people with Type 1 Diabetes lead a normal life?
A6: Absolutely! While Type 1 diabetes requires careful management, many individuals lead full and active lives. With the right resources, support, and education, people can participate in sports, travel, and pursue careers just like anyone else. Community and peer support can also play a vital role in achieving a healthy balance.
Q7: Are there any new advancements in Type 1 Diabetes research?
A7: Researchers are making exciting strides in understanding and treating Type 1 diabetes. Innovations include potential immunotherapy treatments that aim to preserve or restore insulin production, advances in closed-loop insulin delivery systems that automate insulin dosing, and ongoing studies into the role of gut microbiomes and stem cell therapies. The future looks promising!
Q8: Where can I find support and information about Type 1 Diabetes?
A8: Numerous organizations provide resources, support groups, and educational materials for individuals with Type 1 diabetes and their families. The American Diabetes Association and JDRF (formerly known as the Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation) are excellent places to start. Local community groups and online forums can also offer valuable connections and insights.
Type 1 diabetes is a complex condition that requires ongoing care and management. By staying informed and connected, individuals can navigate their journey with resilience and support.
Concluding Remarks
navigating the world of type 1 diabetes is akin to traversing a winding path, rich with challenges yet adorned with moments of triumph. Each day brings a fresh opportunity for learning and adaptation, as individuals and families cultivate resilience amidst the complexities of managing this condition. As science advances and communities rally together, hope flourishes alongside innovation, promising a brighter future for those affected. Ultimately, understanding and compassion are key, reminding us that every story is unique and every journey significant. As we continue to shed light on type 1 diabetes, let us move forward with empathy, knowledge, and a shared commitment to support one another on this enduring journey.