How does prediabetes affect overall health?
Understanding Prediabetes: Causes, Symptoms, and Management
In today’s fast-paced world, the prevalence of prediabetes is alarmingly high, affecting millions of individuals globally. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of prediabetes, including its causes, symptoms, potential complications, and effective management strategies. If you’re looking to understand how to prevent progression to Type 2 diabetes, you’re in the right place!
What is Prediabetes?
Prediabetes is a health condition characterized by higher-than-normal blood sugar levels that are not yet high enough to qualify as Type 2 diabetes. It’s a critical warning sign that insulin resistance is developing, and early intervention can stop its progression.
Understanding Blood Sugar Levels
Blood sugar levels are measured using two primary tests:
- Fasting Plasma Glucose Test: Measures blood sugar after fasting for at least 8 hours.
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test: Measures blood sugar before and 2 hours after consuming a sugary drink.
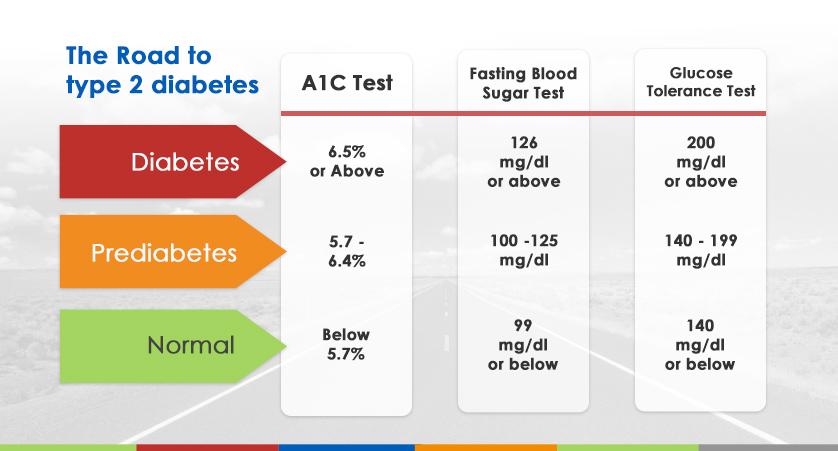
Prediabetes Diagnosis Criteria
| Test | Normal | Prediabetes | Diabetes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fasting Plasma Glucose | Less than 100 mg/dL | 100-125 mg/dL | 126 mg/dL or higher |
| Oral Glucose Tolerance | Less than 140 mg/dL | 140-199 mg/dL | 200 mg/dL or higher |
Causes of Prediabetes
Understanding the underlying causes of prediabetes is essential for prevention and management. Common factors include:
- Genetics: A family history of diabetes increases your risk.
- Obesity: Excess body fat, especially around the abdomen, can lead to insulin resistance.
- Physical Inactivity: A sedentary lifestyle contributes to weight gain and insulin resistance.
- Unhealthy Diet: High intake of sugar and refined carbohydrates can spike blood sugar levels.
- Age: The risk of prediabetes increases with age, particularly after 45.
Symptoms of Prediabetes
Many people with prediabetes show no clear symptoms. However, some may experience:
- Increased thirst
- Frequent urination
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Dark patches of skin (acanthosis nigricans)
Potential Complications
If left untreated, prediabetes can lead to serious health complications, including:
- Type 2 Diabetes: The most common outcome of untreated prediabetes.
- Heart Disease: Increased risk due to high blood sugar and insulin resistance.
- Stroke: Similar risk factors as heart disease.
- Kidney Damage: High blood sugar can damage the kidneys over time.
Benefits of Early Detection and Management
Identifying and managing prediabetes can lead to significant health improvements:
- Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes: Many individuals can revert their blood sugar levels to normal.
- Enhanced Overall Health: Improved diet and lifestyle can lead to better overall wellness.
- Reduced Risk of Complications: Effective management lowers the risk of heart disease and other conditions.
Practical Tips for Managing Prediabetes
Here are some actionable strategies to manage and potentially reverse prediabetes:
1. Adopt a Healthy Diet
Focus on whole foods that are low in sugar and high in fiber. Consider:
- Whole grains
- Fruits and vegetables
- Lean proteins
- Healthy fats (e.g., avocados, nuts)
2. Increase Physical Activity
Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity each week. Great options include:
- Walking
- Swimming
- Cycling
- Strength training exercises
3. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Losing even a small percentage of body weight (5-10%) can significantly improve blood sugar levels.
4. Regular Monitoring
Stay informed about your blood sugar levels by working with healthcare providers for regular screenings and check-ups.
5. Avoid Unhealthy Habits
Limit alcohol consumption and refrain from smoking, as both can exacerbate health risks associated with prediabetes.
Case Study: Success Stories
Consider the story of Mary, a 52-year-old woman diagnosed with prediabetes. By implementing small dietary changes, increasing her physical activity, and losing 10% of her body weight, Mary was able to reduce her blood sugar levels to a normal range within a year. Her journey emphasizes the effectiveness of lifestyle changes in reversing prediabetes.
First-Hand Experience: A Personal Journey
James, a 45-year-old man, was surprised when he learned he had prediabetes during a routine check-up. Initially overwhelmed, he decided to educate himself about the condition. By consulting a nutritionist and joining a local exercise class, James made significant lifestyle changes that helped him lower his blood sugar levels and improve his energy levels. His story highlights the importance of early detection and proactive management.
Conclusion
Prediabetes is a critical health condition that should not be ignored. With early detection, effective management, and lifestyle changes, it is possible to reverse prediabetes and prevent the onset of Type 2 diabetes. By adopting a healthy diet, increasing physical activity, and maintaining a healthy weight, you can take control of your health and significantly reduce your risk of future complications.
If you suspect you may have prediabetes or are at risk, consult with your healthcare provider today to discuss your options for testing and management. Your health is worth it!