What is the difference between a complete and partial molar pregnancy?
Molar Pregnancy: Understanding Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Molar pregnancy is a rare but significant condition that occurs during early pregnancy. Understanding molar pregnancy is crucial for women who are trying to conceive or are currently pregnant. This article explores the types, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and recovery process associated with molar pregnancies.
What is Molar Pregnancy?
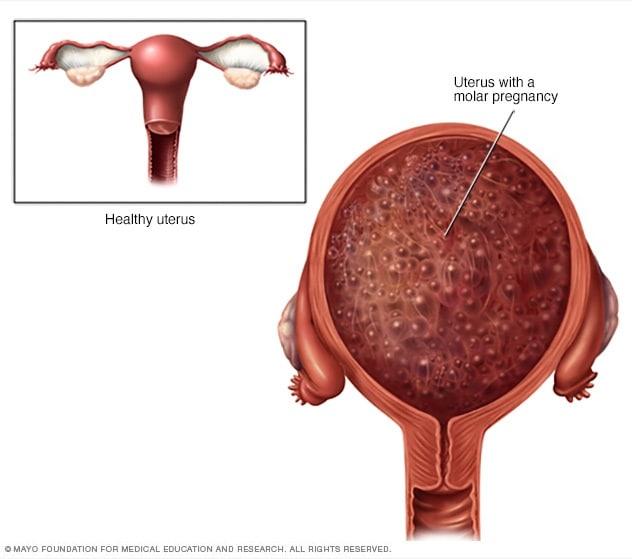
A molar pregnancy is a type of gestational trophoblastic disease (GTD) where abnormal tissue grows inside the uterus instead of a healthy fetus. There are two primary types of molar pregnancies:
- Complete Molar Pregnancy: This occurs when an egg with no genetic material is fertilized. The result is a mass of tissue that can form cysts, without any healthy fetal tissue.
- Partial Molar Pregnancy: In this case, an egg is fertilized by two sperm, leading to some fetal tissue development along with the abnormal tissue.
Symptoms of Molar Pregnancy
Recognizing the symptoms of molar pregnancy is crucial for early diagnosis. Common symptoms include:
- Vaginal bleeding during the first trimester
- Excessive nausea and vomiting
- Pelvic pressure or pain
- Rapid growth of the uterus
- High blood pressure and swelling due to gestational trophoblastic disease
Diagnosis of Molar Pregnancy
If a molar pregnancy is suspected, several diagnostic methods may be employed:
1. Pelvic Exam
A healthcare provider may perform a pelvic exam to check for any abnormal growth.
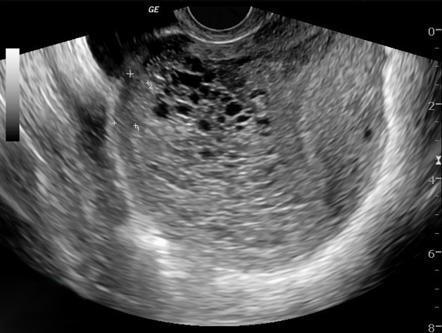
2. Ultrasound
An ultrasound is the most effective method for diagnosing molar pregnancy. It can help visualize the abnormal growth inside the uterus.
3. Blood Tests
Doctors may also check the levels of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), a hormone that is usually elevated in pregnancies. Abnormally high levels may indicate a molar pregnancy.
Treatment Options for Molar Pregnancy
Immediate treatment is crucial to prevent complications, including the risk of developing gestational trophoblastic neoplasia, which can be cancerous. Treatment options include:
1. Dilation and Curettage (D&C)
This surgical procedure involves removing the abnormal tissue from the uterus. It is the most common treatment for molar pregnancy.
2. Monitoring hCG Levels
After the removal of tissue, regular monitoring of hCG levels is essential to ensure all molar tissue has been removed and to check for any signs of persistence.
3. Chemotherapy
If there’s a risk of the disease becoming cancerous, chemotherapy may be required to eliminate any remaining abnormal cells.
Recovery and Follow-Up
After treatment for a molar pregnancy, women are advised to wait for at least six months before trying to conceive again. Regular follow-up appointments to monitor hCG levels are vital during this period. Typically, hCG levels should return to normal within eight weeks after treatment.
Benefits of Early Detection and Treatment
Early detection and treatment of molar pregnancy have several benefits:
- Reduces Risk of Complications: Early intervention can help prevent serious complications, including cancer.
- Emotional Support: Knowing the condition early allows for better emotional and psychological support.
- Future Pregnancies: Effective treatment can ensure a return to normal fertility, allowing for healthier future pregnancies.
First-Hand Experience: A Survivor’s Story
Jane, a 32-year-old mother, shares her experience with molar pregnancy:
“When I first experienced the symptoms, I thought it was just a normal part of pregnancy. However, the ultrasound confirmed my worst fears. The surgical procedure was daunting, but the support from my healthcare team made all the difference. I learned the importance of monitoring my health, and I’m grateful for the opportunity to try again.” – Jane.
Conclusion
Molar pregnancy is an uncommon but significant condition that requires attention and care. Understanding its symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options can help women manage their health better. For those experiencing the symptoms, early consultation with healthcare providers is essential. With appropriate treatment, most women can expect a full recovery and can pursue future pregnancies safely. If you suspect you might be dealing with molar pregnancy, don’t hesitate to seek medical advice.
FAQs about Molar Pregnancy
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| Is molar pregnancy hereditary? | No, molar pregnancy is generally not hereditary. |
| Can I get pregnant after a molar pregnancy? | Yes, but it is advised to wait at least six months before trying to conceive. |
| What are the chances of recurrence? | The recurrence risk is low, occurring in about 1-2% of cases. |