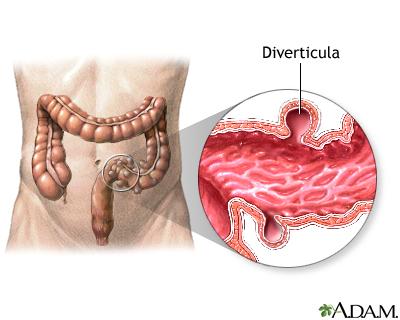
Diverticulitis, a condition that arises from the formation of small pouches in the walls of the colon, has become a significant health concern for many individuals around the world. As these pouches, known as diverticula, become inflamed or infected, they can lead to a range of uncomfortable symptoms that disrupt daily life. Understanding the complexities of diverticulitis is essential for those affected, as well as for their caregivers. In this article, we will explore the latest advancements in diverticulitis treatment, ranging from dietary modifications and lifestyle changes to pharmacological interventions and surgical options. By shedding light on the multifaceted approach to managing this condition, we aim to empower readers with the knowledge needed to navigate their treatment journey and foster a healthier, more informed lifestyle.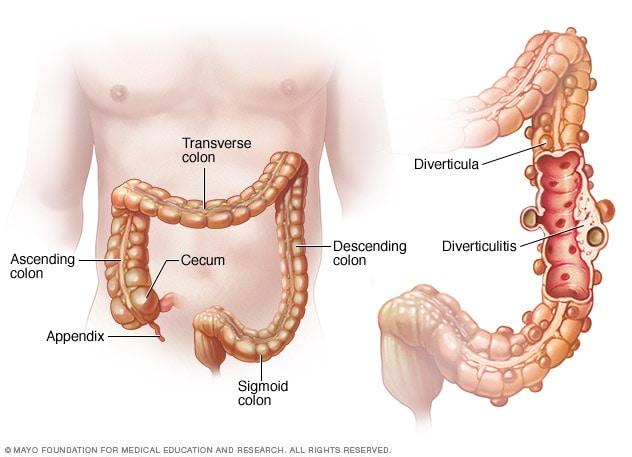
Understanding Diverticulitis: Causes and Symptoms
Diverticulitis occurs when small pouches, known as diverticula, in the lining of the colon become inflamed or infected. Understanding the causes of this condition is crucial for managing it effectively. Common factors contributing to the development of diverticulitis include:
- Diet: A low-fiber diet can lead to constipation, increasing pressure in the colon.
- Age: The risk of diverticulitis increases with age, especially after 40.
- Obesity: Excess weight can elevate the risk of developing diverticular disease.
- Inactivity: A sedentary lifestyle can contribute to digestive issues.
Symptoms of diverticulitis can vary but often include abdominal pain, particularly on the left side, fever, and changes in bowel habits. Recognizing these symptoms early can lead to timely treatment. Key indicators to watch for are:
- Persistent abdominal discomfort: This may be accompanied by tenderness.
- Nausea and vomiting: These can occur if the condition worsens.
- Constipation or diarrhea: Fluctuations in bowel habits may signal an issue.
- Fever and chills: Signs of infection often accompany inflamed diverticula.
Dietary Adjustments for Managing Diverticulitis
Managing diverticulitis often requires attention to dietary choices, particularly during flare-ups. The primary goal is to minimize inflammation and promote healing in the digestive tract. A shift towards a low-fiber diet may be recommended during acute episodes to reduce bowel movement frequency and ease discomfort. Foods that are easy to digest can provide relief and allow the intestines to rest. It’s essential to focus on nutritional balance during this phase. Consider incorporating the following foods:
- Clear broths
- White rice
- Plain pasta
- Applesauce
- Bananas
As symptoms subside, gradually reintroducing fiber-rich foods can help prevent future flare-ups. A high-fiber diet is beneficial for maintaining healthy bowel function and reducing pressure in the colon. Aim for a mix of soluble and insoluble fibers, which can be found in a variety of foods. Below is a simple table outlining some fiber-rich options to include:
| Food Item | Fiber Content (per serving) |
|---|---|
| Chia seeds | 10g |
| Lentils | 15g |
| Whole grain bread | 3g |
| Broccoli | 5g |
| Oats | 4g |
Hydration is equally important; drinking plenty of fluids can aid in fiber digestion and prevent constipation. It’s advisable to avoid certain foods that may exacerbate symptoms, such as nuts, seeds, and popcorn during flare-ups, as they can irritate the digestive tract. Always consult with a healthcare provider or a nutritionist to tailor dietary adjustments to your specific needs and condition.
Medical Treatments and Interventions
Diverticulitis management largely depends on the severity of the condition. For mild cases, some healthcare providers may recommend a conservative approach that includes dietary modifications and symptom management. Patients are often advised to consume a low-fiber diet during acute flare-ups to minimize bowel irritation. As symptoms improve, a gradual reintroduction of fiber-rich foods can help promote healing and prevent recurrence. Key dietary suggestions include:
- Increased hydration to ease digestion
- Incorporation of healthy fruits and vegetables
- Limiting red meat and processed foods
In more severe instances, particularly when complications arise, medical interventions may be necessary. Antibiotics are commonly prescribed to tackle infection, while additional treatments may include pain management medications. Surgical options, such as a partial colectomy, could be recommended for recurrent cases or complications like abscesses. The following table outlines potential treatments and their indications:
| Treatment | Indication |
|---|---|
| Antibiotics | Mild to moderate diverticulitis |
| Dietary Changes | Symptom management |
| Pain Relief Medications | Severe pain control |
| Colonoscopy | Assessment of complications |
| Partial Colectomy | Recurrent issues or complications |
The Role of Probiotics in Gut Health
Probiotics play a pivotal role in maintaining and restoring gut health, particularly for individuals grappling with diverticulitis. These beneficial microorganisms help to balance the gut microbiome, which can become disrupted during episodes of inflammation or infection. By incorporating probiotics into the diet, patients may experience various advantages, including:
- Reduction in inflammation: Probiotics can help modulate the immune response, leading to decreased intestinal inflammation.
- Enhanced digestion: They assist in breaking down food and absorbing nutrients efficiently, which is crucial during recovery.
- Improved gut flora: Probiotics promote the growth of beneficial bacteria, helping to outcompete harmful pathogens.
- Symptom relief: Regular intake can alleviate symptoms such as bloating and discomfort, providing a sense of normalcy.
Clinical studies suggest that certain strains of probiotics, such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, are particularly effective in supporting gut health. They can be found in various sources, including fermented foods and dietary supplements. A brief comparison of popular probiotic sources is illustrated below:
| Probiotic Source | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Yogurt | Rich in protein and calcium; supports digestion. |
| Kefir | Contains more strains of bacteria; boosts immune health. |
| Sauerkraut | High in fiber; promotes gut motility. |
| Kombucha | Contains antioxidants; supports liver health. |
Surgical Options for Severe Cases of Diverticulitis
Lifestyle Changes to Prevent Recurrences
Making intentional lifestyle adjustments can significantly reduce the chances of diverticulitis flare-ups. A diet rich in fiber is fundamental, as it promotes regular bowel movements and minimizes pressure in the colon. Incorporating a variety of fiber-rich foods can help maintain digestive health. Consider including:
- Fruits: Apples, pears, berries, and oranges
- Vegetables: Carrots, broccoli, leafy greens, and bell peppers
- Whole grains: Oats, quinoa, brown rice, and whole wheat bread
- Legumes: Lentils, chickpeas, and black beans
Additionally, staying active plays a crucial role in preventing recurrences. Regular physical activity helps to maintain a healthy weight and promotes effective digestion. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week. Strategies to incorporate more movement into your daily routine include:
- Taking brisk walks during lunch breaks
- Participating in group fitness classes
- Engaging in activities like gardening or cycling
- Finding opportunities to stand or walk while working
Q&A
Q&A on Diverticulitis Treatment
Q: What is diverticulitis, and how does it differ from diverticulosis?
A: Diverticulitis is an inflammatory condition that arises when small pouches, called diverticula, form in the walls of the colon and become infected or inflamed. This condition is a complication of diverticulosis, which is the presence of these pouches without inflammation. While diverticulosis is often asymptomatic, diverticulitis can cause significant discomfort and requires medical attention.
Q: What are the common symptoms of diverticulitis that prompt treatment?
A: Symptoms of diverticulitis may include abdominal pain, usually on the lower left side, fever, nausea, changes in bowel habits, and sometimes vomiting. If you experience severe pain or persistent symptoms, it’s essential to seek medical care.
Q: What are the typical treatment options for diverticulitis?
A: Treatment typically depends on the severity of the condition. For mild cases, dietary changes, oral antibiotics, and over-the-counter pain relievers may be recommended. In more severe cases, hospitalization might be necessary for intravenous antibiotics, hydration, and possibly surgery if complications arise.
Q: How can diet play a role in managing diverticulitis?
A: Diet is crucial in both preventing and managing diverticulitis. During an acute episode, a clear liquid diet may be recommended to give the bowel a chance to rest. Once symptoms improve, a gradual reintroduction of high-fiber foods can help prevent future episodes, as fiber aids in regular bowel movements and reduces pressure in the colon.
Q: Are there lifestyle changes that can help prevent diverticulitis?
A: Yes, adopting a high-fiber diet, staying well-hydrated, exercising regularly, and avoiding smoking can all contribute to better digestive health. These lifestyle changes can help reduce the risk of developing diverticulosis and subsequently diverticulitis.
Q: When should someone with diverticulitis consider surgery?
A: Surgery may be considered for individuals who experience recurrent episodes of diverticulitis or develop complications such as abscesses, perforations, or blockages in the colon. The specific type of surgery, such as a colectomy, would be determined by the severity and location of the condition.
Q: What is the long-term outlook for someone diagnosed with diverticulitis?
A: Most people with mild diverticulitis tend to recover fully with proper treatment and lifestyle modifications. However, recurrent episodes can occur, and those with diverticulosis need to remain vigilant about their diet and health. Regular check-ups and open communication with a healthcare provider can help manage risks effectively.
Q: Are there any new treatments or research developments for diverticulitis?
A: Research into diverticulitis treatment is ongoing, with studies exploring the role of probiotics, dietary supplements, and the impact of various surgical techniques on outcomes. Staying informed through reputable medical sources can provide insights into the latest developments in managing this condition.
Q: Where can I find more information about diverticulitis treatment?
A: For more information, consult healthcare providers, gastroenterology specialists, and trustworthy medical websites. These resources can offer personalized advice and the most current research findings on diverticulitis treatment and management.
Wrapping Up
navigating the landscape of diverticulitis treatment can feel daunting, yet it’s a journey illuminated by knowledge and proactive care. Whether you find solace in dietary adjustments, explore the avenues of medication, or weigh the possibilities of surgical intervention, the key is understanding your body and collaborating closely with your healthcare team. Remember, each case is unique, and what works for one individual may not be the best path for another. As you embark on or continue this journey toward health and well-being, stay informed, remain vigilant, and embrace the small victories along the way. After all, managing diverticulitis isn’t just about treatment; it’s about reclaiming your life and savoring every moment, free from the shadow of discomfort.