Can people with TB still work or go to school during treatment?
Comprehensive Guide to TB Treatment: Effective Strategies & Tips
Tuberculosis (TB) is a serious infectious disease caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It primarily affects the lungs but can also impact other parts of the body. Effective TB treatment is crucial for recovery and preventing the spread of the disease. This article will provide an in-depth look at TB treatment, covering methods, medications, benefits, practical tips, and more.
Understanding Tuberculosis
Before diving into TB treatment, it’s essential to understand what tuberculosis is. TB spreads through the air when a person with active TB coughs, sneezes, or talks. While many people can be infected and remain asymptomatic (latent TB), active TB requires immediate treatment.
Types of TB
- Latent TB: Inactive and non-contagious; no symptoms.
- Active TB: Symptoms present; contagious and requires treatment.
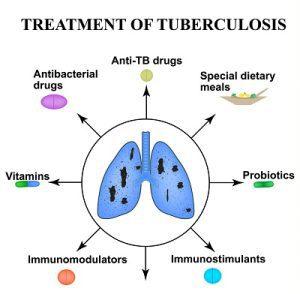
TB Treatment Overview
TB treatment typically involves a combination of antibiotics taken for an extended period. The duration and type of treatment depend on whether the infection is latent or active.
Medications for TB Treatment
The standard treatment for active TB includes a regimen of four primary antibiotics:
- Isoniazid (INH)
- Rifampin (RIF)
- Pyridoxine (Vitamin B6)
- Ethambutol (EMB)
Duration of Treatment
Active TB usually requires 6 to 12 months of treatment, while latent TB generally requires 3 to 9 months of treatment, depending on the specific medication regimen prescribed.
Benefits of TB Treatment
Timely and effective treatment of TB has numerous benefits, including:
- Prevention of Disease Progression: Early treatment prevents the infection from becoming active.
- Reduction in Transmission: Successful treatment reduces the risk of spreading TB to others.
- Improved Quality of Life: Reduces symptoms and improves overall health.
- Economic Benefits: Reduces healthcare costs associated with advanced TB cases.
Practical Tips for Managing TB Treatment
Managing TB treatment effectively can significantly enhance recovery. Here are some practical tips:
- Adhere to Medication: Take medications exactly as prescribed, at the same time each day.
- Regular Check-ups: Attend follow-up appointments to monitor your progress.
- Healthy Diet: Maintain a balanced diet to support your immune system.
- Avoid Alcohol and Tobacco: Both can hamper your recovery and interact negatively with medications.
Case Studies
Let’s look at a few real-world examples of individuals impacted by TB treatment:
Case Study 1: Maria’s Journey
Maria was diagnosed with latent TB. After consulting her doctor, she began a 9-month regimen of Isoniazid. She adhered to her treatment plan, maintained a healthy lifestyle, and completed her medication course without complications.
Case Study 2: John’s Active TB
John presented with active TB and experienced symptoms such as a persistent cough and weight loss. His treatment involved a combination of Rifampin, Ethambutol, and Isoniazid for 6 months. With consistent follow-ups and support from his healthcare team, John successfully completed his treatment and is now healthy.
First-Hand Experience
Many individuals who have gone through TB treatment share similar sentiments about their journey. Common themes include:
- Feeling Overwhelmed: Initial diagnosis can be daunting, but support groups help.
- Importance of Support: Family and friends play a crucial role in maintaining morale.
- Education and Awareness: Understanding TB helps reduce stigma and fear.
Challenges in TB Treatment
While TB treatment is highly effective, several challenges can arise:
- Medication Side Effects: Some patients experience side effects that can deter adherence.
- Multi-Drug Resistant TB (MDR-TB): Strains resistant to standard treatment require alternative therapies.
Conclusion
TB treatment is a critical aspect of public health. Early diagnosis, adherence to prescribed regimens, and regular follow-ups are essential for successful recovery. By understanding the treatment options and challenges associated with TB, individuals can take proactive steps toward managing their health. Remember, if you suspect you have been exposed to TB or are experiencing symptoms, consult a healthcare professional immediately.
| Medication | Duration | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Isoniazid | 6-12 months | Prevents TB bacteria from growing |
| Rifampin | 6-12 months | Kills TB bacteria |
| Ethambutol | 2 months | Stops bacterial growth |
| Pyridoxine | As needed | Prevents side effects from Isoniazid |