What are the symptoms of fatty liver disease?
Understanding Fatty Liver Disease: Causes, Symptoms, and Management
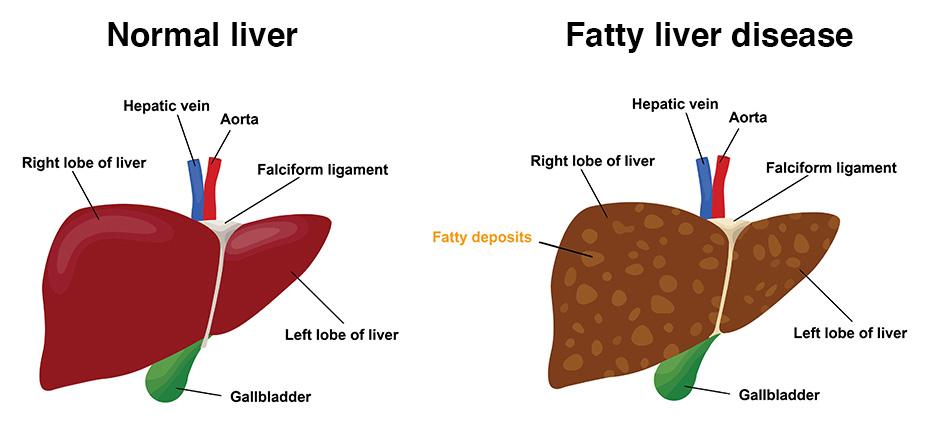
Fatty liver disease, also known as hepatic steatosis, is a condition characterized by the accumulation of fat in liver cells. It is becoming increasingly common globally, often linked to poor dietary habits and sedentary lifestyles. This comprehensive guide will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and practical tips for managing fatty liver disease.
What is Fatty Liver Disease?
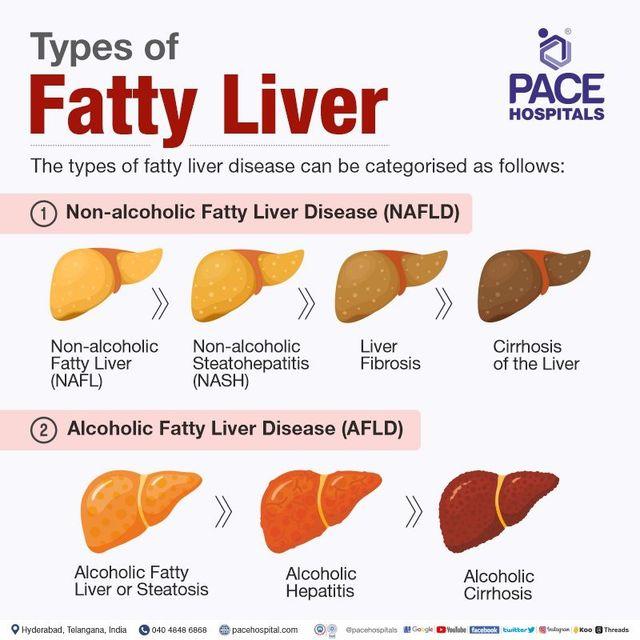
Fatty liver disease can be broadly classified into two types:
- Alcoholic fatty liver disease (AFLD): Caused by excessive alcohol consumption.
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): Occurs in individuals who drink little or no alcohol. This type is further divided into simple fatty liver and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).
Causes of Fatty Liver Disease
Understanding the causes of fatty liver disease is crucial for prevention and management. Here are some primary contributors:
- Obesity: Excess body weight is the most significant risk factor, particularly visceral fat around the abdomen.
- Insulin resistance: Common in people with type 2 diabetes or metabolic syndrome.
- High cholesterol and triglycerides: Elevated levels can lead to fat accumulation in the liver.
- Poor diet: High-calorie diets rich in sugars and fats contribute to liver fat buildup.
- Sedentary lifestyle: Lack of physical activity increases the risk of obesity and insulin resistance.
Symptoms of Fatty Liver Disease
Many individuals with fatty liver disease may not experience symptoms in the early stages. However, as the condition progresses, the following symptoms may appear:
- Fatigue
- Abdominal discomfort or pain
- Unexplained weight loss
- Weakness
- Enlarged liver (hepatomegaly)
Diagnosis of Fatty Liver Disease
Diagnosing fatty liver disease typically involves a combination of medical history assessment, physical examination, and various tests, including:
- Blood tests: To check liver enzymes and overall liver function.
- Imaging tests: Ultrasound, CT scans, or MRIs help visualize fat accumulation in the liver.
- Liver biopsy: In some cases, a small sample of liver tissue is taken for analysis to determine the extent of damage.
Complications of Fatty Liver Disease
If left untreated, fatty liver disease can lead to severe complications, including:
- Cirrhosis: Scarring of the liver tissue.
- Liver cancer: Increased risk in individuals with NASH.
- Liver failure: Severe impairment of liver function.
Treatment Options for Fatty Liver Disease
While there is currently no specific medication for fatty liver disease, management focuses on lifestyle changes and addressing underlying conditions:
- Weight loss: Losing 5-10% of body weight can significantly reduce liver fat.
- Healthy diet: Emphasizing fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins while reducing sugars and saturated fats.
- Regular exercise: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise weekly.
- Control of diabetes and cholesterol: Maintaining blood sugar and lipid levels within a healthy range is essential.
- Limit alcohol consumption: Reducing or eliminating alcohol intake is crucial, especially for AFLD.
Benefits of Managing Fatty Liver Disease
Taking proactive steps to manage fatty liver disease can lead to several health benefits, including:
- Improved liver function and reduced fat accumulation.
- Lowered risk of liver-related complications.
- Enhanced overall health and vitality.
- Improved metabolic health and reduction of insulin resistance.
Practical Tips for Managing Fatty Liver Disease
Here are some practical tips to help manage fatty liver disease effectively:
- Incorporate more fiber into your diet through fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water.
- Choose healthy fats, such as olive oil and avocados, while avoiding trans fats.
- Monitor portion sizes to manage caloric intake.
- Consider regular check-ups with your healthcare provider to monitor liver health.
Case Studies and Personal Experiences
Many individuals have successfully managed fatty liver disease through lifestyle modifications. For example:
- John’s Journey: After a diagnosis of NAFLD, John adopted a Mediterranean diet, lost weight, and incorporated regular exercise. His follow-up liver tests showed a significant reduction in fat accumulation.
- Maria’s Transformation: Maria, diagnosed with AFLD, stopped drinking alcohol entirely, focused on a balanced diet, and began participating in yoga classes. Her liver health improved dramatically within a year.
First-Hand Experience: A Personal Story
As someone who was diagnosed with fatty liver disease a few years ago, I can attest to the life-altering impacts of this condition. Initially, I experienced fatigue and abdominal discomfort, which prompted me to seek medical advice. Upon diagnosis, I feared the worst but was relieved to learn that lifestyle changes could reverse the damage. Through a commitment to a healthier diet and regular exercise, I not only felt more energetic but also saw improvements in my liver function tests. This journey taught me the importance of taking charge of my health.
Conclusion
Fatty liver disease is a serious condition that requires attention and proactive management. By understanding the causes, recognizing symptoms, and embracing lifestyle changes, individuals can significantly improve their liver health. It’s important to consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and support. With the right approach, fatty liver disease can be managed effectively, allowing individuals to lead healthier, happier lives.