In the intricate web of human health, few threats are as insidious as waterborne infections. Often lurking in the very source that sustains us, these pathogens can turn a life-giving resource into a vehicle of disease. From the murky depths of contaminated water supplies to the pristine facades of seemingly safe drinking water, the presence of harmful microorganisms poses a significant challenge to public health worldwide. As we delve into the complex world of water infections, we’ll explore their causes, symptoms, and the vital preventive measures that can safeguard communities. Join us on this journey as we unravel the hidden dangers of water and the steps we can take to protect ourselves and our loved ones from these invisible adversaries.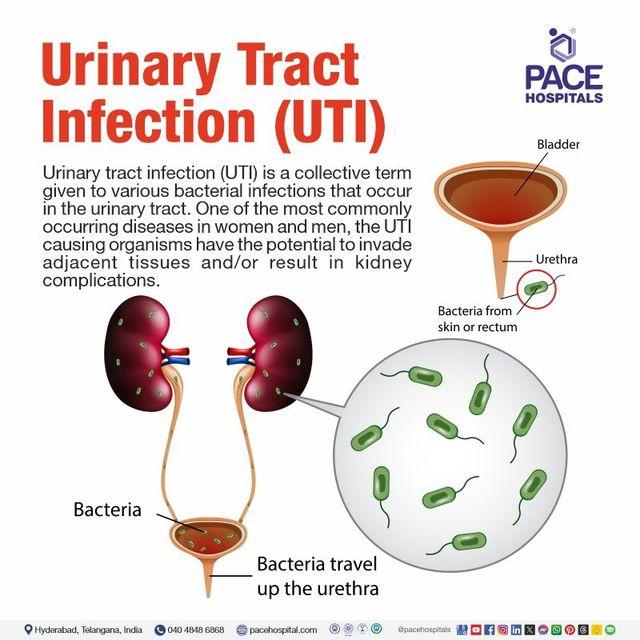
Understanding Water Infections and Their Causes
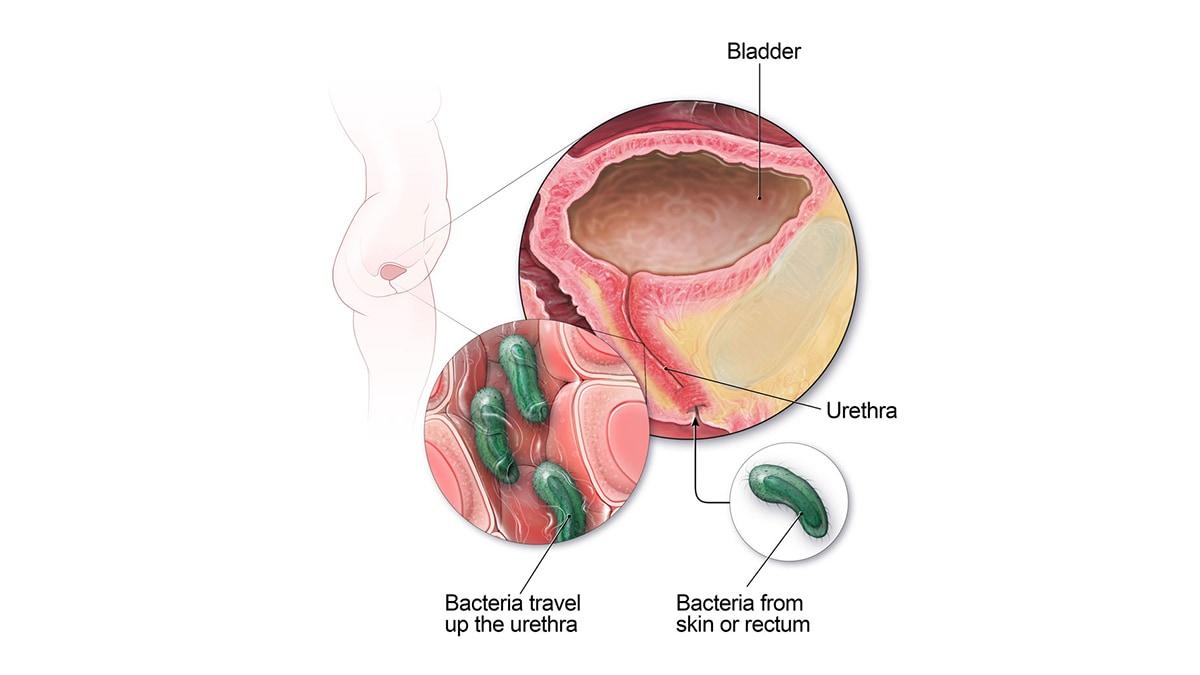
Water infections, often referred to as urinary tract infections (UTIs), occur when harmful bacteria invade the urinary system, leading to inflammation and discomfort. While these infections can affect anyone, they are particularly common among women due to anatomical differences. Understanding the causes of these infections is crucial for prevention and effective treatment. Some of the primary contributors include:
- Improper Hygiene: Poor personal hygiene practices can increase the risk of bacterial growth.
- Sexual Activity: Intercourse can introduce bacteria into the urinary tract.
- Dehydration: Insufficient fluid intake can prevent the urinary system from flushing out potential pathogens.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions like diabetes or urinary tract abnormalities can predispose individuals to infections.
Identifying the causes helps in addressing the proper preventative measures. Environmental factors can also play a role, such as:
- Contaminated Water Sources: Drinking or utilizing contaminated water can introduce harmful bacteria.
- Unclean Swimming Facilities: Public pools or hot tubs that are not adequately treated can serve as breeding grounds for bacteria.
- Improper Waste Disposal: Polluted areas due to negligence can contaminate local water supplies.
| Cause | Description |
|---|---|
| Hygiene | Inadequate cleaning can lead to bacterial growth. |
| Diet | Certain foods can irritate the bladder or promote bacteria. |
| Clothing | Tight clothing can trap moisture and create a breeding ground for bacteria. |
Identifying Symptoms: How to Recognize a Water Infection
Recognizing a water infection can be crucial for timely treatment and recovery. Common symptoms may vary, but there are several telltale signs that can indicate the presence of an infection. Individuals often experience:
- Pain or Discomfort: A sharp or burning sensation during urination.
- Frequent Urination: An increased urge to urinate, often producing little urine.
- Cloudy or Strong-Smelling Urine: Changes in urine appearance and odor can signify infection.
- Fatigue or Fever: Unexpected tiredness or a slight fever might accompany other symptoms.
In some cases, people may also experience more severe signs that should not be overlooked. If you’re noticing:
| Symptom | Severity |
|---|---|
| Lower Abdominal Pain | Moderate to Severe |
| Blood in Urine | Severe |
| Nausea or Vomiting | Moderate |
It’s imperative to seek medical advice if you observe these symptoms, as untreated water infections can lead to more serious health complications.
Preventive Measures: Keeping Your Water Safe and Clean
To ensure that your water remains safe and clean, adopting effective preventive measures is essential. Start by regularly testing your water supply for contaminants. This can be done using home testing kits available at local stores or by hiring professionals. Some common contaminants to check for include:
- Microbial pathogens – Bacteria, viruses, and parasites
- Chemicals – Heavy metals, pesticides, and chlorine
- Physical impurities – Sediments and turbidity
Additionally, maintaining your plumbing system is crucial for preventing waterborne infections. Ensure that all pipes are intact and free from leaks, which can lead to contamination. Consider installing high-quality water filters and regularly replacing their cartridges. For households relying on well water, routine inspections and proper well maintenance can significantly reduce the risk of exposure. Here’s a simple table summarizing key maintenance tips:
| Maintenance Task | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Test water quality | Annually |
| Inspect plumbing for leaks | Every 6 months |
| Replace water filter cartridges | Every 3-6 months |
| Clean and disinfect wells | As needed |
Treatment Options: Navigating the Path to Recovery
When facing a water infection, it’s crucial to explore the various treatment options available to ensure a swift recovery. Typically, the primary course of action involves antibiotics prescribed by a healthcare professional. These medications effectively target the bacteria responsible for the infection. It’s important to complete the full course of antibiotics, even if symptoms improve before finishing the medication. Additionally, practitioners may recommend increased fluid intake to help flush the bacteria from the urinary tract. Here are some supportive measures to consider:
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water can promote urination, which helps to eliminate the infection.
- Cranberry Products: Some studies suggest that cranberry juice or supplements may reduce the risk of recurring infections.
- Pain Relief: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen can help alleviate discomfort associated with the infection.
In cases where a water infection becomes recurrent or is resistant to standard treatments, further evaluation may be necessary. This could involve a thorough examination to identify any underlying issues, such as anatomical abnormalities or dietary factors contributing to the infections. For those with chronic conditions, preventive strategies might include the use of daily prophylactic antibiotics or lifestyle adjustments. Consider the following potential long-term solutions:
| Long-term Solutions | Description |
|---|---|
| Regular Follow-ups | Schedule routine visits to monitor your urinary health. |
| Dietary Changes | Incorporate foods that promote urinary tract health. |
| Hygiene Practices | Adopt habits that reduce the risk of infections, such as proper wiping techniques. |
The Role of Hydration in Preventing Waterborne Illnesses
Staying hydrated is not only crucial for overall health but also plays a significant role in safeguarding our bodies against waterborne illnesses. When the body is sufficiently hydrated, it helps to maintain the integrity of mucous membranes, which act as a barrier against pathogens. Adequate water intake ensures that the kidneys function optimally, assisting in the filtration of toxins and the prevention of infections. Here are some key factors illustrating the importance of hydration in illness prevention:
- Improved Immune Function: Hydration supports immune cell production, enhancing the body’s ability to fight infections.
- Optimal Digestive Health: Adequate fluid intake aids in digestion, reducing the risk of gastrointestinal infections.
- Enhanced Detoxification: Water flushes out harmful substances, decreasing the likelihood of pathogen buildup.
In regions where water quality is compromised, consuming clean and safe water becomes even more critical. Incorporating hydration strategies can mitigate risks associated with contaminated water sources. Here’s a simple overview of recommended hydration practices:
| Practice | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Drink purified water | Reduces exposure to pathogens |
| Set hydration reminders | Ensures consistent fluid intake |
| Consume water-rich foods | Boosts overall hydration |
When to Seek Medical Help: Knowing the Right Time to Act
Understanding when to seek medical assistance for a water infection is crucial for effective treatment and recovery. If you experience any of the following symptoms, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional promptly:
- Persistent Pain or Discomfort: If you have a constant ache in your lower abdomen or back.
- Severe Burning Sensation: A strong burning feeling during urination that doesn’t subside.
- Foul-Smelling Urine: If your urine has a strong, unpleasant odor.
- Blood in Urine: Any visible trace of blood should never be ignored.
- High Fever or Chills: Indicating a potential systemic infection.
Additionally, individuals with underlying health conditions, such as diabetes or a weakened immune system, should be more vigilant. A doctor’s visit is warranted if you notice:
| Symptom | Action |
|---|---|
| Frequent Urination | Monitor frequency; seek help if extreme |
| Nausea or Vomiting | Consult a doctor; dehydration risk |
| Symptoms Lasting More Than 24 Hours | Immediate medical advice necessary |
Q&A
Q&A: Understanding Water Infections
Q: What is a water infection?
A: A water infection, commonly referred to as a urinary tract infection (UTI), occurs when bacteria enter the urinary system, which may include the bladder, urethra, or kidneys. This can happen through various means, such as poor hygiene, sexual activity, or even contamination from water sources.
Q: How do water infections typically manifest in symptoms?
A: Symptoms of a water infection can vary but often include a frequent urge to urinate, a burning sensation during urination, cloudy or strong-smelling urine, and lower abdominal pain. In more severe cases, individuals may experience fever, chills, or back pain, indicating the infection may have reached the kidneys.
Q: Who is most at risk for developing a water infection?
A: While anyone can develop a water infection, certain groups are more susceptible. Women are particularly at risk due to their shorter urethra, which allows bacteria easier access to the bladder. Other risk factors include sexual activity, hormonal changes, a weakened immune system, and certain medical conditions, such as diabetes.
Q: How can one prevent water infections?
A: Prevention involves a few simple practices: maintaining good personal hygiene, urinating before and after sexual intercourse, drinking plenty of fluids, and wiping from front to back after using the restroom. Additionally, avoiding irritants, such as scented soaps or douches, can help reduce the risk.
Q: What should someone do if they suspect they have a water infection?
A: If you suspect a water infection, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional. They may recommend a urine test to confirm the diagnosis and determine the most effective treatment, which typically includes a course of antibiotics. Early treatment is essential to prevent complications.
Q: Are there any home remedies for treating water infections?
A: While it’s crucial to seek medical advice for proper treatment, some home remedies may provide relief alongside prescribed medications. Drinking plenty of water, consuming cranberry juice, and taking probiotics can contribute to urinary health. However, these should not replace medical treatment.
Q: Can water infections recur?
A: Yes, recurrent water infections are common. Individuals with a history of UTIs may experience multiple episodes over time. Identifying and addressing any underlying factors, such as anatomical issues or lifestyle habits, can be key to reducing recurrence.
Q: Is there a connection between water quality and water infections?
A: While water quality can influence overall health, water infections are primarily caused by bacterial infections rather than contaminated water. However, poor sanitation and hygiene in areas with inadequate clean water supply can contribute to increased rates of UTIs in those communities.
Q: When should one seek immediate medical attention regarding a water infection?
A: If you experience severe symptoms such as high fever, nausea, vomiting, or back pain, it’s crucial to seek medical attention promptly, as these may indicate a more serious kidney infection that requires immediate treatment.
Q: What is the long-term outlook for someone with recurrent water infections?
A: With proper management and preventive measures, many individuals can effectively reduce the frequency of water infections. Regular follow-ups with a healthcare provider are recommended to monitor the condition and adjust treatment plans as necessary.
In Summary
navigating the waters of health can sometimes lead us to unexpected challenges, such as water infections. By understanding their causes, symptoms, and preventive measures, we empower ourselves to take charge of our well-being. Just as a river can flow gently or tumultuously, our bodies respond uniquely to various factors in our environment. Staying informed and vigilant not only helps us to avoid these potential pitfalls but also enhances our overall resilience. As we continue to explore the intricate relationship between our health and the world around us, let us remember that knowledge is our strongest ally—one that can help us stay afloat in even the murkiest waters.