Unraveling the Shadows: Understanding Parkinson’s Disease
In the intricate tapestry of human health, few conditions evoke as much intrigue and complexity as Parkinson’s disease. This progressive neurological disorder, often shrouded in mystery, affects millions of individuals worldwide, gradually altering not just the body, but the essence of their daily lives. Characterized by tremors, rigidity, and a host of other symptoms, Parkinson’s challenges both those diagnosed and their loved ones, prompting questions about the origins, progression, and potential treatments. As we delve into the multifaceted nature of this condition, we aim to shed light on the latest research, uncovering the interplay between biology and experience in the journey through Parkinson’s disease. Join us as we explore the current understanding of this enigmatic ailment, fostering a deeper awareness that transcends the clinical and touches the human spirit.
Understanding Parkinsons Disease: Symptoms and Early Detection
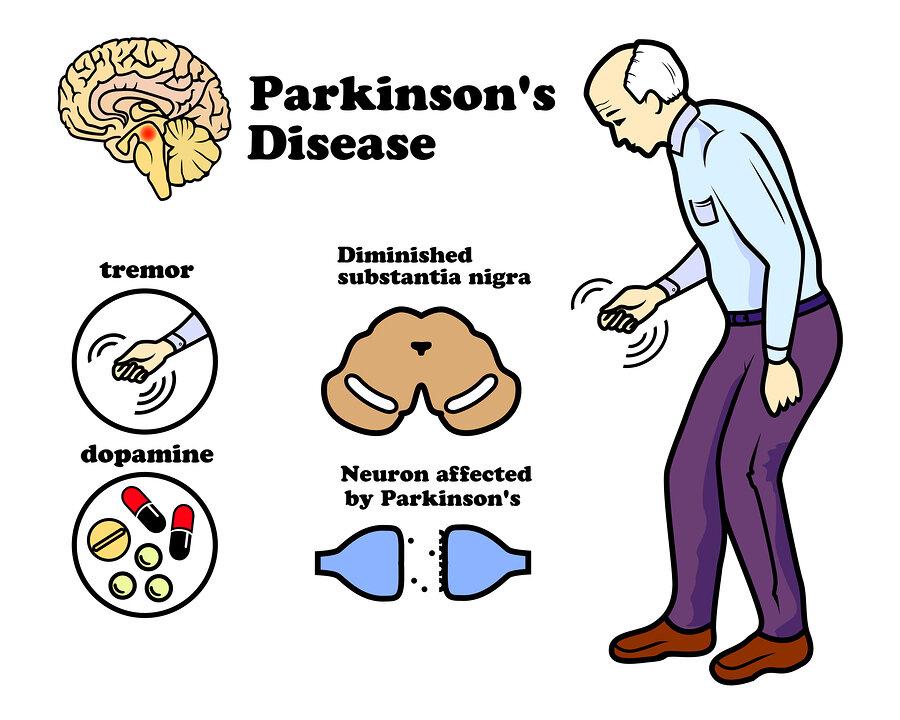
Parkinson’s disease is a progressive neurological disorder that primarily affects movement. Recognizing the early signs can significantly impact the quality of life for those affected. Common symptoms include:
- Tremors: Involuntary shaking, often starting in one hand.
- Bradykinesia: Slowness of movement, making daily tasks more challenging.
- Muscle Rigidity: Stiffness in the limbs and neck, leading to discomfort.
- Postural Instability: Difficulty with balance and coordination.
Prompt early detection is crucial for effective management and treatment. Healthcare professionals often utilize a combination of patient history and physical examinations to assess symptoms. Some additional indicators to consider include:
| Indicator | Description |
|---|---|
| Changes in Speech | Voice may become softer or more monotone. |
| Decreased Facial Expressions | Reduced ability to show emotions through facial movements. |
| Sleep Disturbances | Difficulty falling or staying asleep, leading to fatigue. |
The Role of Genetics and Environment in Parkinsons Disease
In understanding the complexities of Parkinson’s disease, it becomes evident that both genetics and environment play critical roles in its manifestation. Genetic factors contribute to the risk of developing the disease, with certain mutations—such as those in the LRRK2 and SNCA genes—being associated with hereditary forms of Parkinson’s. However, not all cases follow a hereditary pattern; many individuals diagnosed with Parkinson’s do not have a family history of the disorder. This indicates that environmental influences can also significantly impact disease development. Possible environmental factors include:
- Exposure to pesticides and herbicides
- Occupational hazards, such as prolonged exposure to metals
- Head injuries or trauma
- Living in rural areas with high pesticide usage
Research has shown that the interplay between genetic predisposition and environmental triggers can create a complex risk profile. For instance, individuals with a genetic mutation may have a higher chance of developing Parkinson’s if they are also exposed to specific environmental toxins. A recent study highlighted this interaction, indicating that those with a familial history of Parkinson’s who lived in areas with high pesticide levels exhibited symptoms earlier than others. Understanding this gene-environment interaction is paramount, as it could lead to targeted prevention strategies and personalized treatment plans that consider both genetic markers and environmental exposures.
| Factor Type | Examples |
|---|---|
| Genetic Factors | LRRK2, SNCA mutations |
| Environmental Factors | Pesticide exposure, head trauma |
Innovative Treatments and Therapies for Managing Symptoms
Recent advancements in neuroscience and technology have paved the way for an array of innovative therapies aimed at alleviating the symptoms associated with Parkinson’s disease. Among these, neurostimulation techniques such as deep brain stimulation (DBS) have shown remarkable efficacy in reducing motor symptoms. This procedure involves the implantation of electrodes in specific brain regions, which deliver electrical impulses to help regulate abnormal brain activity. Additionally, wearable devices equipped with sensors are emerging as valuable tools for real-time monitoring of symptoms, offering patients and healthcare providers actionable insights to manage their condition effectively.
Another exciting frontier in Parkinson’s management is the use of gene therapy, which aims to address the underlying causes of the disease at a molecular level. Researchers are exploring strategies to deliver genes that can enhance dopamine production or protect neurons from degeneration. Moreover, virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies are being leveraged to create immersive rehabilitation experiences, aiding in physical therapy and improving balance. These therapies not only stimulate cognitive engagement but also provide a novel approach to practicing movement in a safe environment, helping patients regain confidence in their mobility.
Nutritional Considerations for Individuals with Parkinsons Disease
Managing nutrition plays a pivotal role in enhancing the quality of life for individuals with Parkinson’s disease. A balanced diet can help address some of the symptoms associated with the condition and may improve overall well-being. It is essential to focus on nutrient-dense foods that provide the necessary vitamins and minerals. Consider incorporating the following food groups into daily meals:
- Fruits and Vegetables: Rich in antioxidants and fiber, they support immune function and digestive health.
- Whole Grains: Options like brown rice, quinoa, and whole-wheat bread can help maintain energy levels throughout the day.
- Protein Sources: Lean meats, fish, legumes, and nuts are vital for muscle maintenance and repair.
- Healthy Fats: Incorporating sources like avocados, olive oil, and fatty fish can support brain health.
Hydration is another crucial aspect of nutrition that should not be overlooked. People with Parkinson’s often experience difficulties in swallowing, which might lead to reduced fluid intake. Encouraging regular consumption of liquids, such as water, herbal teas, and broths, is fundamental. Additionally, the following table outlines essential nutrients and their benefits for individuals with Parkinson’s:
| Nutrient | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Supports brain function and reduces inflammation. |
| Vitamin D | Enhances bone health and immune response. |
| Antioxidants | Protects cells from oxidative stress. |
The Importance of Support Networks for Patients and Caregivers
For individuals living with Parkinson’s disease, a robust support network can make a significant difference in navigating the complexities of their condition. These networks, which can include family, friends, healthcare professionals, and community resources, provide more than just emotional backing; they serve as a vital lifeline, offering practical assistance in daily activities. Having a well-rounded support system can help patients manage symptoms more effectively, reduce feelings of isolation, and enhance overall well-being. The sharing of experiences within these networks can also empower individuals, fostering a sense of community and belonging that is crucial for emotional health.
Caregivers, too, often face unique challenges and emotional strain while supporting loved ones with Parkinson’s disease. Establishing connections with other caregivers allows for the exchange of valuable insights and coping strategies, reducing stress and preventing burnout. Support networks can include:
- Local Parkinson’s support groups
- Online forums and discussion platforms
- Workshops and educational resources
- Professional counseling services
Engaging in these networks helps caregivers prioritize their own mental and physical health, ensuring they can provide the best care possible. By fostering relationships within these supportive communities, both patients and caregivers can cultivate resilience and hope amidst the challenges posed by Parkinson’s disease.
Emerging Research and Future Directions in Parkinsons Disease Management
The landscape of Parkinson’s disease management is evolving rapidly, fueled by advancements in technology and a deeper understanding of the disease’s underlying mechanisms. Researchers are exploring a variety of innovative approaches, such as gene therapy, neuroprotective agents, and biomarker identification, all aimed at halting or even reversing disease progression. A promising area of research involves the use of stem cell therapy, which holds the potential to regenerate damaged neurons, thereby restoring lost motor functions. Additionally, wearable technology is being integrated into treatment regimens, allowing for real-time monitoring of symptoms and providing valuable data that can inform personalized treatment plans.
Future directions in Parkinson’s disease management may also include the development of digital health solutions that leverage artificial intelligence and machine learning. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data from patient interactions, leading to tailored interventions that enhance the quality of life. Furthermore, interdisciplinary approaches that incorporate psychosocial support, dietary modifications, and physical therapy are gaining traction, recognizing that effective management extends beyond medication. The convergence of these innovative strategies may pave the way for a more holistic and patient-centered approach to Parkinson’s care.
Q&A
Q&A: Understanding Parkinson’s Disease
Q1: What is Parkinson’s disease?
A: Parkinson’s disease is a progressive neurological disorder that primarily affects movement. It occurs when nerve cells in the brain, particularly those that produce dopamine, begin to deteriorate or die. This leads to a variety of motor and non-motor symptoms, impacting daily life.
Q2: What are the primary symptoms of Parkinson’s disease?
A: The symptoms of Parkinson’s can be categorized into motor and non-motor. Motor symptoms often include tremors, stiffness, slowness of movement (bradykinesia), and balance issues. Non-motor symptoms may involve sleep disturbances, depression, anxiety, and cognitive changes.
Q3: How is Parkinson’s disease diagnosed?
A: Diagnosing Parkinson’s disease typically involves a thorough medical history, a review of symptoms, and a neurological examination. There are no definitive tests; instead, doctors often rely on clinical criteria and may order imaging studies or other tests to rule out other conditions.
Q4: What causes Parkinson’s disease?
A: The exact cause of Parkinson’s disease remains unclear. However, a combination of genetic and environmental factors is believed to play a role. Certain genes have been linked to familial forms of the disease, while exposure to toxins and other environmental factors may contribute to sporadic cases.
Q5: Is there a cure for Parkinson’s disease?
A: Currently, there is no cure for Parkinson’s disease. However, there are various treatment options available to manage symptoms. These may include medications that increase dopamine levels, physical therapy, and in some cases, surgical interventions like deep brain stimulation.
Q6: How can lifestyle choices impact Parkinson’s disease?
A: Lifestyle choices can significantly influence the quality of life for individuals with Parkinson’s. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and social engagement can help manage symptoms and improve overall well-being. Additionally, mental health support is crucial for coping with the emotional challenges of the disease.
Q7: What is the prognosis for someone diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease?
A: Parkinson’s disease is a progressive condition, meaning symptoms can worsen over time. However, the rate of progression varies widely among individuals. With advancements in treatment and supportive care, many people with Parkinson’s can lead fulfilling lives for years after diagnosis.
Q8: How can caregivers support someone with Parkinson’s disease?
A: Caregivers play a vital role in supporting individuals with Parkinson’s. They can help by providing emotional support, assisting with daily activities, encouraging physical activity, and ensuring medication adherence. Joining support groups can also be beneficial for both caregivers and those living with the disease.
Q9: What research is currently being conducted on Parkinson’s disease?
A: Research on Parkinson’s disease is extensive and ongoing. Scientists are exploring various areas, including potential genetic links, new therapeutic approaches, and advancements in neuroprotective strategies. Clinical trials are regularly conducted to test new medications and treatment modalities, offering hope for future breakthroughs.
Q10: Where can individuals find more information about Parkinson’s disease?
A: Individuals seeking more information about Parkinson’s disease can visit reputable organizations like the Parkinson’s Foundation, the Michael J. Fox Foundation, and the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. These organizations provide resources, support networks, and the latest research updates.
Concluding Remarks
As we draw the curtain on our exploration of Parkinson’s disease, it becomes evident that this condition is not merely a set of symptoms, but a complex tapestry woven with threads of individual experiences, scientific endeavors, and the unwavering spirit of those affected. While challenges abound, so too do avenues for hope—whether through groundbreaking research, emerging therapies, or the profound resilience of the human spirit.
In understanding Parkinson’s, we not only illuminate the path for those living with the disease but also foster a greater empathy in our communities. As we continue to share stories, support one another, and advocate for advancements in treatment and care, we inch closer to a future where Parkinson’s becomes a chapter rather than a narrative.
Let us carry forward the knowledge we have gained, and remain committed to shining a light on this journey, ensuring that no one walks it alone. The fight against Parkinson’s is ongoing, but together, we can amplify the voices of those who live with it, and champion the advancements that hold the promise of a brighter tomorrow.