Can exercise help reduce high LDL cholesterol?
“`html
Understanding High LDL Cholesterol: Causes, Risks, and Management
High LDL cholesterol, often referred to as “bad” cholesterol, is a crucial health issue that affects millions worldwide. Elevated levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol can lead to serious health problems, including heart disease and stroke. In this article, we will explore what LDL cholesterol is, the risks associated with high levels, symptoms, and practical tips on how to manage and reduce LDL cholesterol effectively.
What is LDL Cholesterol?
Cholesterol is a waxy substance found in your body and is necessary for many functions, including hormone production and cell membrane integrity. However, not all cholesterol is created equal. Cholesterol is carried through the bloodstream by two types of lipoproteins:
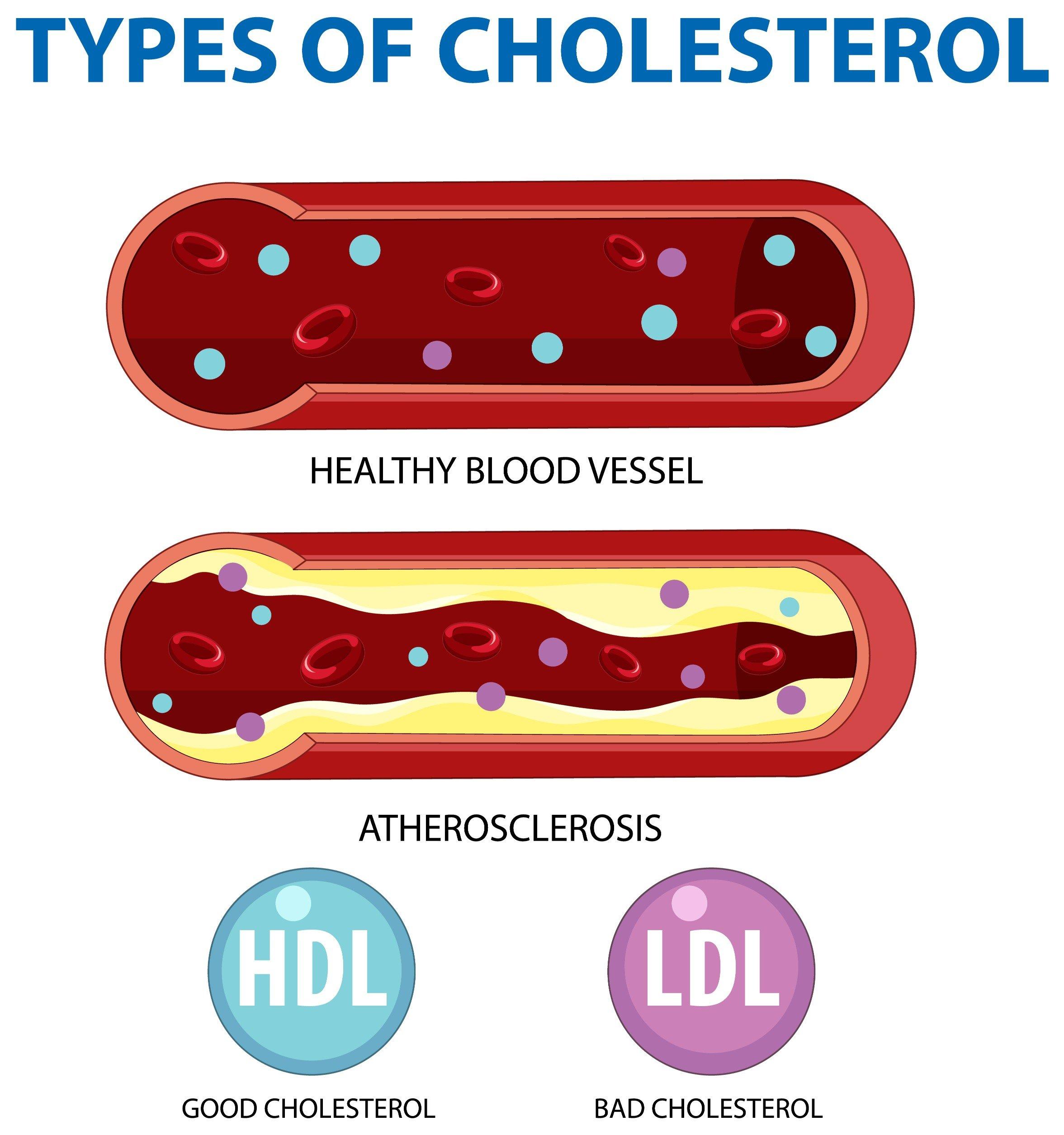
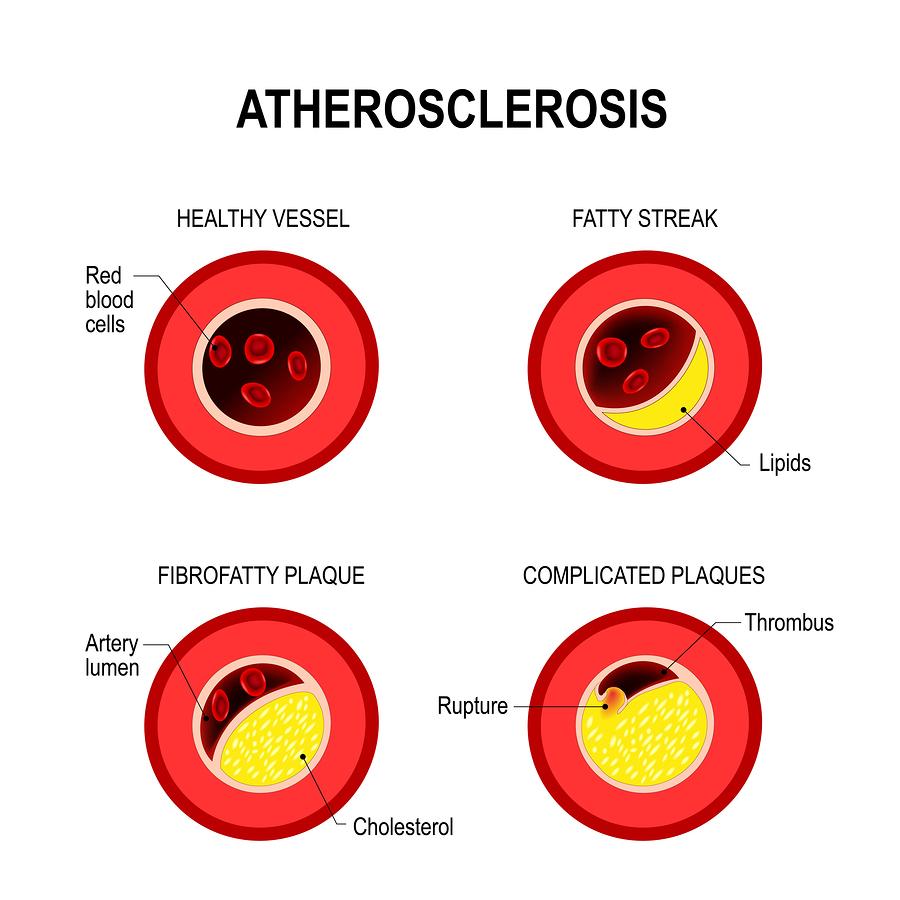
- Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL): Often termed “bad” cholesterol, high levels of LDL can lead to plaque buildup in arteries, increasing the risk of heart disease.
- High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL): Known as “good” cholesterol, HDL helps remove LDL cholesterol from the bloodstream, reducing heart disease risk.
What Causes High LDL Cholesterol?
High LDL cholesterol can result from various factors, including:
- Diet: Consuming saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol-rich foods can raise LDL levels.
- Weight: Being overweight or obese can increase LDL cholesterol.
- Physical Inactivity: Regular exercise helps increase HDL and decrease LDL levels.
- Genetics: Family history plays a significant role; some people inherit genes that cause high cholesterol.
- Age and Gender: Cholesterol levels tend to rise as people age. Before menopause, women typically have lower cholesterol levels than men.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions such as diabetes, hypothyroidism, and liver disease can affect cholesterol levels.
Risks Associated with High LDL Cholesterol
High LDL cholesterol is associated with several serious health risks:
- Heart Disease: The primary risk factor for heart attacks and heart disease.
- Stroke: High cholesterol can lead to narrowing and blockage of blood vessels, increasing stroke risk.
- Peripheral Artery Disease: Reduced blood flow to limbs can cause pain and mobility issues.
Symptoms of High LDL Cholesterol
High LDL cholesterol typically does not present any symptoms, making regular cholesterol screenings essential. However, some signs may indicate related problems:
- Chest Pain: May indicate heart disease.
- Fatigue: Often associated with reduced blood flow.
- Shortness of Breath: May signal cardiovascular issues.
How is LDL Cholesterol Measured?
LDL cholesterol levels are measured through a blood test called a lipid panel. The results typically categorize cholesterol levels as follows:
| Cholesterol Level | LDL Cholesterol (mg/dL) |
|---|---|
| Optimal | Less than 100 |
| Near Optimal | 100-129 |
| Borderline High | 130-159 |
| High | 160-189 |
| Very High | 190 and above |
Benefits of Lowering LDL Cholesterol
Reducing LDL cholesterol levels can have significant health benefits:
- Decreased Risk of Heart Disease: Lowering LDL can reduce your risk of heart attacks and other cardiovascular diseases.
- Improved Overall Health: Lower cholesterol levels may lead to improved energy and quality of life.
- Better Weight Management: Often, lifestyle changes that lower LDL cholesterol also promote weight loss.
Practical Tips to Reduce LDL Cholesterol
Here are effective strategies to manage and reduce high LDL cholesterol:
1. Adopt a Heart-Healthy Diet
- Increase intake of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes.
- Limit saturated fats found in red meat and full-fat dairy products.
- Avoid trans fats found in many processed foods.
- Incorporate healthy fats from sources like olive oil, avocados, and nuts.
2. Increase Physical Activity
Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise weekly can help lower LDL cholesterol. Activities may include:
- Brisk walking
- Running
- Swimming
- Cycling
3. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Even a modest weight loss of 5-10% can significantly improve cholesterol levels. Consider incorporating:
- Regular physical activity
- Balanced diet
4. Avoid Tobacco Smoke
Quitting smoking can improve HDL cholesterol levels, which helps lower LDL cholesterol. Seek support through:
- Counseling
- Support groups
- Smoking cessation programs
5. Consider Medications
If lifestyle changes alone are insufficient, consult a healthcare provider about medications that can help lower LDL cholesterol. Common options include:
- Statins
- Bile acid sequestrants
- Nicotinic acid
Case Studies and Personal Experiences
Many individuals successfully lower their LDL cholesterol through lifestyle changes. For example, John, a 50-year-old man, adopted a Mediterranean diet rich in whole foods and began jogging three times a week. After six months, his LDL cholesterol dropped from 160 mg/dL to 120 mg/dL, significantly reducing his risk of heart disease.
Similarly, Sarah, a 45-year-old woman, struggled with high cholesterol due to family history. She committed to fitness classes and sought guidance from a nutritionist, resulting in a 10% weight loss and a reduction in her LDL cholesterol from 180 mg/dL to 140 mg/dL.
Conclusion
Managing high LDL cholesterol is paramount for maintaining good health and reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Understanding the causes, associated risks, and effective strategies to lower LDL cholesterol can empower individuals to take proactive steps towards better heart health. By adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, regular monitoring, and working with healthcare providers, individuals can significantly improve their cholesterol levels and enhance their overall well-being.
“`
[…] occurs when the virus remains in the body for more than six months. It can lead to serious health problems like cirrhosis or liver […]